
Question Number 212099 by vahid last updated on 30/Sep/24
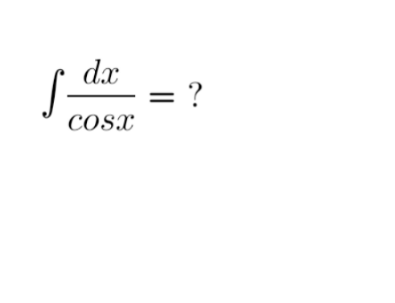
Answered by mehdee7396 last updated on 30/Sep/24
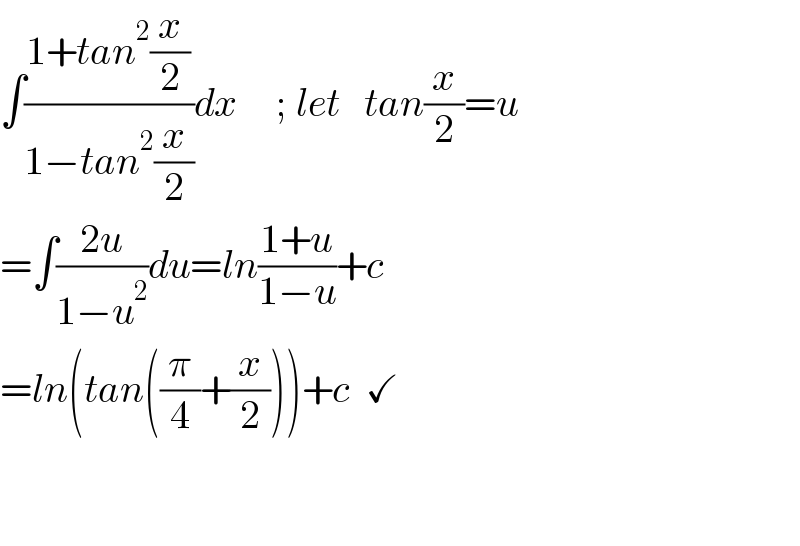
$$\int\frac{\mathrm{1}+{tan}^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{1}−{tan}^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}}{dx}\:\:\:\:\:;\:{let}\:\:\:{tan}\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}={u} \\ $$$$=\int\frac{\mathrm{2}{u}}{\mathrm{1}−{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }{du}={ln}\frac{\mathrm{1}+{u}}{\mathrm{1}−{u}}+{c} \\ $$$$={ln}\left({tan}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}+\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\right)+{c}\:\:\checkmark \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by Frix last updated on 30/Sep/24
![∫(dx/(cos x))=∫sec x dx= =∫sec x ((tan x +sec x)/(tan x +sec x))dx =^([t=tan x +sec x]) =∫(dt/t)=ln t = =ln ∣tan x +sec x∣ +C](Q212102.png)
$$\int\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}=\int\mathrm{sec}\:{x}\:{dx}= \\ $$$$=\int\mathrm{sec}\:{x}\:\frac{\mathrm{tan}\:{x}\:+\mathrm{sec}\:{x}}{\mathrm{tan}\:{x}\:+\mathrm{sec}\:{x}}{dx}\:\overset{\left[{t}=\mathrm{tan}\:{x}\:+\mathrm{sec}\:{x}\right]} {=} \\ $$$$=\int\frac{{dt}}{{t}}=\mathrm{ln}\:{t}\:= \\ $$$$=\mathrm{ln}\:\mid\mathrm{tan}\:{x}\:+\mathrm{sec}\:{x}\mid\:+{C} \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 30/Sep/24
![=∫((d(sin x))/(1−sin^2 x)) =(1/2)[∫((d(sin x))/(1−sin x))+∫((d(sin x))/(1+sin x))] =(1/2)ln ((1+sin x)/(1−sin x))+C](Q212105.png)
$$=\int\frac{{d}\left(\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\right)}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{x}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[\int\frac{{d}\left(\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\right)}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}+\int\frac{{d}\left(\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\right)}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}\right] \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{ln}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}+{C} \\ $$
Commented by MathematicalUser2357 last updated on 02/Oct/24

1/2 ln|(1+sinx)/(1-sinx)|+C*
Commented by Frix last updated on 02/Oct/24
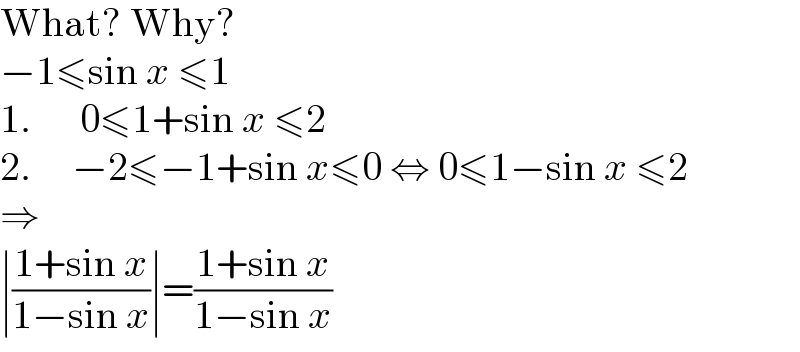
$$\mathrm{What}?\:\mathrm{Why}? \\ $$$$−\mathrm{1}\leqslant\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:\leqslant\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}.\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{0}\leqslant\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:\leqslant\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}.\:\:\:\:\:−\mathrm{2}\leqslant−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\leqslant\mathrm{0}\:\Leftrightarrow\:\mathrm{0}\leqslant\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:\leqslant\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mid\frac{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}\mid=\frac{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{sin}\:{x}} \\ $$
