
Question Number 203774 by Calculusboy last updated on 27/Jan/24
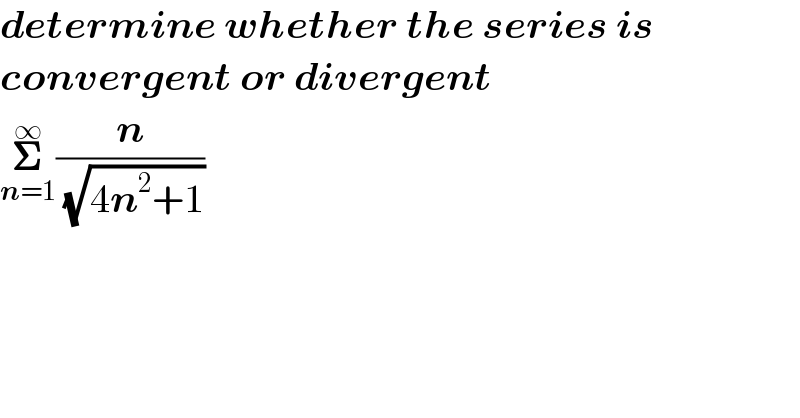
$$\boldsymbol{{determine}}\:\boldsymbol{{whether}}\:\boldsymbol{{the}}\:\boldsymbol{{series}}\:\boldsymbol{{is}} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{convergent}}\:\boldsymbol{{or}}\:\boldsymbol{{divergent}} \\ $$$$\underset{\boldsymbol{{n}}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\boldsymbol{\sum}}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{n}}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{4}\boldsymbol{{n}}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}} \\ $$
Answered by witcher3 last updated on 27/Jan/24
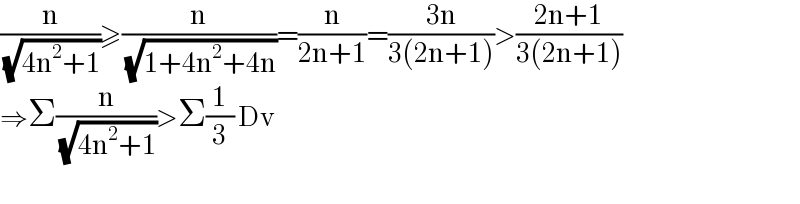
$$\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{4n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}}\geqslant\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{4n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4n}}}=\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{2n}+\mathrm{1}}=\frac{\mathrm{3n}}{\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{2n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}>\frac{\mathrm{2n}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{2n}+\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\Sigma\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{4n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}}>\Sigma\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\:\mathrm{Dv} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by Mathspace last updated on 30/Jan/24

$$\frac{{n}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{4}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}}=\frac{{n}}{\mathrm{2}{n}\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }}} \\ $$$${we}\:{have}\:\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)^{\alpha} =\mathrm{1}+\alpha{x}\:+\frac{\alpha\left(\alpha−\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{o}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}}}=\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)^{−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\left(−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{1}\right){x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{o}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$=\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}×\frac{−\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{o}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$=\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{8}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{o}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){so} \\ $$$${u}_{{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{16}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{16}}×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{16}{n}^{\mathrm{4}} }+{o}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{4}} }\right) \\ $$$${est}\:{un}\:{dev}.{assymtotique}\:{de} \\ $$$${u}_{{n}} \:\:\:\:{ona}\:{lim}\:{u}_{{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\neq\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\Sigma{u}_{{n}} \:{est}\:{divergente}. \\ $$$$ \\ $$
