
Question Number 65356 by aliesam last updated on 28/Jul/19
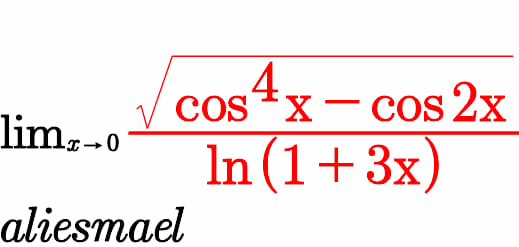
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 29/Jul/19
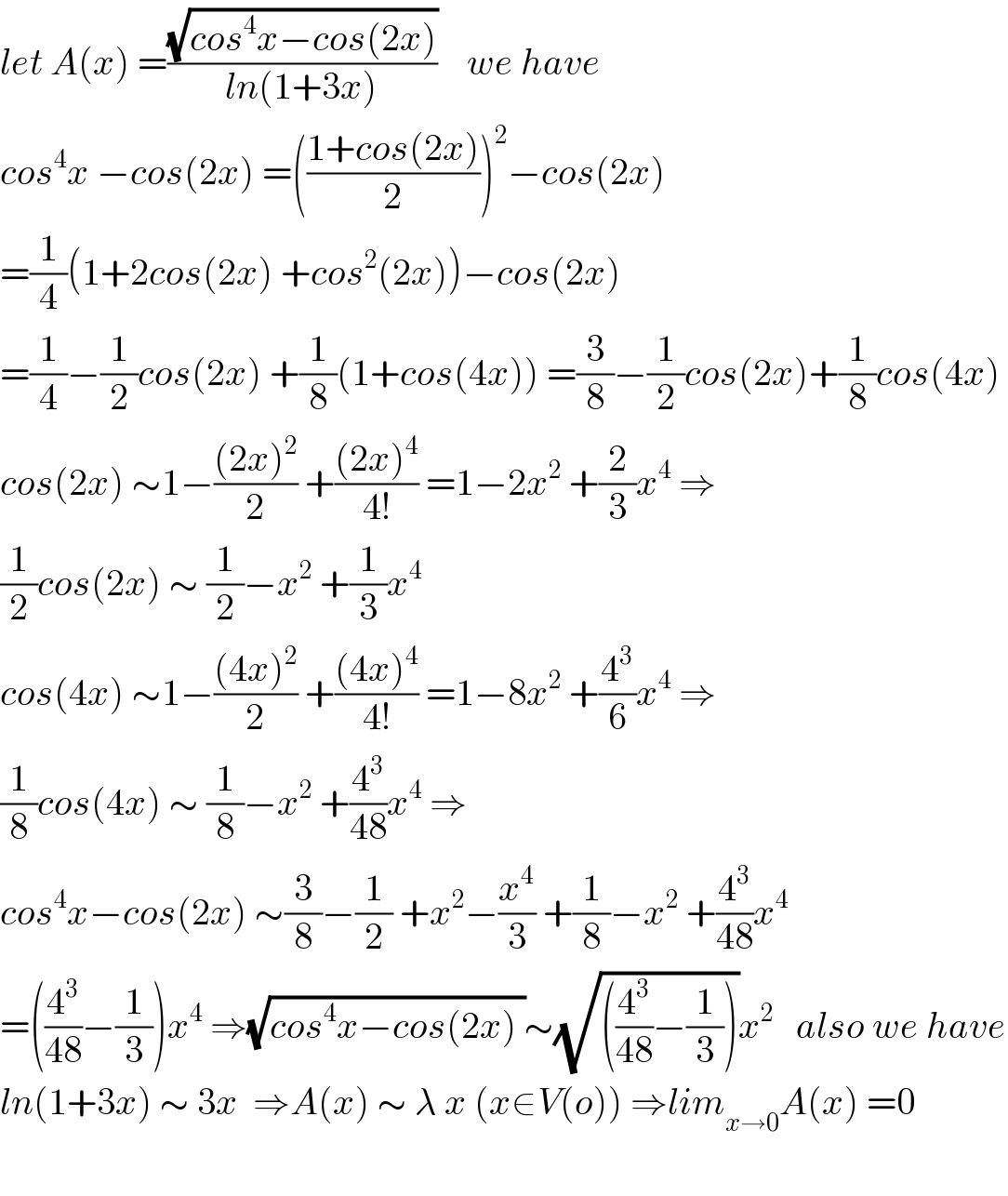
$${let}\:{A}\left({x}\right)\:=\frac{\sqrt{{cos}^{\mathrm{4}} {x}−{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)}}{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{3}{x}\right)}\:\:\:\:{we}\:{have}\: \\ $$$${cos}^{\mathrm{4}} {x}\:−{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\:=\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}+{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right) \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\:+{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\right)−{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right) \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}\left(\mathrm{1}+{cos}\left(\mathrm{4}{x}\right)\right)\:=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{8}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}{cos}\left(\mathrm{4}{x}\right) \\ $$$${cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\:\sim\mathrm{1}−\frac{\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:+\frac{\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{4}!}\:=\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}{x}^{\mathrm{4}} \:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\:\sim\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}{x}^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$${cos}\left(\mathrm{4}{x}\right)\:\sim\mathrm{1}−\frac{\left(\mathrm{4}{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:+\frac{\left(\mathrm{4}{x}\right)^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{4}!}\:=\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{8}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\frac{\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{6}}{x}^{\mathrm{4}} \:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}{cos}\left(\mathrm{4}{x}\right)\:\sim\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\frac{\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{48}}{x}^{\mathrm{4}} \:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${cos}^{\mathrm{4}} {x}−{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\:\sim\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{8}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{3}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\frac{\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{48}}{x}^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$=\left(\frac{\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{48}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\right){x}^{\mathrm{4}} \:\Rightarrow\sqrt{{cos}^{\mathrm{4}} {x}−{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\:}\sim\sqrt{\left(\frac{\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{48}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\:\:{also}\:{we}\:{have} \\ $$$${ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{3}{x}\right)\:\sim\:\mathrm{3}{x}\:\:\Rightarrow{A}\left({x}\right)\:\sim\:\lambda\:{x}\:\left({x}\in{V}\left({o}\right)\right)\:\Rightarrow{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {A}\left({x}\right)\:=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by Tanmay chaudhury last updated on 30/Jul/19

