
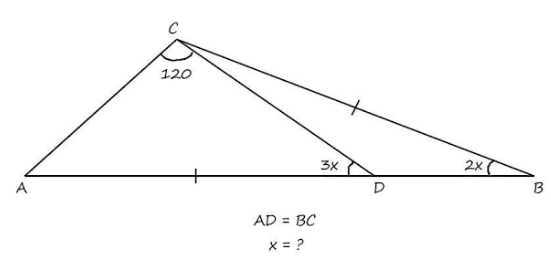
Question Number 177205 by HeferH last updated on 02/Oct/22
Answered by mr W last updated on 02/Oct/22
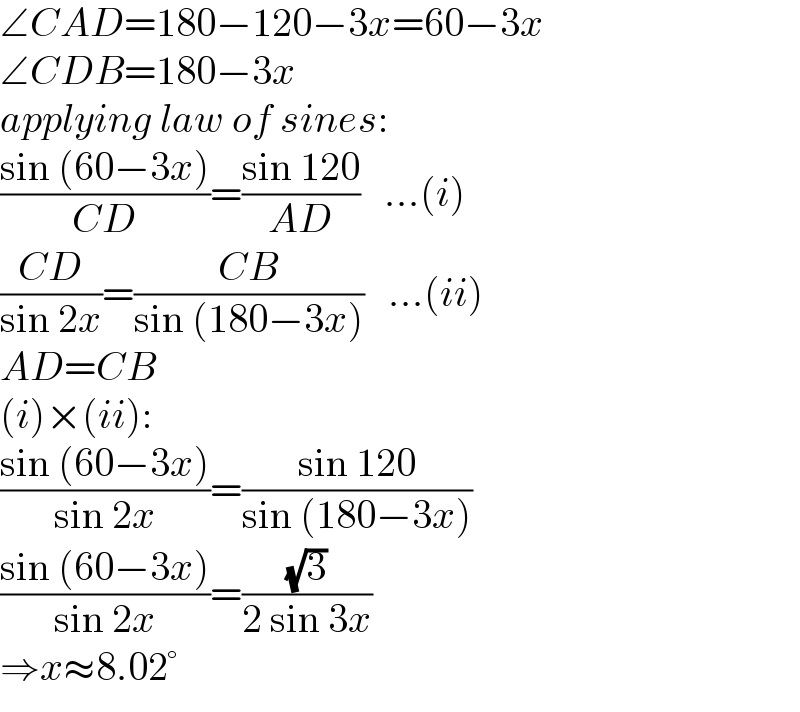
$$\angle{CAD}=\mathrm{180}−\mathrm{120}−\mathrm{3}{x}=\mathrm{60}−\mathrm{3}{x} \\ $$$$\angle{CDB}=\mathrm{180}−\mathrm{3}{x} \\ $$$${applying}\:{law}\:{of}\:{sines}: \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{60}−\mathrm{3}{x}\right)}{{CD}}=\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{120}}{{AD}}\:\:\:...\left({i}\right) \\ $$$$\frac{{CD}}{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x}}=\frac{{CB}}{\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{180}−\mathrm{3}{x}\right)}\:\:\:...\left({ii}\right) \\ $$$${AD}={CB} \\ $$$$\left({i}\right)×\left({ii}\right): \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{60}−\mathrm{3}{x}\right)}{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x}}=\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{120}}{\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{180}−\mathrm{3}{x}\right)} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{60}−\mathrm{3}{x}\right)}{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x}}=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{3}{x}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}\approx\mathrm{8}.\mathrm{02}° \\ $$
Commented by Tawa11 last updated on 02/Oct/22

$$\mathrm{Great}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
