
Question Number 130149 by liberty last updated on 22/Jan/21
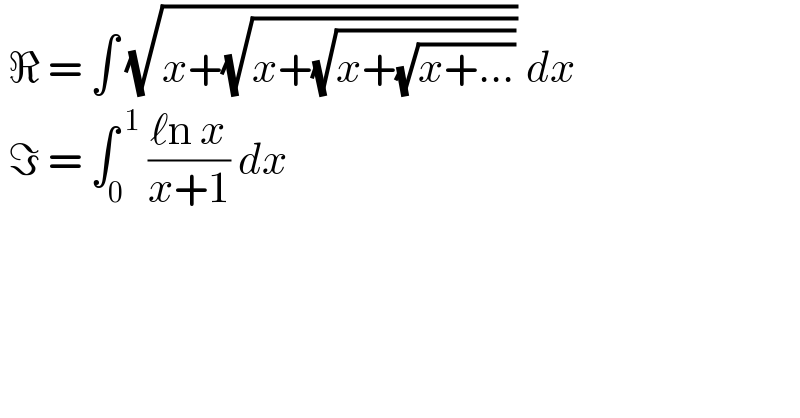
$$\:\Re\:=\:\int\:\sqrt{{x}+\sqrt{{x}+\sqrt{{x}+\sqrt{{x}+...}}}}\:{dx} \\ $$$$\:\Im\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{\ell\mathrm{n}\:{x}}{{x}+\mathrm{1}}\:{dx}\: \\ $$
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 22/Jan/21
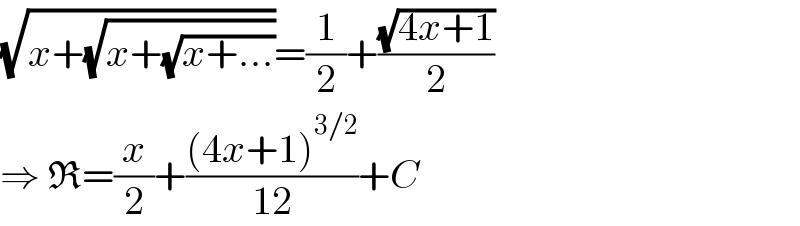
$$\sqrt{{x}+\sqrt{{x}+\sqrt{{x}+...}}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{4}{x}+\mathrm{1}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathfrak{R}=\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\left(\mathrm{4}{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}/\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{12}}+{C} \\ $$
Commented by liberty last updated on 22/Jan/21
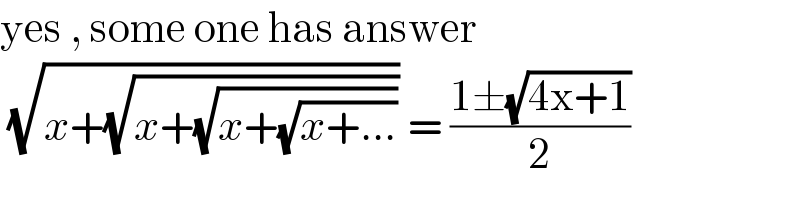
$$\mathrm{yes}\:,\:\mathrm{some}\:\mathrm{one}\:\mathrm{has}\:\mathrm{answer}\: \\ $$$$\:\sqrt{{x}+\sqrt{{x}+\sqrt{{x}+\sqrt{{x}+...}}}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{4x}+\mathrm{1}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 23/Jan/21

$${y}=\sqrt{{x}+\sqrt{{x}+\sqrt{{x}+...}}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{both}\:\mathrm{sides}\:\geqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${y}^{\mathrm{2}} ={x}+\sqrt{{x}+\sqrt{{x}+\sqrt{{x}+...}}} \\ $$$${y}^{\mathrm{2}} ={x}+{y} \\ $$$$\mathrm{this}\:\mathrm{has}\:\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{solutions}\:\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{only}\:\mathrm{the}\:``+''\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{right}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{try}\:\mathrm{with}\:\mathrm{any}\:{x}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{see} \\ $$
Commented by liberty last updated on 23/Jan/21

$$\mathrm{yes}...\mathrm{correct} \\ $$
Answered by Lordose last updated on 23/Jan/21
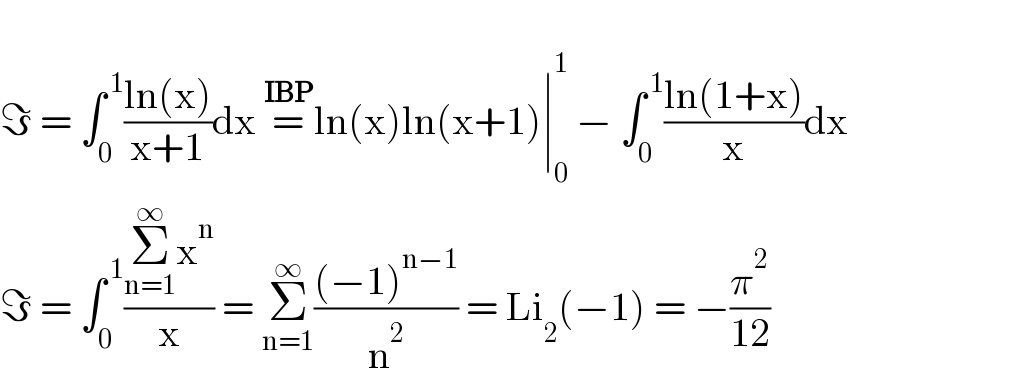
$$ \\ $$$$\Im\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{1}}\mathrm{dx}\:\overset{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{IBP}}} {=}\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\mid_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:−\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}\right)}{\mathrm{x}}\mathrm{dx}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\: \\ $$$$\Im\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\mathrm{1}} \frac{\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{n}} }{\mathrm{x}}\:=\:\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\:\mathrm{Li}_{\mathrm{2}} \left(−\mathrm{1}\right)\:=\:−\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{12}} \\ $$
Commented by benjo_mathlover last updated on 23/Jan/21

$$−\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{12}} \\ $$
Answered by benjo_mathlover last updated on 23/Jan/21
![ℑ= ∫_0 ^( 1) ((ln x)/(x+1)) dx = ∫_0 ^( 1) ln x (Σ_(k=0) ^∞ (−1)^k x^k ) dx = Σ_(k=0) ^∞ (−1)^k ∫_0 ^( 1) x^k ln x dx = Σ_(k=0) ^∞ (−1)^k [(x^(k+1) /(k+1)) ln x−(x^(k+1) /((k+1)^2 ))]_0 ^1 = Σ_(k=0) ^∞ (−1)^k (1/((k+1)^2 )) = −Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (((−1)^(n−1) )/n^2 ) = −[Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (1/n^2 )−Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (2/((2n)^2 )) ] = −(1−(1/2))Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (1/n^2 ) = −(1/2).(π^2 /6)= −(π^2 /(12))](Q130162.png)
$$\Im=\:\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{1}}\:\mathrm{dx}\:=\:\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{x}\:\left(\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{k}} \:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{k}} \right)\:\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$=\:\:\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{k}} \int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{k}} \:\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{x}\:\mathrm{dx}\: \\ $$$$=\:\:\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{k}} \:\left[\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{k}+\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{k}+\mathrm{1}}\:\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{x}−\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{k}+\mathrm{1}} }{\left(\mathrm{k}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\:\:\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{k}} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{k}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\:\:−\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=\:\:−\left[\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\left(\mathrm{2n}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\right]\: \\ $$$$=\:\:−\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\:\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}.\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{6}}=\:\:−\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{12}} \\ $$
