
Question Number 155399 by 0731619 last updated on 30/Sep/21
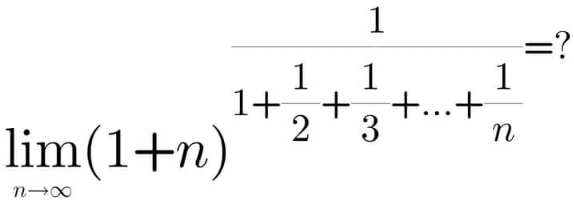
Answered by TheHoneyCat last updated on 30/Sep/21
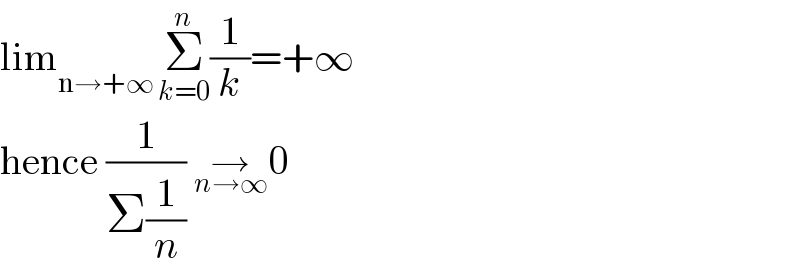
$$\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{n}\rightarrow+\infty\:} \underset{{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{k}}=+\infty \\ $$$$\mathrm{hence}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\Sigma\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}}\:\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\rightarrow}\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Answered by Niiicooooo last updated on 30/Sep/21
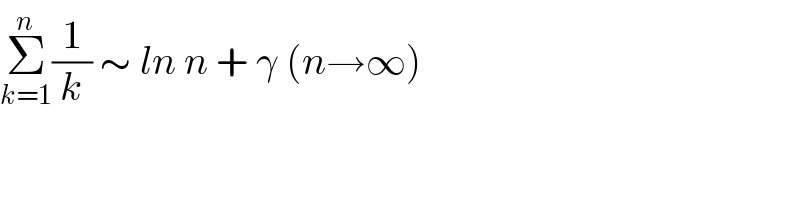
$$\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{k}}\:\sim\:{ln}\:{n}\:+\:\gamma\:\left({n}\rightarrow\infty\right) \\ $$
Commented by puissant last updated on 30/Sep/21
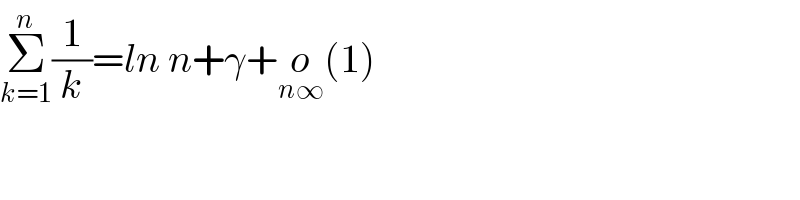
$$\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{k}}={ln}\:{n}+\gamma+\underset{{n}\infty} {{o}}\left(\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$
