
Question Number 46973 by rahul 19 last updated on 03/Nov/18
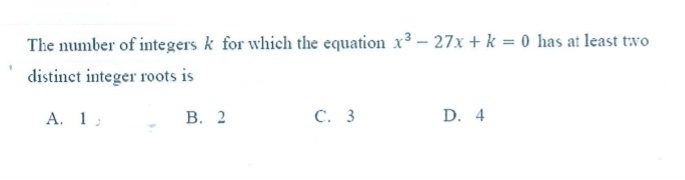
Answered by MJS last updated on 03/Nov/18

$${x}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{27}{x}+{k}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${D}=\frac{{k}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{4}}−\mathrm{729}<\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\:−\mathrm{54}\leqslant{k}\leqslant\mathrm{54} \\ $$$$\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{need}\:\mathrm{integer}\:\mathrm{solutions} \\ $$$$\mathrm{case}\:\mathrm{1}:\:\mathrm{3}\:\mathrm{solutions} \\ $$$$\left({x}−{o}\right)\left({x}−{p}\right)\left({x}−{q}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${o}+{p}+{q}=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\:{q}=−\left({o}+{p}\right) \\ $$$${op}+{oq}+{pq}=−\mathrm{27}\Rightarrow\:{o}^{\mathrm{2}} +{op}+{p}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{27}\:\Rightarrow\:{p}=−\frac{{o}}{\mathrm{2}}\pm\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{108}−\mathrm{3}{o}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$−{opq}={k}\:\Rightarrow\:{k}={op}\left({o}+{p}\right) \\ $$$$\sqrt{\mathrm{108}−\mathrm{3}{o}^{\mathrm{2}} }\in\mathbb{N}\:\Rightarrow\:{o}\in\left\{−\mathrm{6},\:−\mathrm{3},\:\mathrm{3},\:\mathrm{6}\right\} \\ $$$${p}=−\frac{{o}}{\mathrm{2}}\pm\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{108}−\mathrm{3}{o}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{\mathrm{2}}\wedge{q}=−\left({o}+{p}\right)\wedge{k}={op}\left({o}+{p}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\begin{pmatrix}{{o}}\\{{p}}\\{{q}}\\{{k}}\end{pmatrix}\:\in\left\{\begin{pmatrix}{−\mathrm{6}}\\{\mathrm{3}}\\{−\mathrm{3}}\\{\mathrm{54}}\end{pmatrix}\:,\begin{pmatrix}{−\mathrm{3}}\\{−\mathrm{3}}\\{−\mathrm{6}}\\{\mathrm{54}}\end{pmatrix}\:,\begin{pmatrix}{−\mathrm{3}}\\{\mathrm{6}}\\{\mathrm{3}}\\{−\mathrm{54}}\end{pmatrix}\:,\begin{pmatrix}{\mathrm{3}}\\{−\mathrm{6}}\\{−\mathrm{3}}\\{\mathrm{54}}\end{pmatrix}\:,\begin{pmatrix}{\mathrm{3}}\\{\mathrm{3}}\\{\mathrm{6}}\\{\mathrm{54}}\end{pmatrix}\:,\begin{pmatrix}{\mathrm{6}}\\{−\mathrm{3}}\\{\mathrm{3}}\\{−\mathrm{54}}\end{pmatrix}\:\right\} \\ $$$$\mathrm{case}\:\mathrm{2}:\:\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{solutions}\:\left({q}={p}\right) \\ $$$$\left({x}−{o}\right)\left({x}−{p}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${o}+\mathrm{2}{p}=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\:{p}=−\frac{{o}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{op}+{p}^{\mathrm{2}} =−\mathrm{27}\:\Rightarrow\:{o}=\pm\mathrm{6}\:\Rightarrow\:{p}=\mp\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$−{op}^{\mathrm{2}} ={k}\:\Rightarrow\:{k}=\mp\mathrm{54} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\begin{pmatrix}{{o}}\\{{p}}\\{{q}={p}}\\{{k}}\end{pmatrix}\:\in\left\{\begin{pmatrix}{−\mathrm{6}}\\{\mathrm{3}}\\{\mathrm{3}}\\{\mathrm{54}}\end{pmatrix}\:,\begin{pmatrix}{\mathrm{6}}\\{−\mathrm{3}}\\{−\mathrm{3}}\\{−\mathrm{54}}\end{pmatrix}\:\right\} \\ $$$$\mathrm{so}\:\mathrm{answer}\:\mathrm{B}\:\mathrm{seems}\:\mathrm{right}:\:\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{integer}\:\mathrm{values}\:\mathrm{for}\:{k} \\ $$
Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 04/Nov/18
thanks sir����
