
Question Number 62122 by aliesam last updated on 15/Jun/19
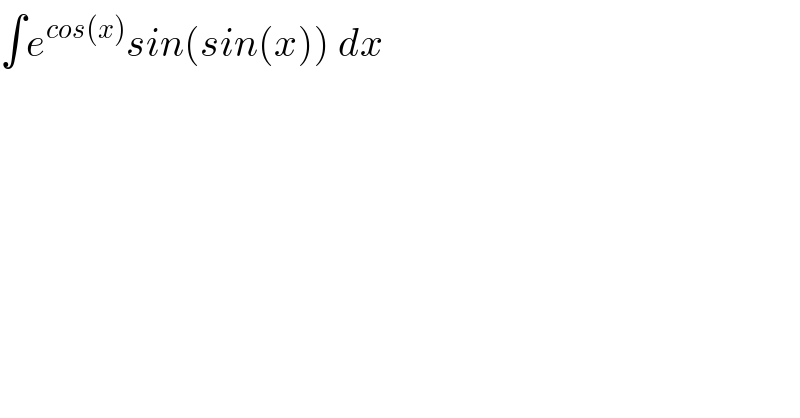
$$\int{e}^{{cos}\left({x}\right)} {sin}\left({sin}\left({x}\right)\right)\:{dx}\: \\ $$
Commented by MJS last updated on 15/Jun/19
![∫e^(cos x) sin sin x dx=−(i/2)∫(e^((e^(ix) −e^(−ix) )/2) −e^(−((e^(ix) −e^(−ix) )/2)) )e^((e^(ix) +e^(−ix) )/2) dx= =−(i/2)∫(e^e^(ix) −e^e^(−ix) )dx=−(i/2)∫e^e^(ix) dx+(i/2)∫e^e^(−ix) dx −(i/2)∫e^e^(ix) dx= [t=e^(ix) → dx=−ie^(−ix) dt] =−(1/2)∫(e^t /t)dt (i/2)∫e^e^(−ix) dx= [t=e^(−ix) → dx=ie^(ix) dt] =−(1/2)∫(e^t /t)dt ⇒ both lead to the incomplete gamma function](Q62125.png)
$$\int\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}} \mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:{dx}=−\frac{\mathrm{i}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\left(\mathrm{e}^{\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{i}{x}} −\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{i}{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}} −\mathrm{e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{i}{x}} −\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{i}{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}} \right)\mathrm{e}^{\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{i}{x}} +\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{i}{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}} {dx}= \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{i}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\left(\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{i}{x}} } −\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{i}{x}} } \right){dx}=−\frac{\mathrm{i}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{i}{x}} } {dx}+\frac{\mathrm{i}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{i}{x}} } {dx} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$−\frac{\mathrm{i}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{i}{x}} } {dx}= \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\left[{t}=\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{i}{x}} \:\rightarrow\:{dx}=−\mathrm{ie}^{−\mathrm{i}{x}} {dt}\right] \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\frac{\mathrm{e}^{{t}} }{{t}}{dt} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{i}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{i}{x}} } {dx}= \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\left[{t}=\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{i}{x}} \:\rightarrow\:{dx}=\mathrm{ie}^{\mathrm{i}{x}} {dt}\right] \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\frac{\mathrm{e}^{{t}} }{{t}}{dt} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{both}\:\mathrm{lead}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{incomplete}\:\mathrm{gamma}\:\mathrm{function} \\ $$
