
Question Number 163704 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 09/Jan/22
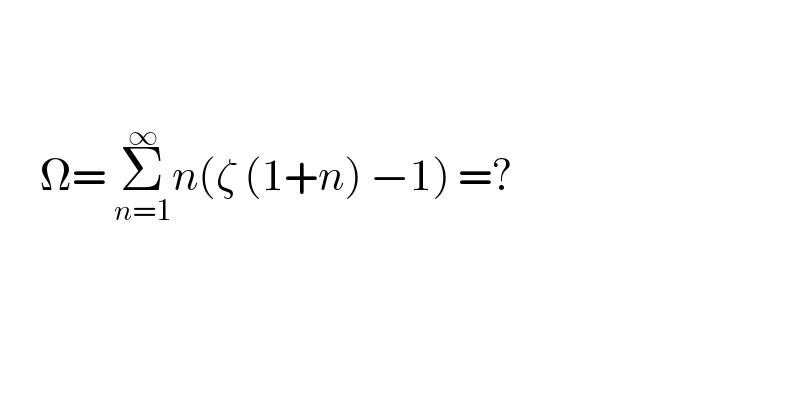
$$ \\ $$$$\:\:\:\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\Omega=\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}{n}\left(\zeta\:\left(\mathrm{1}+{n}\right)\:−\mathrm{1}\right)\:=? \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by Kamel last updated on 09/Jan/22
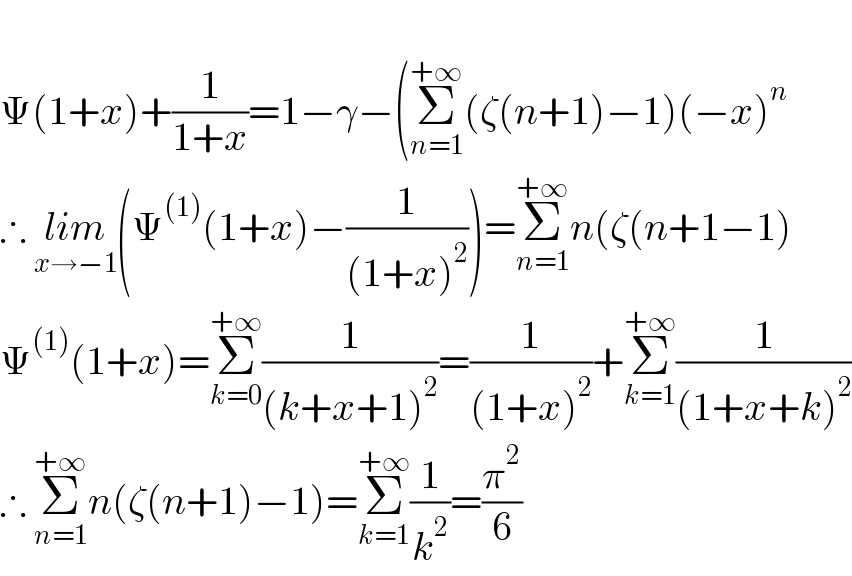
$$ \\ $$$$\Psi\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}=\mathrm{1}−\gamma−\left(\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{+\infty} {\sum}}\left(\zeta\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{1}\right)\left(−{x}\right)^{{n}} \right. \\ $$$$\therefore\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow−\mathrm{1}} {{lim}}\left(\Psi^{\left(\mathrm{1}\right)} \left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)=\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{+\infty} {\sum}}{n}\left(\zeta\left({n}+\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}\right)\right. \\ $$$$\Psi^{\left(\mathrm{1}\right)} \left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)=\underset{{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{+\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left({k}+{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }+\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{+\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}+{k}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\therefore\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{+\infty} {\sum}}{n}\left(\zeta\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{1}\right)=\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{+\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{k}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 10/Jan/22
$${very}\:{nice}\:{solution}... \\ $$
Answered by qaz last updated on 10/Jan/22
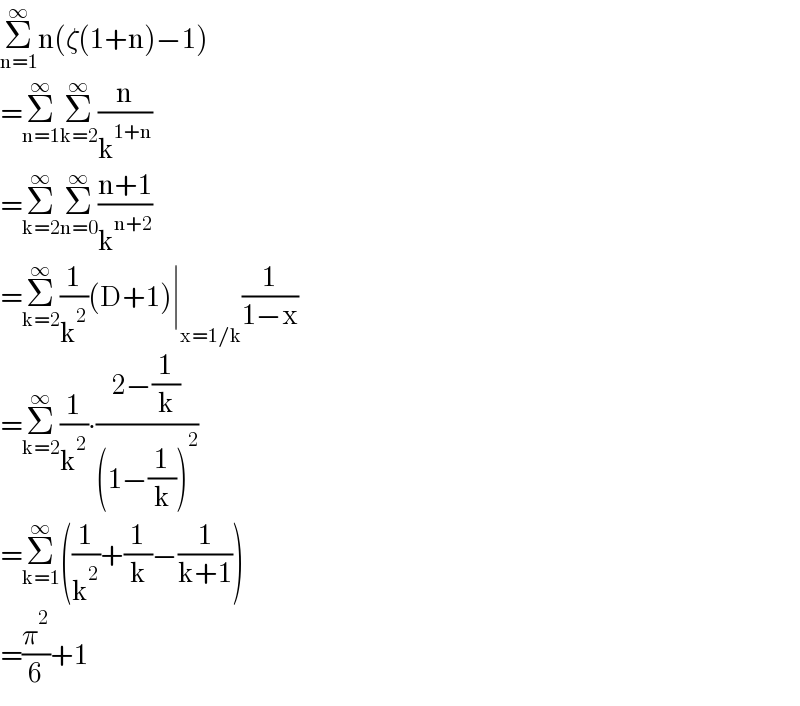
$$\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\mathrm{n}\left(\zeta\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{n}\right)−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$=\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{2}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{k}^{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{n}} } \\ $$$$=\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{2}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{k}^{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{2}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{k}^{\mathrm{2}} }\left(\mathrm{D}+\mathrm{1}\right)\mid_{\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{1}/\mathrm{k}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{x}} \\ $$$$=\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{2}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{k}^{\mathrm{2}} }\centerdot\frac{\mathrm{2}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{k}}}{\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{k}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{k}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{k}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{k}+\mathrm{1}}\right) \\ $$$$=\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{6}}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 10/Jan/22
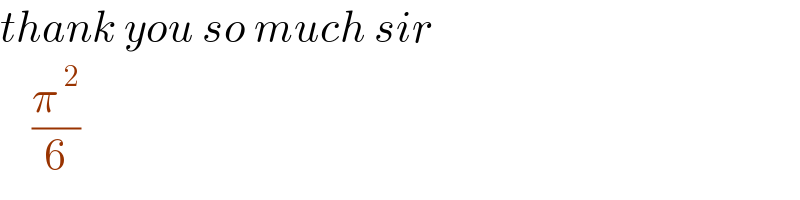
$${thank}\:{you}\:{so}\:{much}\:{sir} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\frac{\pi^{\:\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$
