
Question Number 210172 by efronzo1 last updated on 01/Aug/24
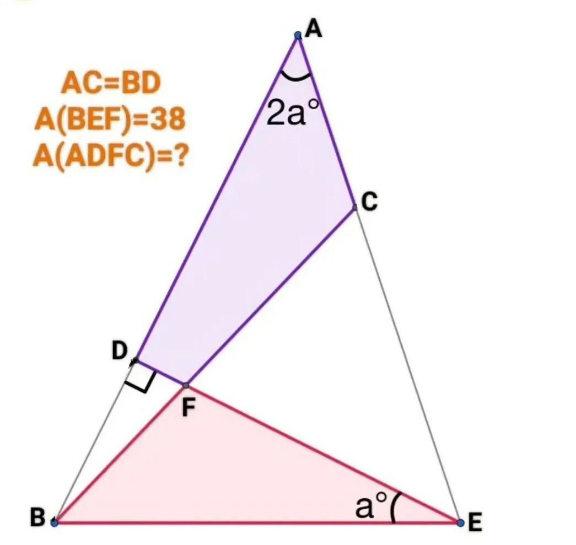
Answered by a.lgnaoui last updated on 02/Aug/24

$$\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{a}}}{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{BE}}}=\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{a}}}{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{AB}}}\:\:\:\:\left(\measuredangle\mathrm{AED}=\mathrm{90}−\mathrm{2a}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{AB}=\frac{\mathrm{DEcos}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{a}}}{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{a}}}.=\frac{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{BE}}}{\mathrm{2sin}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{a}}} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{\mathrm{Aire}}\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{ABC}}\right)=\boldsymbol{\mathrm{Air}}\mathrm{e}\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{ADFC}}\right)+\boldsymbol{\mathrm{Aire}}\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{DBF}}\right) \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{\mathrm{A}}\mathrm{ire}\left(\mathrm{BDE}\right)=\mathrm{Aire}\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{BEF}}\right)+\boldsymbol{\mathrm{Aire}}\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{BDF}}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\: \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{Aire}\left(\mathrm{ABC}\right)−\left(\mathrm{ADFC}\right)= \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{Aire}\left(\mathrm{BDE}\right)−\mathrm{38} \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{Aire}}\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{ABC}}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{AB}}×\boldsymbol{\mathrm{AC}}\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{a}}}\\{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{Aire}}\:\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{BDE}}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{BD}}.\boldsymbol{\mathrm{BE}}\mathrm{cos}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{a}}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{\mathrm{AC}}=\boldsymbol{\mathrm{BD}}\:\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{alors}} \\ $$$$\:\:\frac{\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{BE}}.\mathrm{cos}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{a}}}{\mathrm{4}}−\boldsymbol{\mathrm{A}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{BE}}\mathrm{cos}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{a}}−\mathrm{38} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{\mathrm{Donc}}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{Aire}}\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{ADFC}}\right)=\mathrm{38} \\ $$
Commented by a.lgnaoui last updated on 02/Aug/24
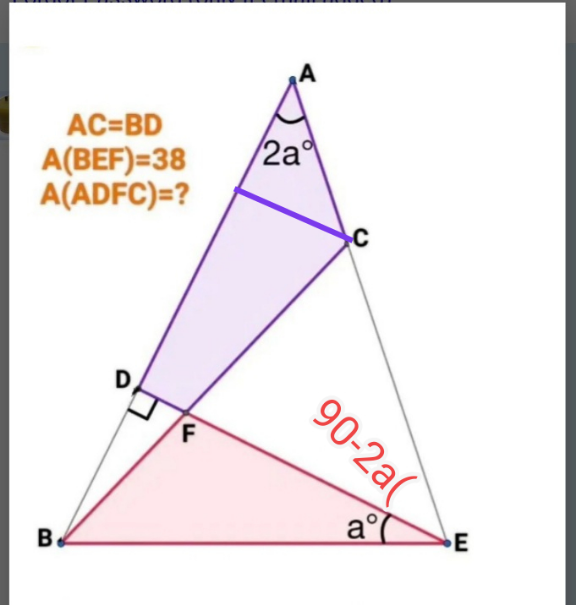
Answered by mr W last updated on 02/Aug/24

$${say}\:{AC}={BD}={b} \\ $$$${DE}=\frac{{b}}{\mathrm{tan}\:\alpha} \\ $$$${AD}=\frac{{b}}{\mathrm{tan}\:\alpha\:\mathrm{tan}\:\mathrm{2}\alpha} \\ $$$${Area}\left({BDE}\right)=\frac{{b}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{tan}\:\alpha} \\ $$$${Area}\left({ABC}\right)=\frac{{b}\:\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}\alpha}{\mathrm{2}}\left({b}+\frac{{b}}{\mathrm{tan}\:\alpha\:\mathrm{tan}\:\mathrm{2}\alpha}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:=\frac{{b}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{tan}\:\alpha}\left(\mathrm{tan}\:\alpha\:\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}\alpha+\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2}\alpha\right) \\ $$$$\:\:=\frac{{b}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{tan}\:\alpha}\left(\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\alpha+\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\alpha\right) \\ $$$$\:\:=\frac{{b}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{tan}\:\alpha}={Area}\left({DBE}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{Area}\left({ADFC}\right)={Area}\left({BEF}\right)=\mathrm{38} \\ $$
Answered by A5T last updated on 02/Aug/24
![(([ABC])/([BDE]))=((AB×ACsin(2a))/(BD×DE))=((ABsin(2a))/(DE)) sin(2a)=((DE)/(AE)); ∠BEA=90−a=∠ABE⇒AB=AE ⇒(([ABC])/([BDE]))=((ABsin(2a))/(AEsin(2a)))=1 ⇒38+[DBF]=[ADFC]+[DBF]⇒[ADFC]=38](Q210209.png)
$$\frac{\left[{ABC}\right]}{\left[{BDE}\right]}=\frac{{AB}×{ACsin}\left(\mathrm{2}{a}\right)}{{BD}×{DE}}=\frac{{ABsin}\left(\mathrm{2}{a}\right)}{{DE}} \\ $$$${sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{a}\right)=\frac{{DE}}{{AE}};\:\angle{BEA}=\mathrm{90}−{a}=\angle{ABE}\Rightarrow{AB}={AE} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{\left[{ABC}\right]}{\left[{BDE}\right]}=\frac{{ABsin}\left(\mathrm{2}{a}\right)}{{AEsin}\left(\mathrm{2}{a}\right)}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{38}+\left[{DBF}\right]=\left[{ADFC}\right]+\left[{DBF}\right]\Rightarrow\left[{ADFC}\right]=\mathrm{38} \\ $$
