
Question Number 121973 by bemath last updated on 13/Nov/20
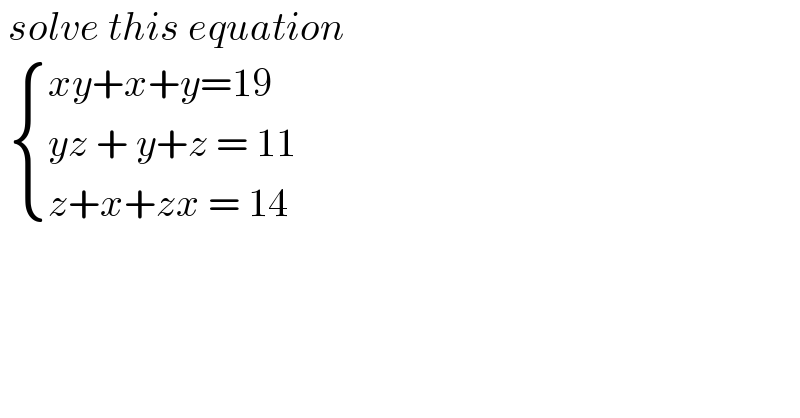
$$\:{solve}\:{this}\:{equation}\: \\ $$$$\:\begin{cases}{{xy}+{x}+{y}=\mathrm{19}}\\{{yz}\:+\:{y}+{z}\:=\:\mathrm{11}}\\{{z}+{x}+{zx}\:=\:\mathrm{14}}\end{cases} \\ $$
Commented by liberty last updated on 13/Nov/20

$$\rightarrow\:\mathrm{x}\left(\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{19}−\mathrm{y}\:\wedge\:\mathrm{z}\left(\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{11}−\mathrm{y} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\begin{cases}{\mathrm{x}=\frac{\mathrm{19}−\mathrm{y}}{\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{1}}}\\{\mathrm{z}=\frac{\mathrm{11}−\mathrm{y}}{\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{1}}}\end{cases}\:\Leftrightarrow\:\mathrm{substitution}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{eq}\left(\mathrm{3}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{give}\:\frac{\mathrm{19}−\mathrm{y}}{\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{1}}\:+\:\frac{\mathrm{11}−\mathrm{y}}{\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{1}}\:+\:\frac{\left(\mathrm{19}−\mathrm{y}\right)\left(\mathrm{11}−\mathrm{y}\right)}{\left(\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\:\mathrm{14} \\ $$$$\mathrm{which}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{equivalent}\:\mathrm{to}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{14}\left(\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\left(\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{30}−\mathrm{2y}\right)−\left(\mathrm{19}−\mathrm{y}\right)\left(\mathrm{11}−\mathrm{y}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{simplifying}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2y}−\mathrm{15}=\mathrm{0}\:\rightarrow\begin{cases}{\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{3}}\\{\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{2}} =−\mathrm{5}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{corresponding}\:\mathrm{values}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{x}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{z}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{computed}\:\mathrm{from}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{previous}\:\mathrm{formulas} \\ $$$$\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{get}\:\begin{cases}{\mathrm{x}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{4}\:,\:\mathrm{x}_{\mathrm{2}} =−\mathrm{6}}\\{\mathrm{z}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{2}\:,\:\mathrm{z}_{\mathrm{2}} =−\mathrm{4}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\mathrm{so}\:\mathrm{there}\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{exactly}\:\mathrm{two}\:\mathrm{solution} \\ $$$$\mathrm{triples}\:\left(\mathrm{x},\mathrm{y},\mathrm{z}\right):\:\left(\mathrm{4},\mathrm{3},\mathrm{2}\right)\:\mathrm{and}\:\left(−\mathrm{6},−\mathrm{5},−\mathrm{4}\right).\blacktriangle \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 13/Nov/20
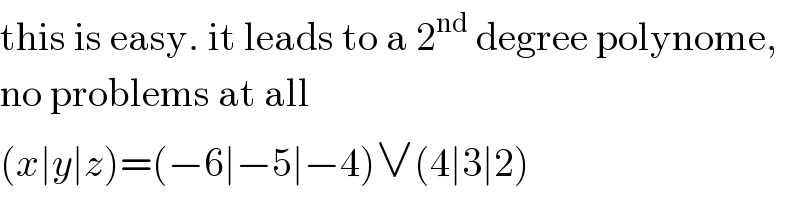
$$\mathrm{this}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{easy}.\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{leads}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{nd}} \:\mathrm{degree}\:\mathrm{polynome}, \\ $$$$\mathrm{no}\:\mathrm{problems}\:\mathrm{at}\:\mathrm{all} \\ $$$$\left({x}\mid{y}\mid{z}\right)=\left(−\mathrm{6}\mid−\mathrm{5}\mid−\mathrm{4}\right)\vee\left(\mathrm{4}\mid\mathrm{3}\mid\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$
Commented by bemath last updated on 13/Nov/20

$${thank}\:{you}\:{both}\: \\ $$
Commented by soumyasaha last updated on 13/Nov/20
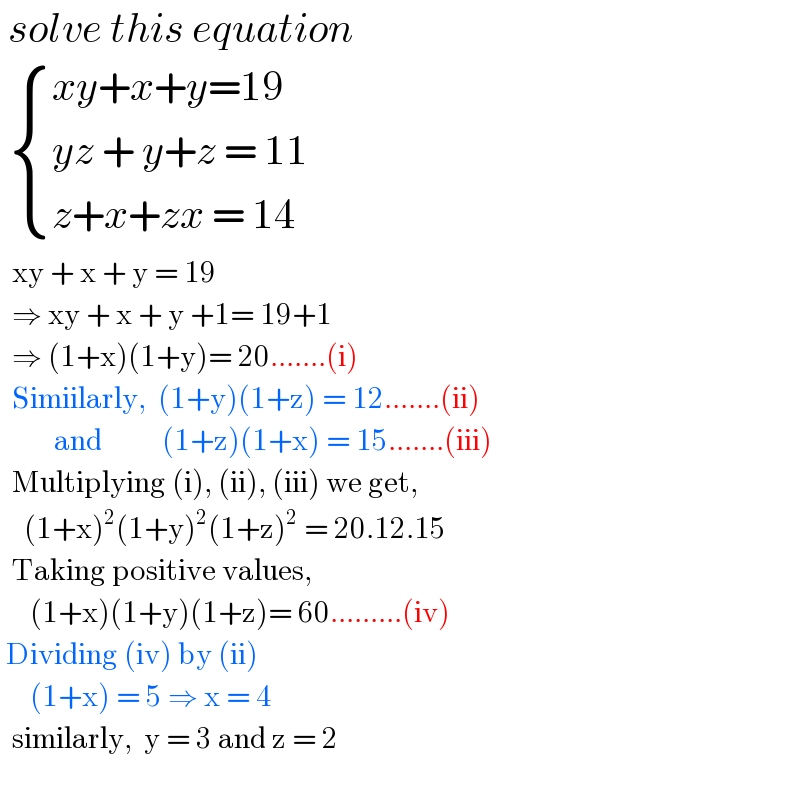
