
Question Number 22263 by kasiulka202 last updated on 14/Oct/17

Answered by Joel577 last updated on 14/Oct/17

$$\frac{\mathrm{0}}{\mathrm{0}}\:{is}\:{an}\:{indeterminate}\:{form} \\ $$
Answered by FilupS last updated on 14/Oct/17
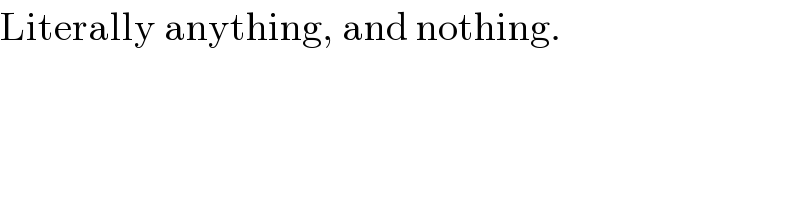
$$\mathrm{Literally}\:\mathrm{anything},\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{nothing}. \\ $$
Commented by FilupS last updated on 26/Oct/17
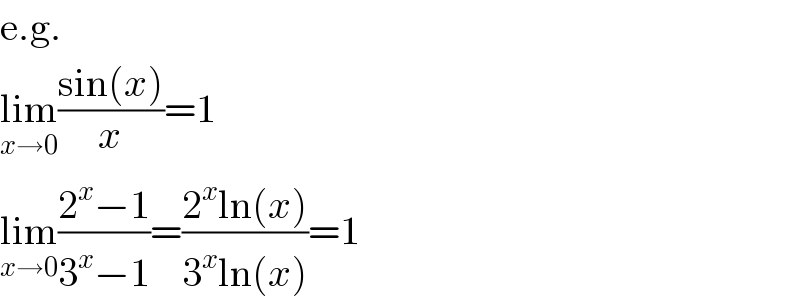
$$\mathrm{e}.\mathrm{g}. \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{sin}\left({x}\right)}{{x}}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{2}^{{x}} −\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}^{{x}} −\mathrm{1}}=\frac{\mathrm{2}^{{x}} \mathrm{ln}\left({x}\right)}{\mathrm{3}^{{x}} \mathrm{ln}\left({x}\right)}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by ajfour last updated on 26/Oct/17
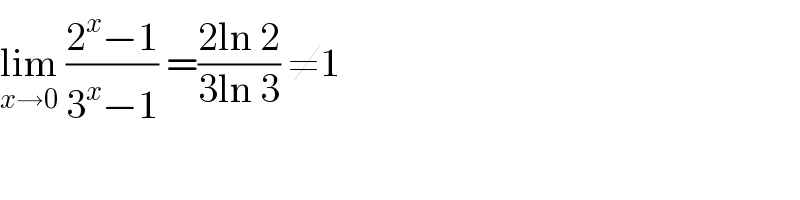
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{2}^{{x}} −\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}^{{x}} −\mathrm{1}}\:=\frac{\mathrm{2ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3ln}\:\mathrm{3}}\:\neq\mathrm{1} \\ $$
