
Question Number 145011 by mim24 last updated on 01/Jul/21
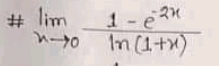
Answered by ArielVyny last updated on 01/Jul/21
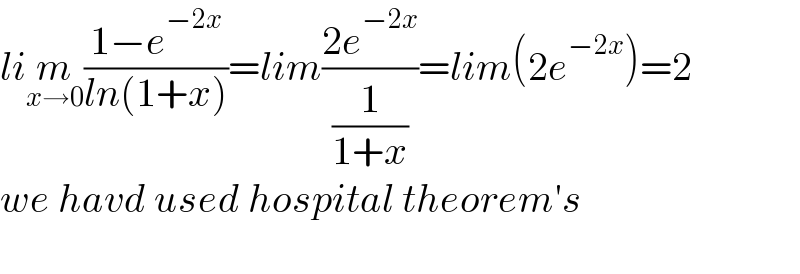
$${li}\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {{m}}\frac{\mathrm{1}−{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} }{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)}={lim}\frac{\mathrm{2}{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} }{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}}={lim}\left(\mathrm{2}{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} \right)=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${we}\:{havd}\:{used}\:{hospital}\:{theorem}'{s} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 01/Jul/21
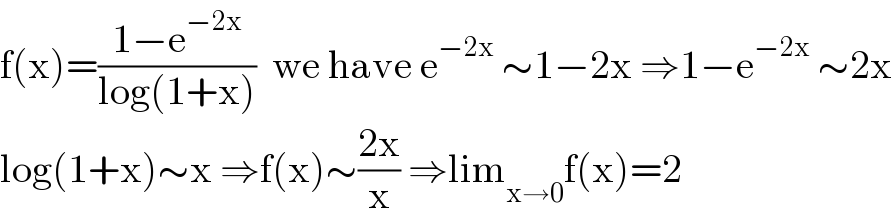
$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2x}} }{\mathrm{log}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}\right)}\:\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{have}\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2x}} \:\sim\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{2x}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2x}} \:\sim\mathrm{2x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{log}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}\right)\sim\mathrm{x}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\sim\frac{\mathrm{2x}}{\mathrm{x}}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\mathrm{2} \\ $$
