
Previous in Differential Equation Next in Differential Equation
Question Number 91353 by jagoll last updated on 30/Apr/20
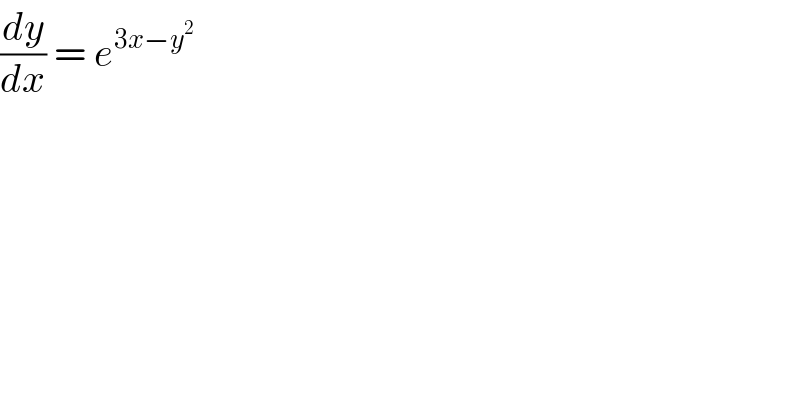
$$\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:=\:{e}^{\mathrm{3}{x}−{y}^{\mathrm{2}} } \: \\ $$
Answered by niroj last updated on 30/Apr/20
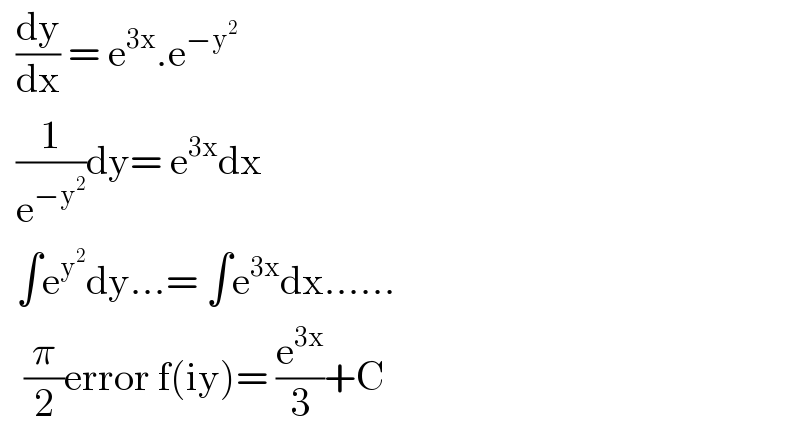
$$\:\:\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\:=\:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3x}} .\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} } }\mathrm{dy}=\:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3x}} \mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\int\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} } \mathrm{dy}...=\:\int\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3x}} \mathrm{dx}...... \\ $$$$\:\:\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{error}\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{iy}\right)=\:\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3x}} }{\mathrm{3}}+\mathrm{C} \\ $$
