
Question Number 119473 by help last updated on 24/Oct/20
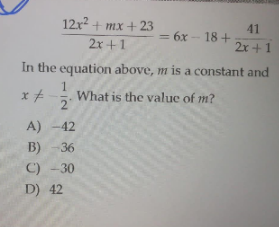
Commented by 1549442205PVT last updated on 25/Oct/20

$$\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{think}\:\mathrm{that}\:\mathrm{question}\:\mathrm{isn}'\mathrm{t}\:\mathrm{clearly}.\mathrm{You} \\ $$$$\mathrm{need}\:\mathrm{must}\:\mathrm{add}\:\mathrm{that}\:\mathrm{above}\:\mathrm{equality}\:\mathrm{be} \\ $$$$\mathrm{an}\:\mathrm{identity}\:\mathrm{that}\:\mathrm{means}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{true}\:\mathrm{for} \\ $$$$\forall\mathrm{x}\neq−\mathrm{1}/\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{othewise}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{can}\:\mathrm{find}\:\mathrm{infinite} \\ $$$$\mathrm{many}\:\mathrm{values}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{m}\:\mathrm{satisfying}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{condition} \\ $$$$\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{above}\:\mathrm{problem} \\ $$
Answered by Sach last updated on 24/Oct/20

$$\frac{\mathrm{12}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{mx}+\mathrm{23}}{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}=\mathrm{6}{x}−\mathrm{18}+\frac{\mathrm{41}}{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\mathrm{12}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{mx}+\mathrm{23}=\mathrm{6}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}−\mathrm{3}\right)+\mathrm{41} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\mathrm{12}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{mx}=\mathrm{6}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}−\mathrm{3}\right)+\mathrm{18}=\mathrm{12}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{30}{x} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow{m}=−\mathrm{30} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${that}\:{last}\:''\Leftrightarrow''\:{is}\:{not}\:{so}\:{obvious} \\ $$$${you}\:{can}\:{convince}\:{yourself}\:{that}\:{it}\:{is}\:{true}\:{by}\:{triing}\:{a}\:{few}\:{values}\:\left({for}\:{instance}\:{x}=\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$${this}\:{gives}\:{that}\:{m}\:{can}\:{only}\:{be}\:−\mathrm{30}\:\left(\Rightarrow\right) \\ $$$${and}\:{then}\:{you}\:{can}\:{recalculate}\:{to}\:{see}\:{that}\:−\mathrm{30}\:{works}\:\left(\Leftarrow\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${if}\:{you}\:{want}\:{to}\:{be}\:{both}\:{rigorous}\:{and}\:{short}\:{you}\:{can}\:{use}\:{the}\:{fact}\:{that}\:{there}\:{is}\:{a}\:{unique}\:{simplified}\:{expression}\:{of}\:{elements}\:{of}\:\mathbb{R}\left(\mathrm{X}\right)\:{but}\:{this}\:{is}\:{may}\:{be}\:{too}\:{advanced}\:{to}\:{be}\:{wath}\:{is}\:{expected}\:{here}... \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by 1549442205PVT last updated on 25/Oct/20

