
Question Number 215593 by mr W last updated on 11/Jan/25
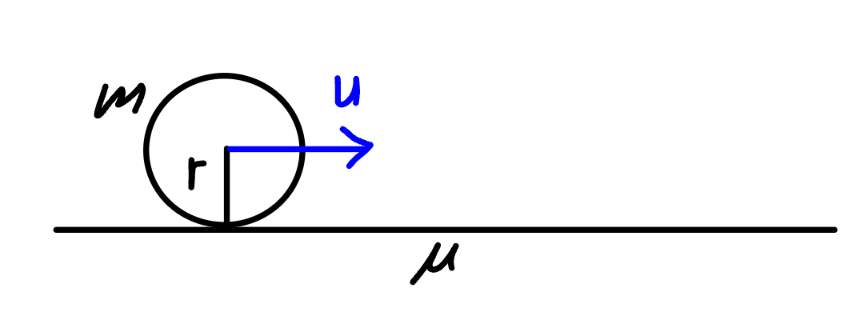
Commented by mr W last updated on 11/Jan/25

$${a}\:{solid}\:{ball}\:{with}\:{radius}\:\boldsymbol{{r}}\:{and}\:{mass} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{m}}\:{is}\:{given}\:{a}\:{speed}\:\boldsymbol{{u}}\:{on}\:{a}\:{rough}\: \\ $$$${horizontal}\:{surface}.\:{the}\:{friction} \\ $$$${coefficient}\:{is}\:\boldsymbol{\mu}. \\ $$$${find}\:{after}\:{what}\:{a}\:{distance}\:{and}\:{with} \\ $$$${what}\:{a}\:{speed}\:{the}\:{ball}\:{only}\:{rolls}\:{over}\: \\ $$$${the}\:{surface}. \\ $$$$\left({original}\:{question}\:{see}\:{youtube}\:\right. \\ $$$$\left.{channel}\:{from}\:{ajfour}\:{sir}\right) \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 11/Jan/25
https://youtu.be/Hg4sQD7xK9g?si=iWhsrRN19lc2lkzb
Answered by mahdipoor last updated on 11/Jan/25
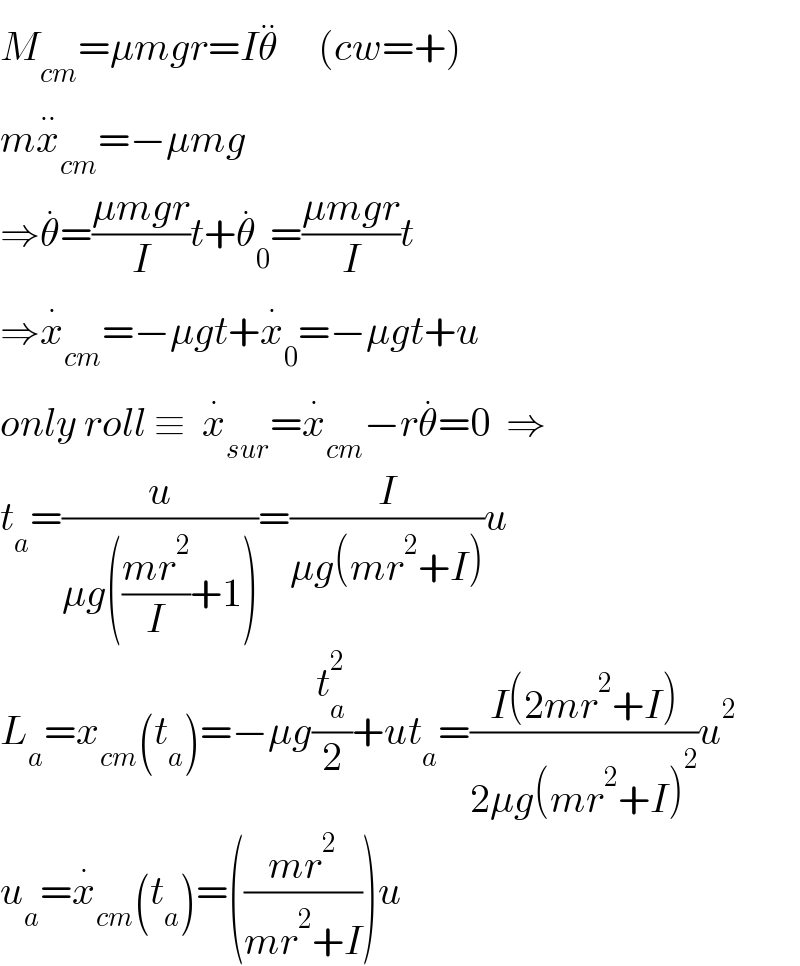
$${M}_{{cm}} =\mu{mgr}={I}\overset{..} {\theta}\:\:\:\:\:\left({cw}=+\right) \\ $$$${m}\overset{..} {{x}}_{{cm}} =−\mu{mg}\:\:\:\: \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\overset{.} {\theta}=\frac{\mu{mgr}}{{I}}{t}+\overset{.} {\theta}_{\mathrm{0}} =\frac{\mu{mgr}}{{I}}{t} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\overset{.} {{x}}_{{cm}} =−\mu{gt}+\overset{.} {{x}}_{\mathrm{0}} =−\mu{gt}+{u} \\ $$$${only}\:{roll}\:\equiv\:\:\overset{.} {{x}}_{{sur}} =\overset{.} {{x}}_{{cm}} −{r}\overset{.