
Question Number 116078 by Study last updated on 30/Sep/20
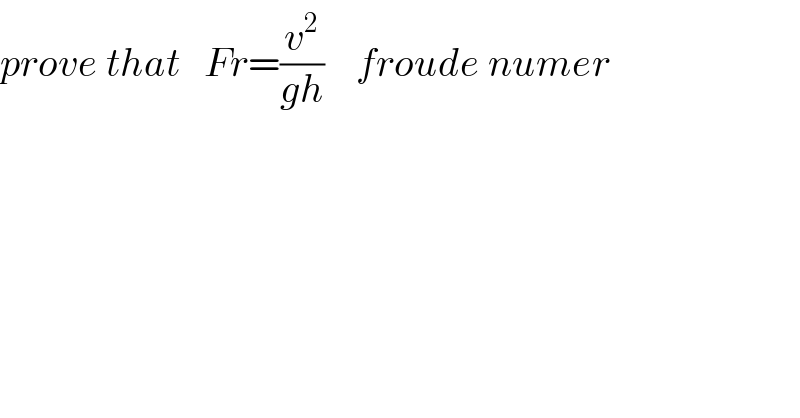
$${prove}\:{that}\:\:\:{Fr}=\frac{{v}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{gh}}\:\:\:\:{froude}\:{numer} \\ $$
Answered by MrGaster last updated on 06/Jan/25
![F_r =(v^2 /(gh))(froude numer) Let v be the velocity of the object,g be the acceleration due to gravity,and h be the characteristic length From dimensional analysis: ∣Fr∣=((∣v∣^2 )/(∣g∣∣h∣)) ∣v∣=(L/T),[g]=(L/T^2 ),[h]=L [Fr]=((((L/T)))/((L/T^2 )∙L))=((L^2 /T^2 )/(L^2 /T^2 ))=1 Thus the Froude number isidimensonless. Consider the forces acting on thejobect: Gravitational force F_G ∝ρgL^3 The Froude number is the ratio ofn iertial force to gravitational force: F_r =(F_1 /F_G )=((ρv^2 L^2 )/(ρgL^3 ))=(v^2 /(gL)) Therefore it is proven that F_r =(v^2 /(hh)).](Q215415.png)
$${F}_{{r}} =\frac{{v}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{gh}}\left({froude}\:{numer}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{Let}\:{v}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{velocity}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{object},{g}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{acceleration}\:\mathrm{due}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{gravity},\mathrm{and}\:{h}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{characteristic}\:\mathrm{length} \\ $$$$\mathrm{From}\:\mathrm{dimensional}\:\mathrm{analysis}: \\ $$$$\mid{Fr}\mid=\frac{\mid{v}\mid^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mid{g}\mid\mid{h}\mid} \\ $$$$\mid{v}\mid=\frac{{L}}{{T}},\left[{g}\right]=\frac{{L}}{{T}^{\mathrm{2}} },\left[{h}\right]={L} \\ $$$$\left[{Fr}\right]=\frac{\left(\frac{{L}}{{T}}\right)}{\frac{{L}}{{T}^{\mathrm{2}} }\centerdot{L}}=\frac{\frac{{L}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{T}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{\frac{{L}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{T}^{\mathrm{2}} }}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Thus}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{Froude}\:\mathrm{number}\:\mathrm{isidimensonless}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{Consider}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{forces}\:\mathrm{acting}\:\mathrm{on}\:\mathrm{thejobect}: \\ $$$$\mathrm{Gravitational}\:\mathrm{force}\:{F}_{{G}} \propto\rho{gL}^{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{The}\:\mathrm{Froude}\:\mathrm{number}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{ratio}\:\mathrm{ofn} \\ $$$$\mathrm{iertial}\:\mathrm{force}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{gravitational}\:\mathrm{force}: \\ $$$${F}_{{r}} =\frac{{F}_{\mathrm{1}} }{{F}_{{G}} }=\frac{\rho{v}^{\mathrm{2}} {L}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\rho{gL}^{\mathrm{3}} }=\frac{{v}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{gL}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Therefore}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{proven}\:\mathrm{that}\:{F}_{{r}} =\frac{{v}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{hh}}. \\ $$
