
Question Number 203747 by patrice last updated on 27/Jan/24
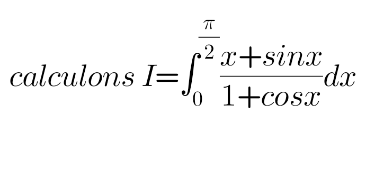
Answered by esmaeil last updated on 27/Jan/24
![I=∫_0 ^(π/2) (x/(1+cosx))dx+∫_0 ^(π/2) ((sinx)/(1+cosx))dx x=u→dx=du (dx/(1+cosx))=dv→v=tan(x/2) →I=xtan(x/2)−∫_0 ^(π/2) tan(x/2)dx+ ∫_0 ^(π/2) ((sinx)/(1+cosx))dx= xtan(x/2)+2ln(cos(x/2))+ln(1+cosx)]_0 ^(π/2) = (π/2)+2ln(((√2)/2))−ln2=(π/2)+ln(1/2)−ln2 =(π/2)−2ln2](Q203756.png)
$${I}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \frac{{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{cosx}}{dx}+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \frac{{sinx}}{\mathrm{1}+{cosx}}{dx} \\ $$$${x}={u}\rightarrow{dx}={du} \\ $$$$\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+{cosx}}={dv}\rightarrow{v}={tan}\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\rightarrow{I}={xtan}\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} {tan}\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}{dx}+ \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \frac{{sinx}}{\mathrm{1}+{cosx}}{dx}= \\ $$$$\left.{xtan}\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{2}{ln}\left({cos}\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)+{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{cosx}\right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} = \\ $$$$\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{2}{ln}\left(\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)−{ln}\mathrm{2}=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}+{ln}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−{ln}\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{2}{ln}\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by MathematicalUser2357 last updated on 28/Jan/24

$${I}=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{2ln}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$