} {\theta}=\mathrm{0}\:\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${t}_{{a}} =\frac{{u}}{\mu{g}\left(\frac{{mr}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{I}}+\mathrm{1}\right)}=\frac{{I}}{\mu{g}\left({mr}^{\mathrm{2}} +{I}\right)}{u} \\ $$$${L}_{{a}} ={x}_{{cm}} \left({t}_{{a}} \right)=−\mu{g}\frac{{t}_{{a}} ^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}+{ut}_{{a}} =\frac{{I}\left(\mathrm{2}{mr}^{\mathrm{2}} +{I}\right)}{\mathrm{2}\mu{g}\left({mr}^{\mathrm{2}} +{I}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${u}_{{a}} =\overset{.} {{x}}_{{cm}} \left({t}_{{a}} \right)=\left(\frac{{mr}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{mr}^{\mathrm{2}} +{I}}\right){u} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 11/Jan/25

$${thanks}! \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 11/Jan/25
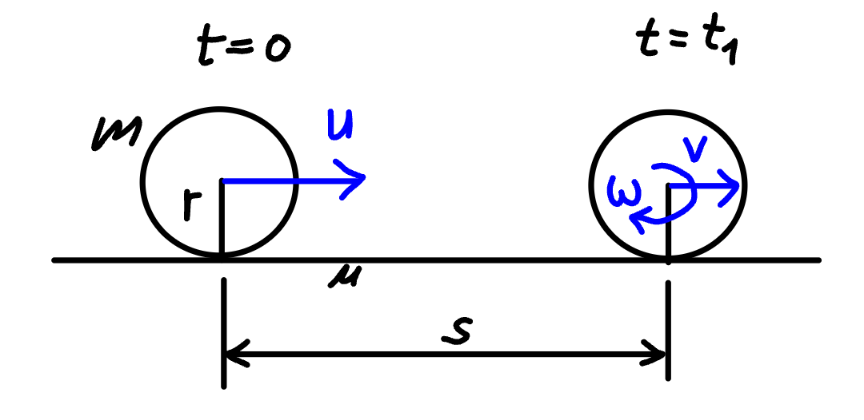
Commented by mr W last updated on 11/Jan/25
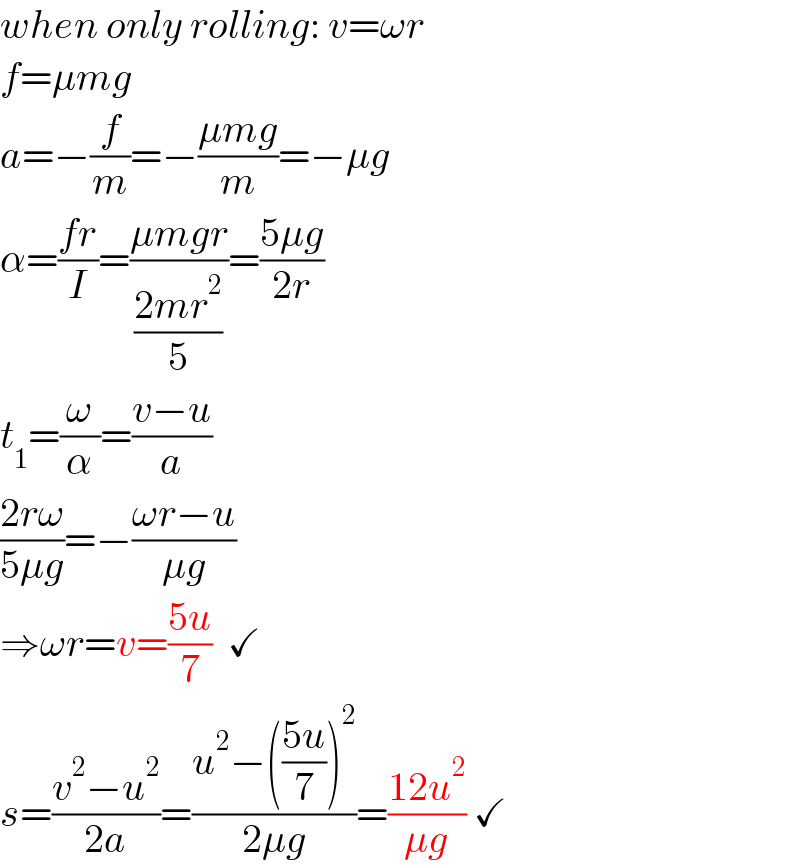
$${when}\:{only}\:{rolling}:\:{v}=\omega{r} \\ $$$${f}=\mu{mg} \\ $$$${a}=−\frac{{f}}{{m}}=−\frac{\mu{mg}}{{m}}=−\mu{g} \\ $$$$\alpha=\frac{{fr}}{{I}}=\frac{\mu{mgr}}{\frac{\mathrm{2}{mr}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{5}}}=\frac{\mathrm{5}\mu{g}}{\mathrm{2}{r}} \\ $$$${t}_{\mathrm{1}} =\frac{\omega}{\alpha}=\frac{{v}−{u}}{{a}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{2}{r}\omega}{\mathrm{5}\mu{g}}=−\frac{\omega{r}−{u}}{\mu{g}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\omega{r}={v}=\frac{\mathrm{5}{u}}{\mathrm{7}}\:\:\checkmark \\ $$$${s}=\frac{{v}^{\mathrm{2}} −{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}{a}}=\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} −\left(\frac{\mathrm{5}{u}}{\mathrm{7}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}\mu{g}}=\frac{\mathrm{12}{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mu{g}}\:\checkmark \\ $$
