
Question Number 170855 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 01/Jun/22
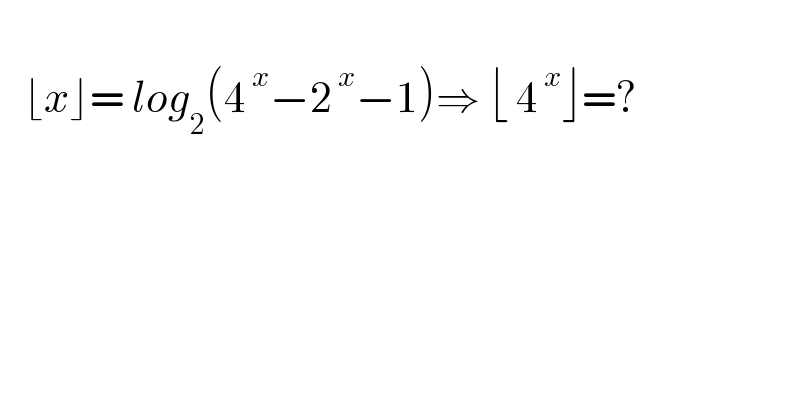
$$ \\ $$$$\:\:\:\lfloor{x}\rfloor=\:{log}_{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{4}^{\:{x}} −\mathrm{2}^{\:{x}} −\mathrm{1}\right)\Rightarrow\:\lfloor\:\mathrm{4}^{\:{x}} \rfloor=? \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by floor(10²Eta[1]) last updated on 01/Jun/22
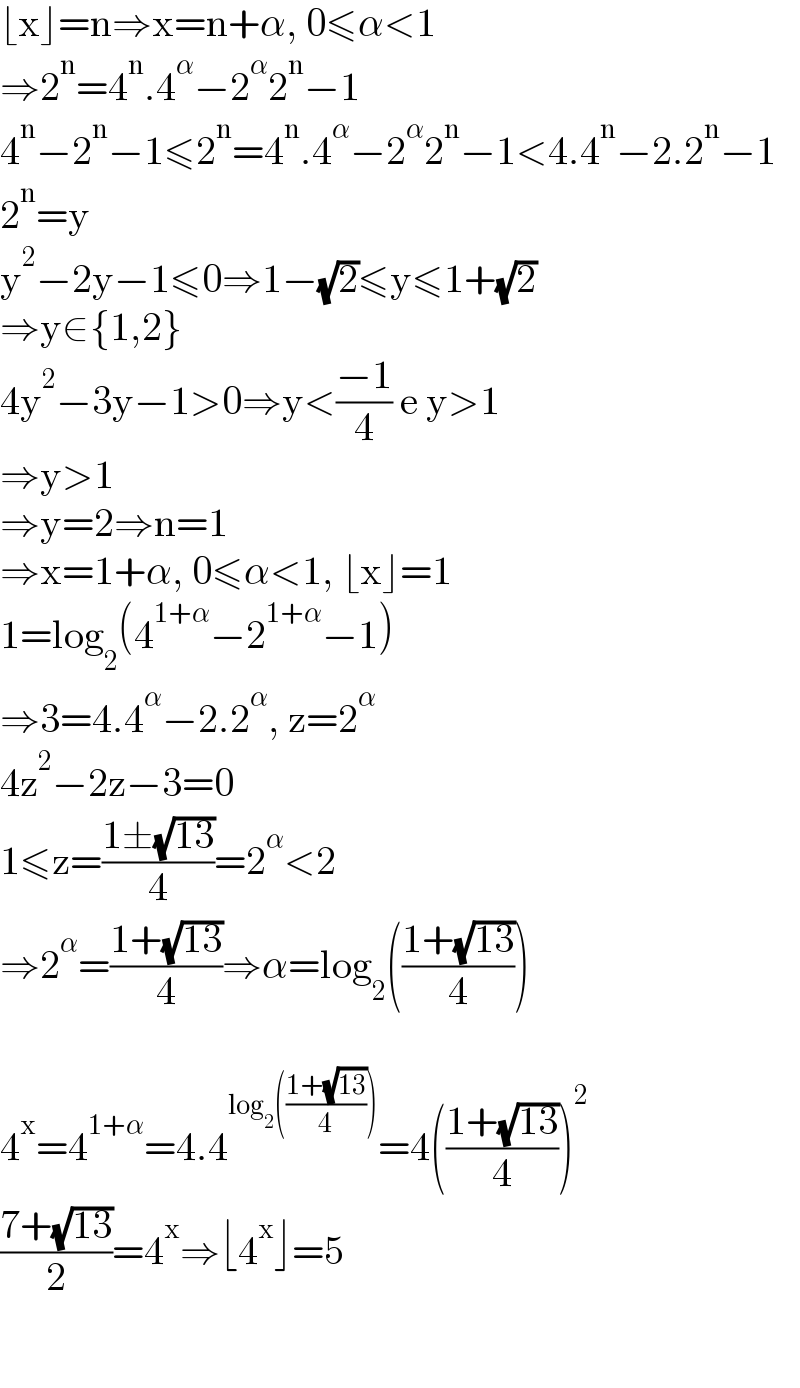
$$\lfloor\mathrm{x}\rfloor=\mathrm{n}\Rightarrow\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{n}+\alpha,\:\mathrm{0}\leqslant\alpha<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}} =\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{n}} .\mathrm{4}^{\alpha} −\mathrm{2}^{\alpha} \mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}} −\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{n}} −\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}} −\mathrm{1}\leqslant\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}} =\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{n}} .\mathrm{4}^{\alpha} −\mathrm{2}^{\alpha} \mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}} −\mathrm{1}<\mathrm{4}.\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{n}} −\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}} −\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}} =\mathrm{y} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2y}−\mathrm{1}\leqslant\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow\mathrm{1}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\leqslant\mathrm{y}\leqslant\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}\in\left\{\mathrm{1},\mathrm{2}\right\} \\ $$$$\mathrm{4y}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3y}−\mathrm{1}>\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}<\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\:\mathrm{e}\:\mathrm{y}>\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}>\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{2}\Rightarrow\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{1}+\alpha,\:\mathrm{0}\leqslant\alpha<\mathrm{1},\:\lfloor\mathrm{x}\rfloor=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{log}_{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{1}+\alpha} −\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{1}+\alpha} −\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{4}.\mathrm{4}^{\alpha} −\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{2}^{\alpha} ,\:\mathrm{z}=\mathrm{2}^{\alpha} \\ $$$$\mathrm{4z}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2z}−\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}\leqslant\mathrm{z}=\frac{\mathrm{1}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{13}}}{\mathrm{4}}=\mathrm{2}^{\alpha} <\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}^{\alpha} =\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{13}}}{\mathrm{4}}\Rightarrow\alpha=\mathrm{log}_{\mathrm{2}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{13}}}{\mathrm{4}}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{x}} =\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{1}+\alpha} =\mathrm{4}.\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{log}_{\mathrm{2}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{13}}}{\mathrm{4}}\right)} =\mathrm{4}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{13}}}{\mathrm{4}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{7}+\sqrt{\mathrm{13}}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{x}} \Rightarrow\lfloor\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{x}} \rfloor=\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by Tawa11 last updated on 02/Jun/22

$$\mathrm{Great}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
