
Previous in Probability and Statistics Next in Probability and Statistics
Question Number 192375 by Spillover last updated on 16/May/23

$${Show}\:{that}\:{E}\left({Z}\right)=\mathrm{0}\:\:\:{and}\:{Var}\left({Z}\right)=\mathrm{1}\:{where} \\ $$$${Z}\:{is}\:{the}\:{standard}\:{normal}\:{variable} \\ $$
Answered by mehdee42 last updated on 16/May/23
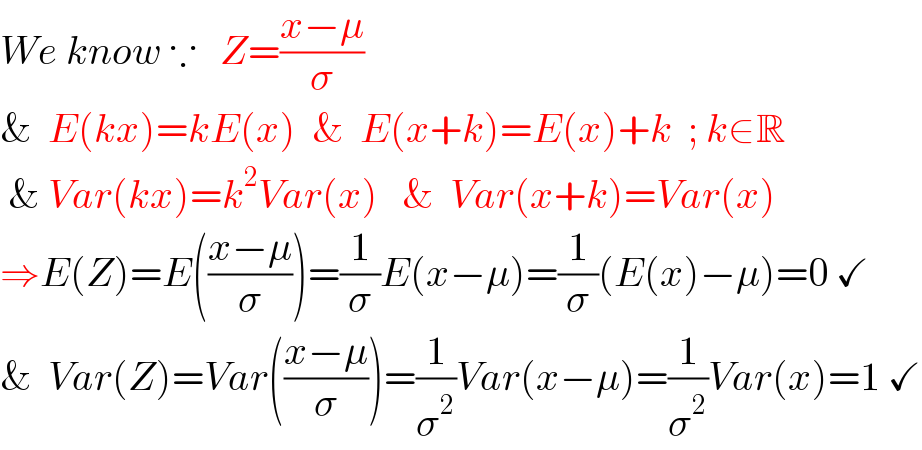
$${We}\:{know}\:\because\:\:\:{Z}=\frac{{x}−\mu}{\sigma}\:\:\: \\ $$$$\&\:\:{E}\left({kx}\right)={kE}\left({x}\right)\:\:\&\:\:{E}\left({x}+{k}\right)={E}\left({x}\right)+{k}\:\:;\:{k}\in\mathbb{R} \\ $$$$\:\&\:{Var}\left({kx}\right)={k}^{\mathrm{2}} {Var}\left({x}\right)\:\:\:\&\:\:{Var}\left({x}+{k}\right)={Var}\left({x}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{E}\left({Z}\right)={E}\left(\frac{{x}−\mu}{\sigma}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sigma}{E}\left({x}−\mu\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sigma}\left({E}\left({x}\right)−\mu\right)=\mathrm{0}\:\checkmark \\ $$$$\&\:\:{Var}\left({Z}\right)={Var}\left(\frac{{x}−\mu}{\sigma}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sigma^{\mathrm{2}} }{Var}\left({x}−\mu\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sigma^{\mathrm{2}} }{Var}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{1}\:\checkmark \\ $$
Commented by Spillover last updated on 17/May/23

$${thanks} \\ $$
