
Question Number 46586 by naka3546 last updated on 28/Oct/18
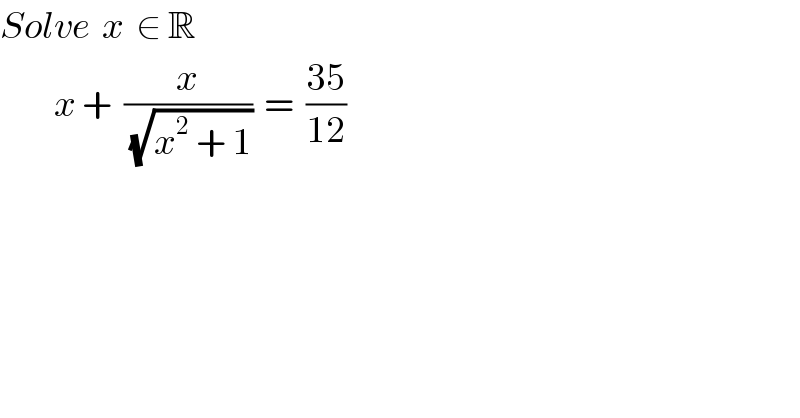
$${Solve}\:\:{x}\:\:\in\:\mathbb{R} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}\:+\:\:\frac{{x}}{\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\:\mathrm{1}}}\:\:=\:\:\frac{\mathrm{35}}{\mathrm{12}} \\ $$
Answered by Kunal12588 last updated on 29/Oct/18
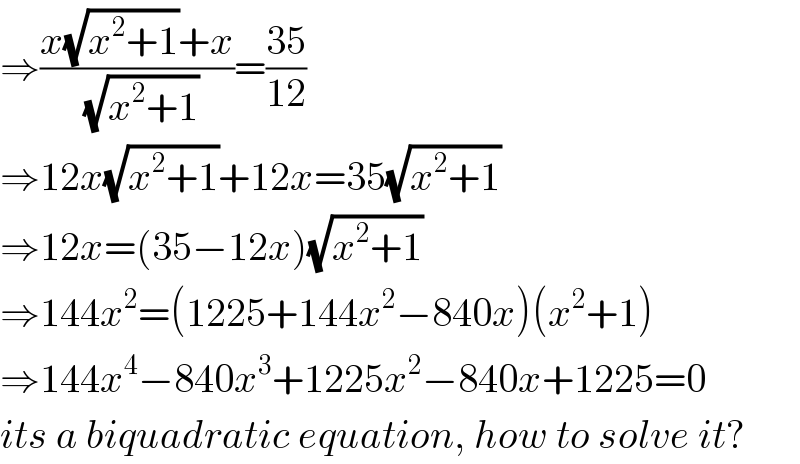
$$\Rightarrow\frac{{x}\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}+{x}}{\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}}=\frac{\mathrm{35}}{\mathrm{12}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{12}{x}\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}+\mathrm{12}{x}=\mathrm{35}\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{12}{x}=\left(\mathrm{35}−\mathrm{12}{x}\right)\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{144}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} =\left(\mathrm{1225}+\mathrm{144}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{840}{x}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{144}{x}^{\mathrm{4}} −\mathrm{840}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{1225}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{840}{x}+\mathrm{1225}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${its}\:{a}\:{biquadratic}\:{equation},\:{how}\:{to}\:{solve}\:{it}? \\ $$
Commented by Kunal12588 last updated on 29/Oct/18
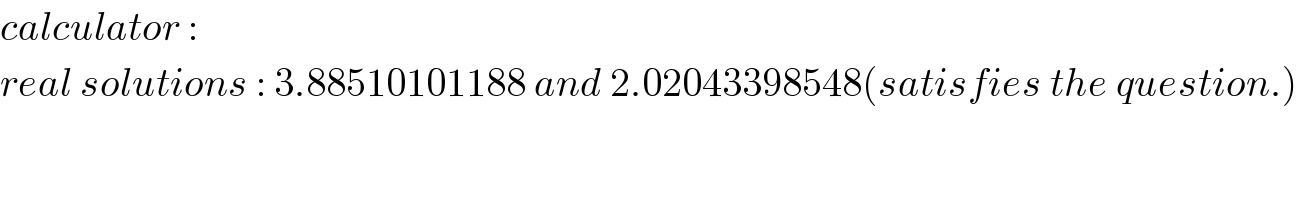
$${calculator}\::\: \\ $$$${real}\:{solutions}\::\:\mathrm{3}.\mathrm{88510101188}\:{and}\:\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{02043398548}\left({satisfies}\:{the}\:{question}.\right) \\ $$
Commented by MJS last updated on 29/Oct/18
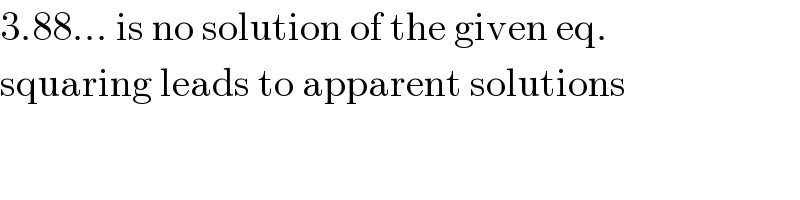
$$\mathrm{3}.\mathrm{88}...\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{no}\:\mathrm{solution}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{given}\:\mathrm{eq}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{squaring}\:\mathrm{leads}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{apparent}\:\mathrm{solutions} \\ $$
Commented by Kunal12588 last updated on 29/Oct/18
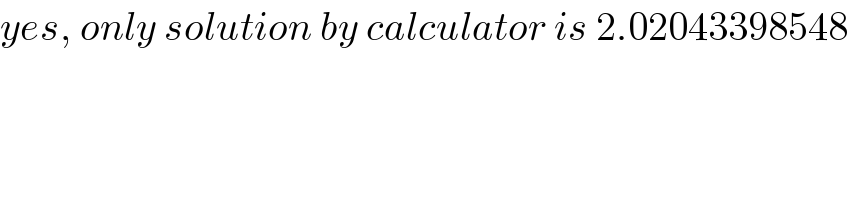
$${yes},\:{only}\:{solution}\:{by}\:{calculator}\:{is}\:\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{02043398548} \\ $$
Answered by MJS last updated on 29/Oct/18

$${f}\left({x}\right)={x}+\frac{{x}}{\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}}−\frac{\mathrm{35}}{\mathrm{12}} \\ $$$${f}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=−\frac{\mathrm{35}}{\mathrm{12}}<\mathrm{0}\wedge{f}\left(\frac{\mathrm{35}}{\mathrm{12}}\right)=\frac{\frac{\mathrm{35}}{\mathrm{12}}}{\sqrt{\left(\frac{\mathrm{35}}{\mathrm{12}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${f}'\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }}>\mathrm{0}\forall{x}\in\mathbb{R} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:\mathrm{has}\:\mathrm{got}\:\mathrm{exactly}\:\mathrm{one}\:\mathrm{zero} \\ $$$$\mathrm{approximation}\:\mathrm{leads}\:\mathrm{to}\:{x}\approx\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{02043} \\ $$$$\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{exact}\:\mathrm{solution}\:\mathrm{by}\:\mathrm{solving}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{resulting} \\ $$$$\mathrm{polynome}\:{x}^{\mathrm{4}} −\frac{\mathrm{35}}{\mathrm{6}}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\frac{\mathrm{1225}}{\mathrm{144}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{35}}{\mathrm{6}}{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1225}}{\mathrm{144}}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{manageable} \\ $$