$$\mathrm{Ok},\mathrm{excuse}\:\mathrm{me}\:.\mathrm{The}\:\mathrm{equation}\:\mathrm{that}\:\mathrm{you} \\ $$$$\mathrm{given}\:\mathrm{here}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{special}\:,\mathrm{so}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{has}\:\:\mathrm{only}\:\mathrm{one} \\ $$$$\mathrm{unique}\:\mathrm{value}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{m}. \\ $$
Answered by TANMAY PANACEA last updated on 25/Oct/20
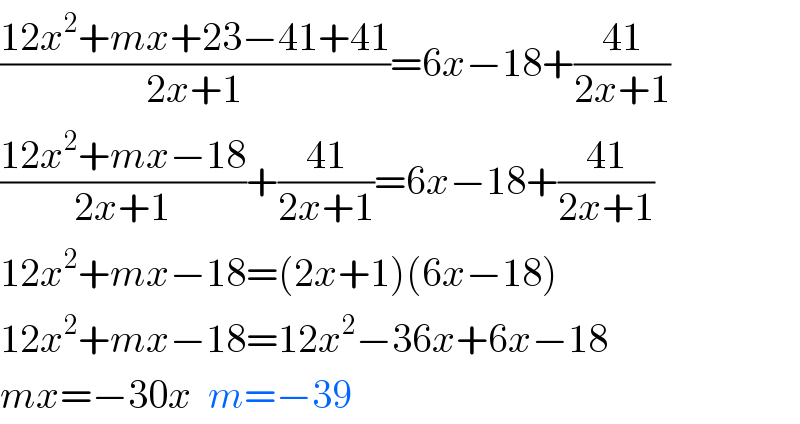
$$\frac{\mathrm{12}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{mx}+\mathrm{23}−\mathrm{41}+\mathrm{41}}{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}=\mathrm{6}{x}−\mathrm{18}+\frac{\mathrm{41}}{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{12}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{mx}−\mathrm{18}}{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{41}}{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}=\mathrm{6}{x}−\mathrm{18}+\frac{\mathrm{41}}{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{12}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{mx}−\mathrm{18}=\left(\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{6}{x}−\mathrm{18}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{12}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{mx}−\mathrm{18}=\mathrm{12}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{36}{x}+\mathrm{6}{x}−\mathrm{18} \\ $$$${mx}=−\mathrm{30}{x}\:\:{m}=−\mathrm{39} \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 25/Oct/20
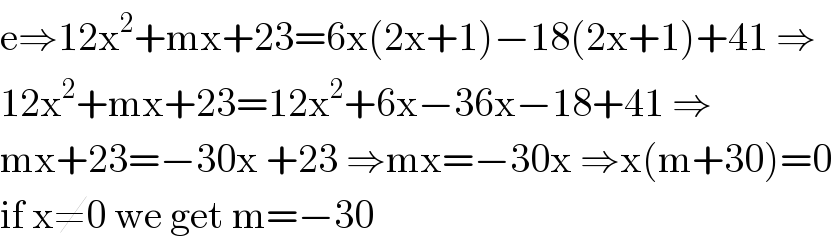
$$\mathrm{e}\Rightarrow\mathrm{12x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{mx}+\mathrm{23}=\mathrm{6x}\left(\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{18}\left(\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{1}\right)+\mathrm{41}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{12x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{mx}+\mathrm{23}=\mathrm{12x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{6x}−\mathrm{36x}−\mathrm{18}+\mathrm{41}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{mx}+\mathrm{23}=−\mathrm{30x}\:+\mathrm{23}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{mx}=−\mathrm{30x}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{x}\left(\mathrm{m}+\mathrm{30}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{x}\neq\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{get}\:\mathrm{m}=−\mathrm{30} \\ $$
Answered by Jamshidbek2311 last updated on 25/Oct/20
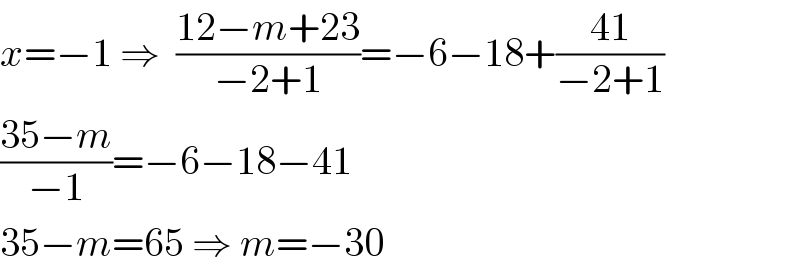
$${x}=−\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\:\:\frac{\mathrm{12}−{m}+\mathrm{23}}{−\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{1}}=−\mathrm{6}−\mathrm{18}+\frac{\mathrm{41}}{−\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{35}−{m}}{−\mathrm{1}}=−\mathrm{6}−\mathrm{18}−\mathrm{41} \\ $$$$\mathrm{35}−{m}=\mathrm{65}\:\Rightarrow\:{m}=−\mathrm{30} \\ $$