Commented by aliesam last updated on 15/Jun/19
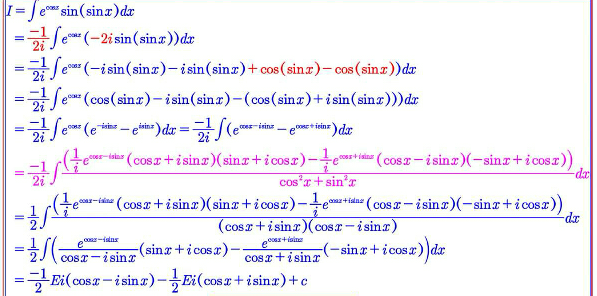
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 15/Jun/19
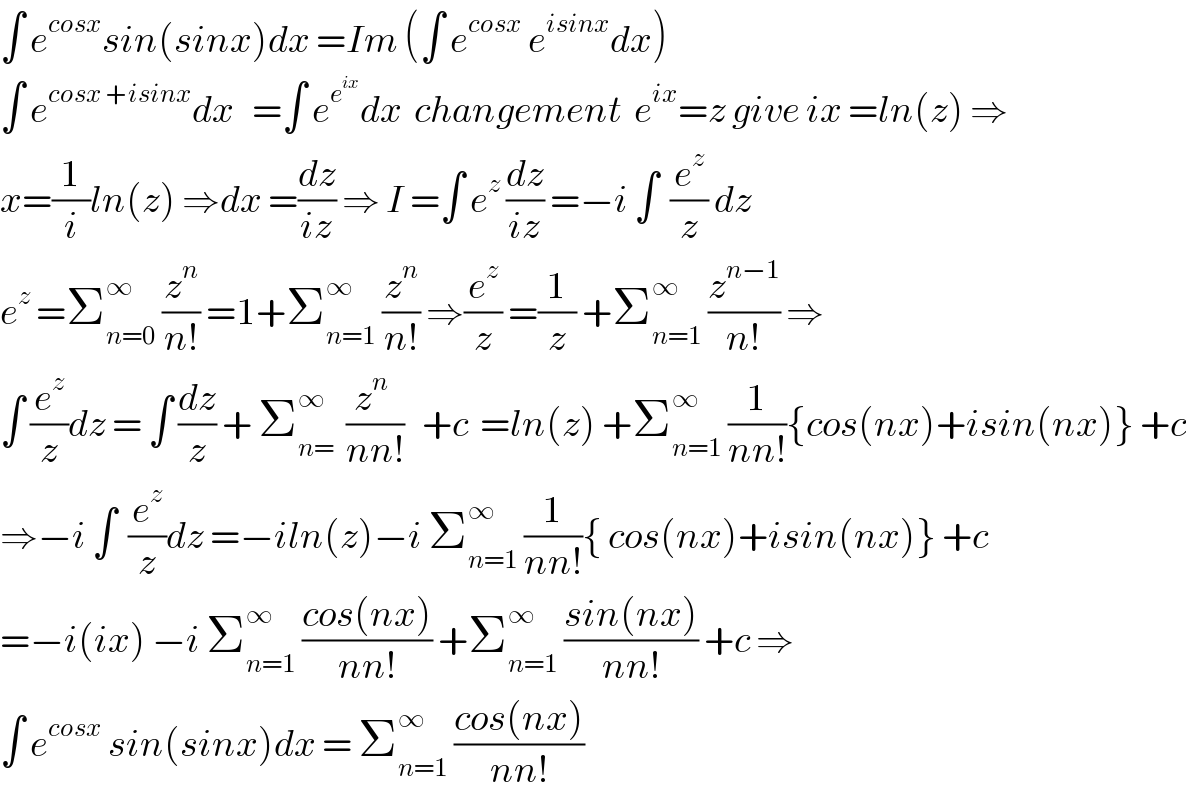
$$\int\:{e}^{{cosx}} {sin}\left({sinx}\right){dx}\:={Im}\:\left(\int\:{e}^{{cosx}} \:{e}^{{isinx}} {dx}\right) \\ $$$$\int\:{e}^{{cosx}\:+{isinx}} {dx}\:\:\:=\int\:{e}^{{e}^{{ix}} } {dx}\:\:{changement}\:\:{e}^{{ix}} ={z}\:{give}\:{ix}\:={ln}\left({z}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{i}}{ln}\left({z}\right)\:\Rightarrow{dx}\:=\frac{{dz}}{{iz}}\:\Rightarrow\:{I}\:=\int\:{e}^{{z}} \:\frac{{dz}}{{iz}}\:=−{i}\:\int\:\:\frac{{e}^{{z}} }{{z}}\:{dz}\:\: \\ $$$${e}^{{z}} \:=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{{z}^{{n}} }{{n}!}\:=\mathrm{1}+\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{{z}^{{n}} }{{n}!}\:\Rightarrow\frac{{e}^{{z}} }{{z}}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{z}}\:+\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{{z}^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} }{{n}!}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\int\:\frac{{e}^{{z}} }{{z}}{dz}\:=\:\int\:\frac{{dz}}{{z}}\:+\:\sum_{{n}=} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{{z}^{{n}} \:}{{nn}!}\:\:\:+{c}\:\:={ln}\left({z}\right)\:+\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{nn}!}\left\{{cos}\left({nx}\right)+{isin}\left({nx}\right)\right\}\:+{c} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow−{i}\:\int\:\:\frac{{e}^{{z}} }{{z}}{dz}\:=−{iln}\left({z}\right)−{i}\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{nn}!}\left\{\:{cos}\left({nx}\right)+{isin}\left({nx}\right)\right\}\:+{c} \\ $$$$=−{i}\left({ix}\right)\:−{i}\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{{cos}\left({nx}\right)}{{nn}!}\:+\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{{sin}\left({nx}\right)}{{nn}!}\:+{c}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\int\:{e}^{{cosx}} \:{sin}\left({sinx}\right){dx}\:=\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{{cos}\left({nx}\right)}{{nn}!} \\ $$
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 16/Jun/19
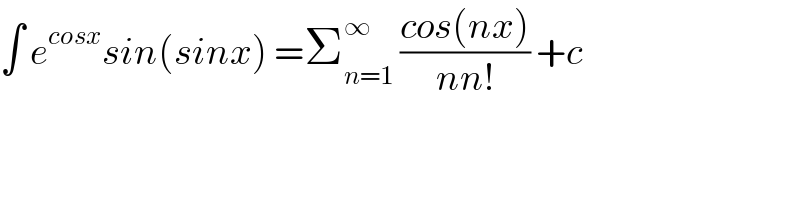
$$\int\:{e}^{{cosx}} {sin}\left({sinx}\right)\:=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{{cos}\left({nx}\right)}{{nn}!}\:+{c}\: \\ $$
