
Question Number 153464 by roxceefocus last updated on 07/Sep/21

Commented by roxceefocus last updated on 07/Sep/21
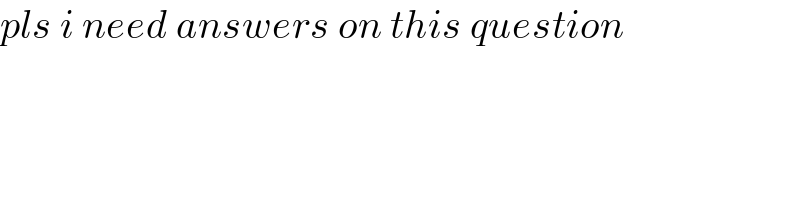
$${pls}\:{i}\:{need}\:{answers}\:{on}\:{this}\:{question} \\ $$
Answered by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 07/Sep/21

$$\sqrt{\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{1}}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\left(\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{1}}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}}=\mathrm{1}\:\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\left(\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right.}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\left(\:\mathrm{5}{x}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\left(\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)}\:\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{5}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{25}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{10}{x}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{6}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{25}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{10}{x}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{24}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}{x}−\mathrm{4} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{6}{x}+\mathrm{5}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}−\mathrm{5}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{1}\:\mid\:{x}=\mathrm{5} \\ $$$${On}\:{verification}\:{we}\:{can}\:{see}\:{that} \\ $$$${both}\:{roots}\:{satisfy}\:{the}\:{original}\:{eqn} \\ $$
Answered by puissant last updated on 07/Sep/21
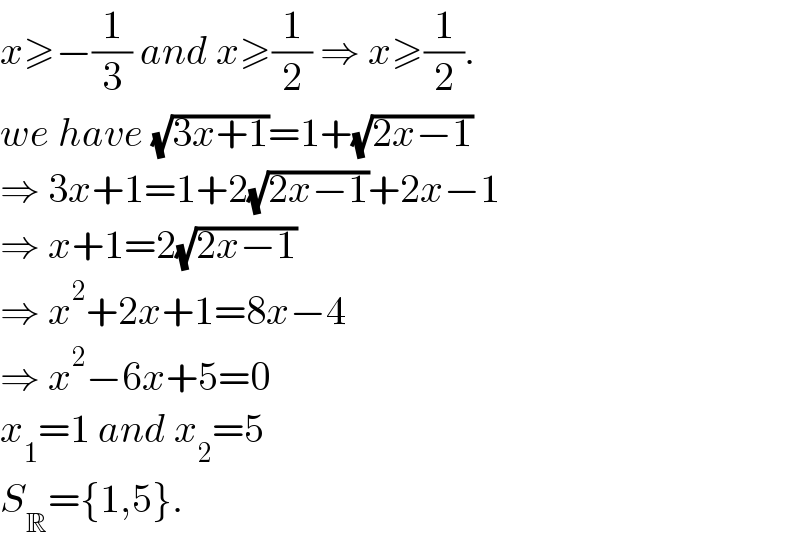
$${x}\geqslant−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\:{and}\:{x}\geqslant\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\Rightarrow\:{x}\geqslant\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}. \\ $$$${we}\:{have}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{1}}=\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}}+\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{x}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{8}{x}−\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{6}{x}+\mathrm{5}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{1}\:{and}\:{x}_{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{5} \\ $$$${S}_{\mathbb{R}} =\left\{\mathrm{1},\mathrm{5}\right\}. \\ $$
Answered by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 08/Sep/21

$$\equiv\mathbb{A}\mathrm{n}\:\mathbb{A}\mathrm{lternative}\equiv \\ $$$$\sqrt{\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{1}}\:−\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}}\:=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\:\Rightarrow\:{p}−{q}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${p}^{\mathrm{2}} −{q}^{\mathrm{2}} =\left(\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)−\left(\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)={x}+\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\left({p}−{q}\right)\left({p}+{q}\right)={x}+\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${p}+{q}={x}+\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${p}−{q}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{p}={x}+\mathrm{3}\Rightarrow{p}=\frac{{x}+\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{q}={x}+\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow{q}=\frac{{x}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${p}=\sqrt{\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{1}}=\frac{{x}+\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)={x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{6}{x}+\mathrm{9} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{6}{x}+\mathrm{5}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}−\mathrm{5}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}=\mathrm{1},\mathrm{5} \\ $$$${On}\:{verification}\:{it}\:{can}\:{be}\:{verified} \\ $$$${that}\:{both}\:{roots}\:{are}\:{true}. \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\left({Same}\:{result}\:{can}\:{be}\:{obtained}\right. \\ $$$${by} \\ $$$${q}=\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}}\:=\frac{{x}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)={x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\left.\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{6}{x}+\mathrm{5}=\mathrm{0}\right) \\ $$