$${or}\:{method} \\ $$$${N}_{{r}} =\sqrt{{cos}^{\mathrm{4}} {x}−\left(\mathrm{2}{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}−\mathrm{1}\right)}\: \\ $$$$=\sqrt{\left({cos}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\: \\ $$$$=\sqrt{\left(\mathrm{1}−{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\: \\ $$$$={sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{3}{x}\right)} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\left(\frac{{sinx}}{{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} ×{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\frac{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{3}{x}\right)}{\mathrm{3}{x}}×\mathrm{3}{x}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}^{\mathrm{2}} ×\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{1}×\mathrm{3}\boldsymbol{{x}}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{x}}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{edited}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}×\mathrm{0}}{\mathrm{1}×\mathrm{3}}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by Tanmay chaudhury last updated on 29/Jul/19
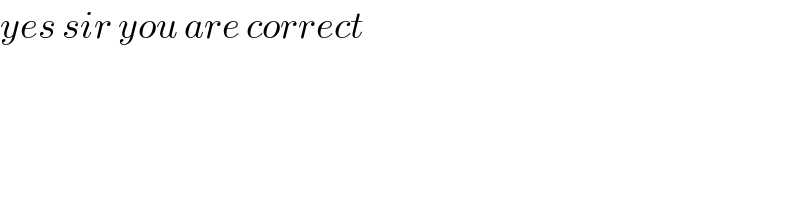
$${yes}\:{sir}\:{you}\:{are}\:{correct} \\ $$
Commented by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 29/Jul/19
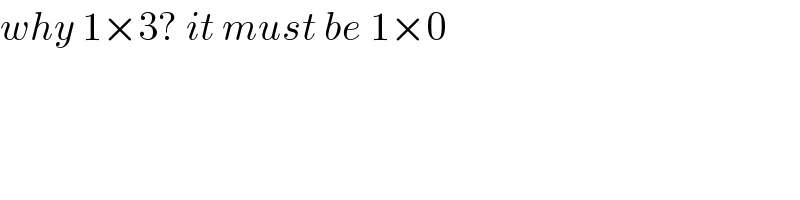
$${why}\:\mathrm{1}×\mathrm{3}?\:{it}\:{must}\:{be}\:\mathrm{1}×\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 29/Jul/19
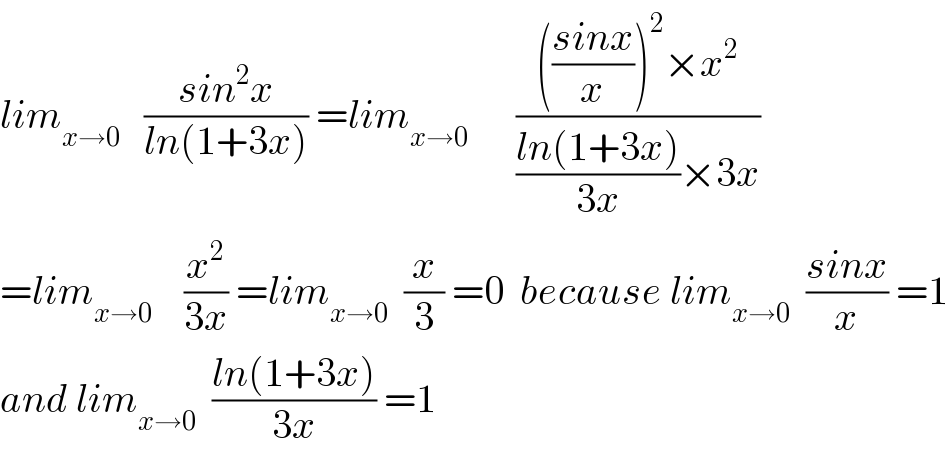
$${lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \:\:\:\frac{{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{3}{x}\right)}\:={lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{\left(\frac{{sinx}}{{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} ×{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\frac{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{3}{x}\right)}{\mathrm{3}{x}}×\mathrm{3}{x}} \\ $$$$={lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \:\:\:\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{3}{x}}\:={lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \:\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{3}}\:=\mathrm{0}\:\:{because}\:{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \:\:\frac{{sinx}}{{x}}\:=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${and}\:{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \:\:\frac{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{3}{x}\right)}{\mathrm{3}{x}}\:=\mathrm{1} \\ $$