$$\:{solve}\:{this}\:{equation}\: \\ $$$$\:\begin{cases}{{xy}+{x}+{y}=\mathrm{19}}\\{{yz}\:+\:{y}+{z}\:=\:\mathrm{11}}\\{{z}+{x}+{zx}\:=\:\mathrm{14}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{xy}\:+\:\mathrm{x}\:+\:\mathrm{y}\:=\:\mathrm{19} \\ $$$$\:\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{xy}\:+\:\mathrm{x}\:+\:\mathrm{y}\:+\mathrm{1}=\:\mathrm{19}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\:\:\Rightarrow\:\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}\right)\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{y}\right)=\:\mathrm{20}.......\left(\mathrm{i}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{Simiilarly},\:\:\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{y}\right)\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{z}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{12}.......\left(\mathrm{ii}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{and}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{z}\right)\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{15}.......\left(\mathrm{iii}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{Multiplying}\:\left(\mathrm{i}\right),\:\left(\mathrm{ii}\right),\:\left(\mathrm{iii}\right)\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{get}, \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{y}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{z}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:=\:\mathrm{20}.\mathrm{12}.\mathrm{15} \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{Taking}\:\mathrm{positive}\:\mathrm{values}, \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}\right)\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{y}\right)\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{z}\right)=\:\mathrm{60}.........\left(\mathrm{iv}\right) \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{Dividing}\:\left(\mathrm{iv}\right)\:\mathrm{by}\:\left(\mathrm{ii}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{5}\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{x}\:=\:\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{similarly},\:\:\mathrm{y}\:=\:\mathrm{3}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{z}\:=\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by nimnim last updated on 13/Nov/20
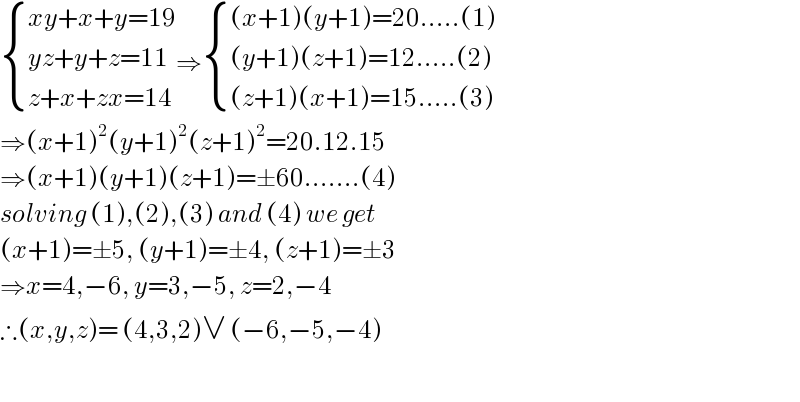
$$\begin{cases}{{xy}+{x}+{y}=\mathrm{19}}\\{{yz}+{y}+{z}=\mathrm{11}}\\{{z}+{x}+{zx}=\mathrm{14}}\end{cases}\Rightarrow\begin{cases}{\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({y}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{20}.....\left(\mathrm{1}\right)}\\{\left({y}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({z}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{12}.....\left(\mathrm{2}\right)}\\{\left({z}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{15}.....\left(\mathrm{3}\right)}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left({y}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left({z}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{20}.\mathrm{12}.\mathrm{15} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({y}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({z}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\pm\mathrm{60}.......\left(\mathrm{4}\right) \\ $$$${solving}\:\left(\mathrm{1}\right),\left(\mathrm{2}\right),\left(\mathrm{3}\right)\:{and}\:\left(\mathrm{4}\right)\:{we}\:{get} \\ $$$$\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\pm\mathrm{5},\:\left({y}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\pm\mathrm{4},\:\left({z}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\pm\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{4},−\mathrm{6},\:{y}=\mathrm{3},−\mathrm{5},\:{z}=\mathrm{2},−\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\therefore\left({x},{y},{z}\right)=\:\left(\mathrm{4},\mathrm{3},\mathrm{2}\right)\vee\:\left(−\mathrm{6},−\mathrm{5},−\mathrm{4}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$
