
Question Number 66412 by aliesam last updated on 14/Aug/19
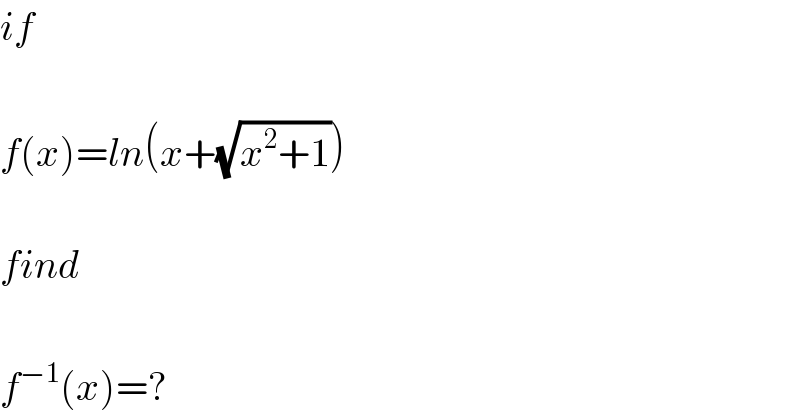
$${if} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)={ln}\left({x}+\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${find} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${f}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({x}\right)=? \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 14/Aug/19
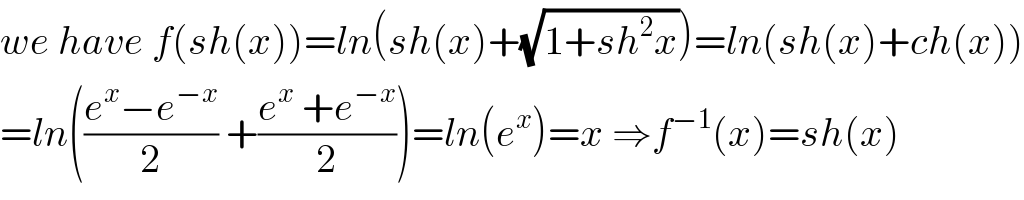
$${we}\:{have}\:{f}\left({sh}\left({x}\right)\right)={ln}\left({sh}\left({x}\right)+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{sh}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}\right)={ln}\left({sh}\left({x}\right)+{ch}\left({x}\right)\right) \\ $$$$={ln}\left(\frac{{e}^{{x}} −{e}^{−{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:+\frac{{e}^{{x}} \:+{e}^{−{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}\right)={ln}\left({e}^{{x}} \right)={x}\:\Rightarrow{f}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({x}\right)={sh}\left({x}\right) \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 14/Aug/19
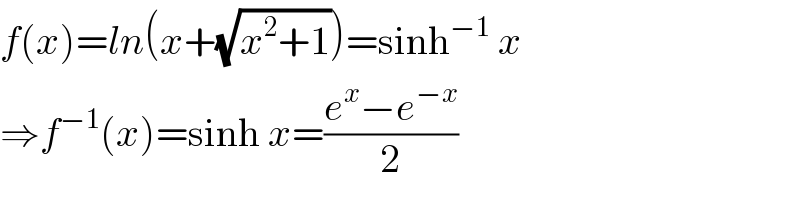
$${f}\left({x}\right)={ln}\left({x}+\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}\right)=\mathrm{sinh}^{−\mathrm{1}} \:{x} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{f}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({x}\right)=\mathrm{sinh}\:{x}=\frac{{e}^{{x}} −{e}^{−{x}} }{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 15/Aug/19
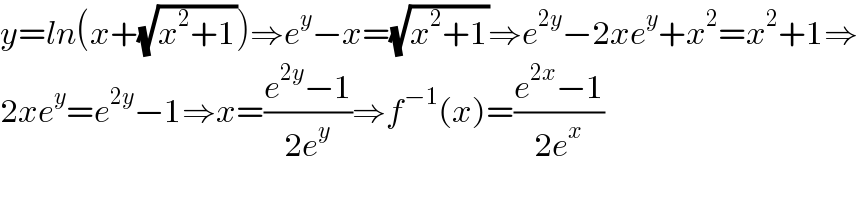
$${y}={ln}\left({x}+\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}\right)\Rightarrow{e}^{{y}} −{x}=\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}\Rightarrow{e}^{\mathrm{2}{y}} −\mathrm{2}{xe}^{{y}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} ={x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{xe}^{{y}} ={e}^{\mathrm{2}{y}} −\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow{x}=\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{y}} −\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{e}^{{y}} }\Rightarrow{f}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({x}\right)=\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} −\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{e}^{{x}} } \\ $$
Answered by MJS last updated on 14/Aug/19
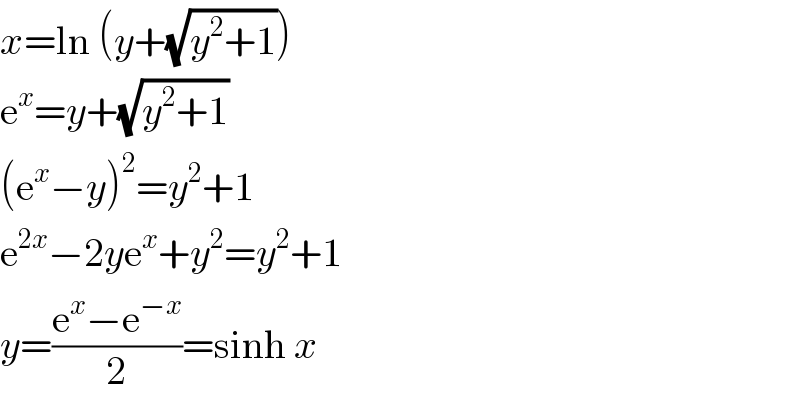
$${x}=\mathrm{ln}\:\left({y}+\sqrt{{y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{e}^{{x}} ={y}+\sqrt{{y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{e}^{{x}} −{y}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} ={y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} −\mathrm{2}{y}\mathrm{e}^{{x}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} ={y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${y}=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{{x}} −\mathrm{e}^{−{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{sinh}\:{x} \\ $$
Commented by Mikael last updated on 15/Aug/19

$${nice}\:{Sir}. \\ $$
