
Question Number 26649 by Mr eaay last updated on 27/Dec/17
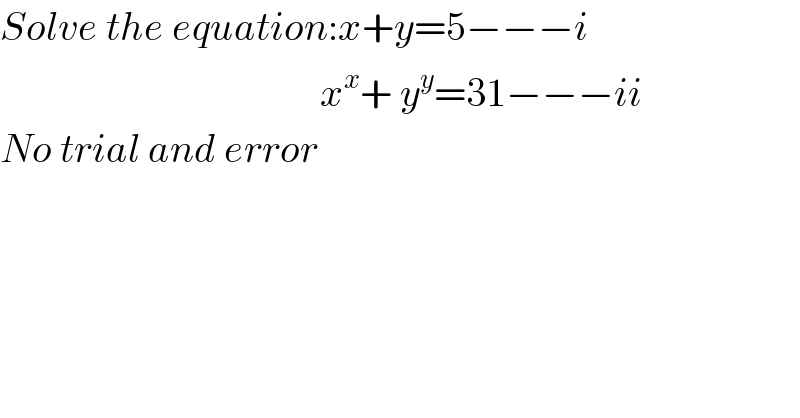
$${Solve}\:{the}\:{equation}:{x}+{y}=\mathrm{5}−−−{i} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}^{{x}} +\:{y}^{{y}} =\mathrm{31}−−−{ii} \\ $$$${No}\:{trial}\:{and}\:{error} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by mrW1 last updated on 27/Dec/17

$${If}\:{you}\:{want}\:{to}\:{get}\:{an}\:{analytic}\:{formula}, \\ $$$${I}\:{think}\:{there}\:{is}\:{no}\:{chance}. \\ $$$${For}\:{concrete}\:{values}\:{you}\:{can}\:{find} \\ $$$${the}\:{solution}\:{via}\:{graphic}\:{method}. \\ $$
Answered by Amstrongmazoka last updated on 28/Dec/17
![from equ(i), y=(5−x) substituting for y in equ(ii), gives, x^x +(5−x)^((5−x)) =31 ⇒x^x +(5−x)^((5−x)) −31=0 Now, let f(x)=x^x +(5−x)^((5−x)) −31 ⇒((df(x))/dx)=f′(x)=x^x (1+lnx)−(5−x)^((5−x)) [1+ln(5−x)] Now, by the Newton′s iterative formula, x_2 =x_1 −((f(x_1 ))/(f′(x_1 ))), now for this particular f(x), x_2 =x_1 −((x_1 ^x_1 +(5−x_1 )^((5−x_1 )) −31)/(x_1 ^x_1 (1+lnx_1 )−(5−x_1 )^((5−x_1 )) [1+ln(5−x_1 )])) Now, choosing any arbitrary value of x_1 that makes lnx and ln(5−x) defined, then we can only choose from 0<x<5 Now, taking x_1 =1 for instance, gives x_2 =1.3706, x_3 =1.6905, x_4 =1.9049, x_5 =1.9888 x_6 =1.9998, x_7 =2.0000, x_8 =2.0000 Thus lim_(x→2) x_n =2, ∴ x=2 is a solution. Similarly, choosing another arbitrary value of say x_1 =4, gives x_2 =3.6294, x_3 =3.3095, x_4 =3.0952, x_5 =3.0112, x_6 =3.0002, x_7 =3.0000, x_8 =3.0000 Again, lim_(x→3) x_n =3, ∴ x=3 is also a solution to the equation. Any other arbitrarily chosen value of x_(1 ) only points to either 2 or 3. Thus these are the only solutions. ∴ either x=2 or x=3. But x+y=5, −⇒y=5−x ∴ when x=2, y=5−2=3, and when x=3, y=5−3=2 Finally, for the system of equations, x=2 and y=3, or x=3 and y=2.](Q26718.png)
$${from}\:{equ}\left({i}\right),\:{y}=\left(\mathrm{5}−{x}\right) \\ $$$${substituting}\:{for}\:{y}\:{in}\:{equ}\left({ii}\right),\:{gives}, \\ $$$${x}^{{x}} +\left(\mathrm{5}−{x}\right)^{\left(\mathrm{5}−{x}\right)} =\mathrm{31} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}^{{x}} +\left(\mathrm{5}−{x}\right)^{\left(\mathrm{5}−{x}\right)} −\mathrm{31}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${Now},\:{let}\:{f}\left({x}\right)={x}^{{x}} +\left(\mathrm{5}−{x}\right)^{\left(\mathrm{5}−{x}\right)} −\mathrm{31} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{df}\left({x}\right)}{{dx}}={f}'\left({x}\right)={x}^{{x}} \left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{ln}{x}\right)−\left(\mathrm{5}−{x}\right)^{\left(\mathrm{5}−{x}\right)} \left[\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{5}−{x}\right)\right] \\ $$$${Now},\:{by}\:{the}\:{Newton}'{s}\:{iterative}\:{formula}, \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{2}} ={x}_{\mathrm{1}} −\frac{{f}\left({x}_{\mathrm{1}} \right)}{{f}'\left({x}_{\mathrm{1}} \right)},\:{now}\:{for}\:{this}\:{particular}\:{f}\left({x}\right), \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{2}} ={x}_{\mathrm{1}} −\frac{{x}_{\mathrm{1}} ^{{x}_{\mathrm{1}} } +\left(\mathrm{5}−{x}_{\mathrm{1}} \right)^{\left(\mathrm{5}−{x}_{\mathrm{1}} \right)} −\mathrm{31}}{{x}_{\mathrm{1}} ^{{x}_{\mathrm{1}} } \left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{ln}{x}_{\mathrm{1}} \right)−\left(\mathrm{5}−{x}_{\mathrm{1}} \right)^{\left(\mathrm{5}−{x}_{\mathrm{1}} \right)} \left[\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{5}−{x}_{\mathrm{1}} \right)\right]} \\ $$$${Now},\:{choosing}\:{any}\:{arbitrary}\:{value}\:{of}\:{x}_{\mathrm{1}} \:{that}\:{makes}\:{lnx}\:{and}\:{ln}\left(\mathrm{5}−{x}\right)\:{defined}, \\ $$$${then}\:{we}\:{can}\:{only}\:{choose}\:{from}\:\mathrm{0}<{x}<\mathrm{5} \\ $$$${Now},\:{taking}\:{x}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{1}\:\:{for}\:{instance},\:{gives}\:\: \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{3706},\:\:\:\:{x}_{\mathrm{3}} =\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{6905},\:\:\:\:\:{x}_{\mathrm{4}} =\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{9049},\:\:\:\:{x}_{\mathrm{5}} =\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{9888} \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{6}} =\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{9998},\:\:\:\:\:{x}_{\mathrm{7}} =\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{0000},\:\:\:\:\:{x}_{\mathrm{8}} =\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{0000} \\ $$$${Thus}\:\:\:\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}}{x}_{{n}} \:=\mathrm{2},\:\:\therefore\:{x}=\mathrm{2}\:{is}\:{a}\:{solution}. \\ $$$${Similarly},\:{choosing}\:{another}\:{arbitrary}\:{value}\:{of}\:{say}\:{x}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{4},\:{gives} \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{3}.\mathrm{6294},\:\:\:\:{x}_{\mathrm{3}} =\mathrm{3}.\mathrm{3095},\:\:\:\:{x}_{\mathrm{4}} =\mathrm{3}.\mathrm{0952}, \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{5}} =\mathrm{3}.\mathrm{0112},\:\:\:\:\:{x}_{\mathrm{6}} =\mathrm{3}.\mathrm{0002},\:\:\:{x}_{\mathrm{7}} =\mathrm{3}.\mathrm{0000},\:\:\:\:{x}_{\mathrm{8}} =\mathrm{3}.\mathrm{0000} \\ $$$${Again},\:\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{3}} {\mathrm{lim}}{x}_{{n}} \:=\mathrm{3},\:\:\:\therefore\:{x}=\mathrm{3}\:{is}\:{also}\:{a}\:{solution}\:{to}\:{the}\:{equation}. \\ $$$${Any}\:{other}\:{arbitrarily}\:{chosen}\:{value}\:{of}\:{x}_{\mathrm{1}\:} {only}\:{points} \\ $$$${to}\:{either}\:\mathrm{2}\:{or}\:\mathrm{3}.\:{Thus}\:{these}\:{are}\:{the}\:{only}\:{solutions}. \\ $$$$\therefore\:{either}\:{x}=\mathrm{2}\:{or}\:{x}=\mathrm{3}. \\ $$$${But}\:{x}+{y}=\mathrm{5},\:\:−\Rightarrow{y}=\mathrm{5}−{x} \\ $$$$\therefore\:{when}\:{x}=\mathrm{2},\:\:{y}=\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{3},\:\:{and}\:{when}\:{x}=\mathrm{3},\:\:{y}=\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${Finally},\:{for}\:{the}\:{system}\:{of}\:{equations}, \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{2}\:{and}\:{y}=\mathrm{3},\:\:\:{or}\:\:\:\:{x}=\mathrm{3}\:{and}\:{y}=\mathrm{2}. \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
