
Question Number 115095 by aurpeyz last updated on 23/Sep/20

Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 23/Sep/20
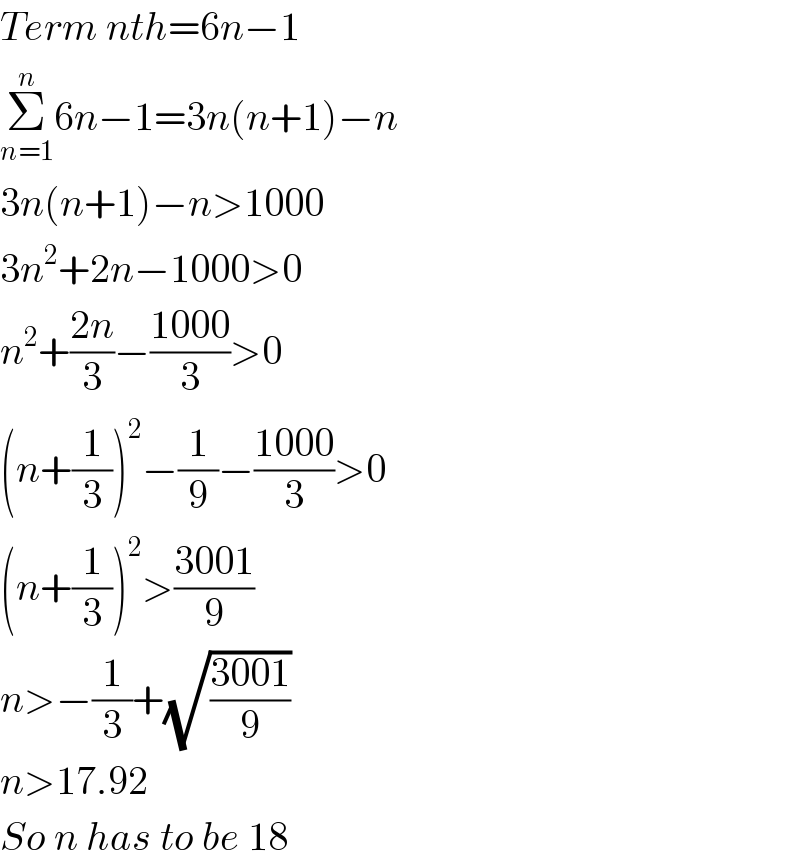
$${Term}\:{nth}=\mathrm{6}{n}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\mathrm{6}{n}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{3}{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)−{n} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)−{n}>\mathrm{1000} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{n}−\mathrm{1000}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{2}{n}}{\mathrm{3}}−\frac{\mathrm{1000}}{\mathrm{3}}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({n}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{9}}−\frac{\mathrm{1000}}{\mathrm{3}}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({n}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} >\frac{\mathrm{3001}}{\mathrm{9}} \\ $$$${n}>−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}+\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{3001}}{\mathrm{9}}} \\ $$$${n}>\mathrm{17}.\mathrm{92} \\ $$$${So}\:{n}\:{has}\:{to}\:{be}\:\mathrm{18}\: \\ $$
Commented by aurpeyz last updated on 23/Sep/20
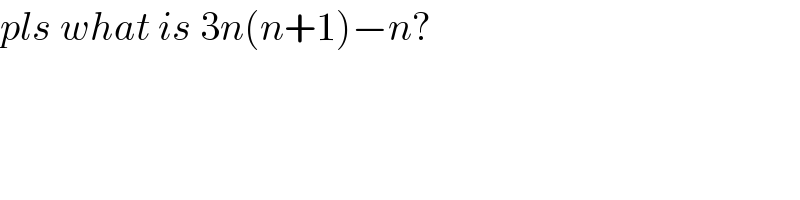
$${pls}\:{what}\:{is}\:\mathrm{3}{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)−{n}? \\ $$
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 23/Sep/20
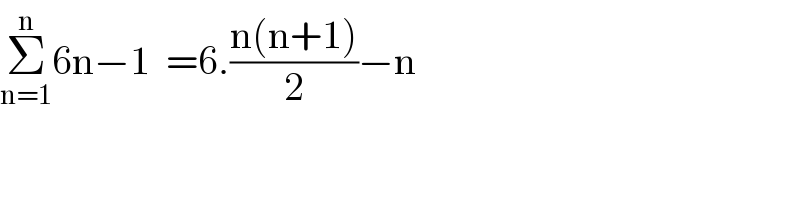
$$\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{n}} {\sum}}\mathrm{6n}−\mathrm{1}\:\:=\mathrm{6}.\frac{\mathrm{n}\left(\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{n} \\ $$
Answered by Aziztisffola last updated on 23/Sep/20
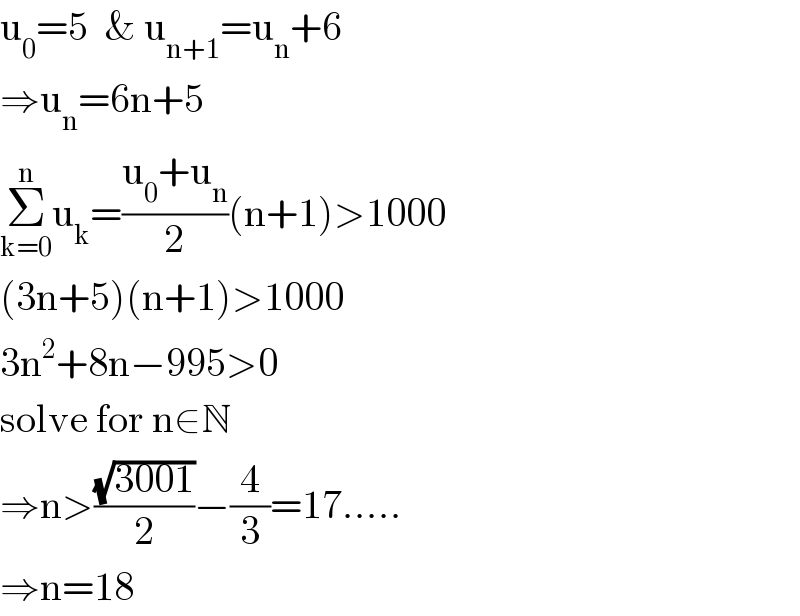
$$\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{0}} =\mathrm{5}\:\:\&\:\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{n}} +\mathrm{6} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{n}} =\mathrm{6n}+\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{n}} {\sum}}\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{k}} =\frac{\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{0}} +\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{n}} }{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)>\mathrm{1000} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{3n}+\mathrm{5}\right)\left(\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)>\mathrm{1000} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{8n}−\mathrm{995}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{solve}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{n}\in\mathbb{N} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{n}>\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3001}}}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{3}}=\mathrm{17}..... \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{18} \\ $$
