
Question Number 26858 by $@ty@m last updated on 30/Dec/17
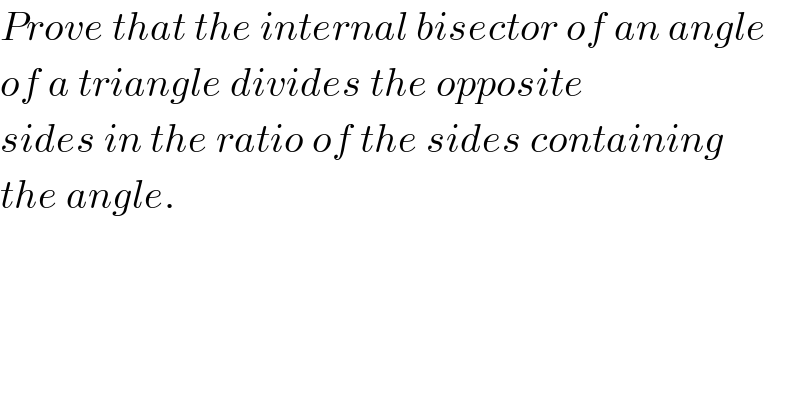
$${Prove}\:{that}\:{the}\:{internal}\:{bisector}\:{of}\:{an}\:{angle}\: \\ $$$${of}\:{a}\:{triangle}\:{divides}\:{the}\:{opposite} \\ $$$${sides}\:{in}\:{the}\:{ratio}\:{of}\:{the}\:{sides}\:{containing} \\ $$$${the}\:{angle}. \\ $$
Answered by mrW1 last updated on 30/Dec/17
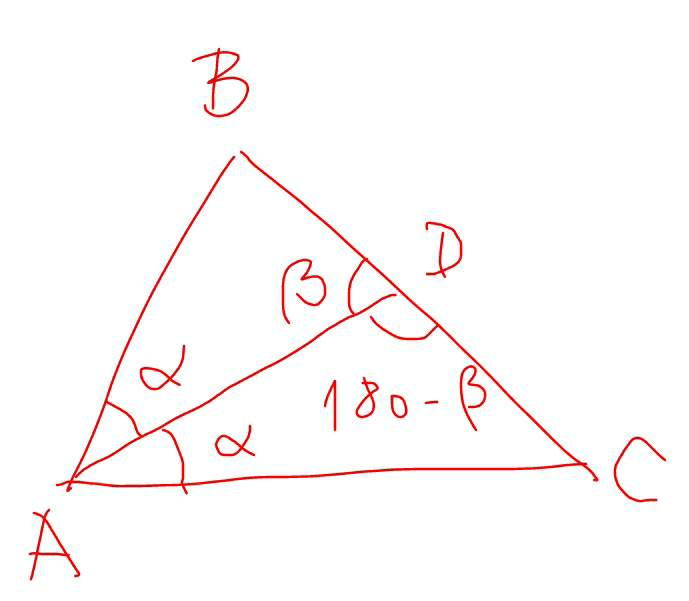
Commented by mrW1 last updated on 30/Dec/17

$$\frac{{BD}}{\mathrm{sin}\:\angle{BAD}}=\frac{{AB}}{\mathrm{sin}\:\angle{ADB}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{BD}}{\mathrm{sin}\:\alpha}=\frac{{AB}}{\mathrm{sin}\:\beta} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{BD}}{{AB}}=\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\alpha}{\mathrm{sin}\:\beta} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\frac{{DC}}{\mathrm{sin}\:\angle{DAC}}=\frac{{AC}}{\mathrm{sin}\:\angle{ADC}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{DC}}{\mathrm{sin}\:\alpha}=\frac{{AC}}{\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{180}−\beta\right)}=\frac{{AC}}{\mathrm{sin}\:\beta} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{DC}}{{AC}}=\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\alpha}{\mathrm{sin}\:\beta} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{BD}}{{AB}}=\frac{{DC}}{{AC}}\:{or}\:\frac{{BD}}{{DC}}=\frac{{AB}}{{AC}} \\ $$
Commented by $@ty@m last updated on 31/Dec/17

$${Thanks}... \\ $$
Answered by mrW1 last updated on 31/Dec/17
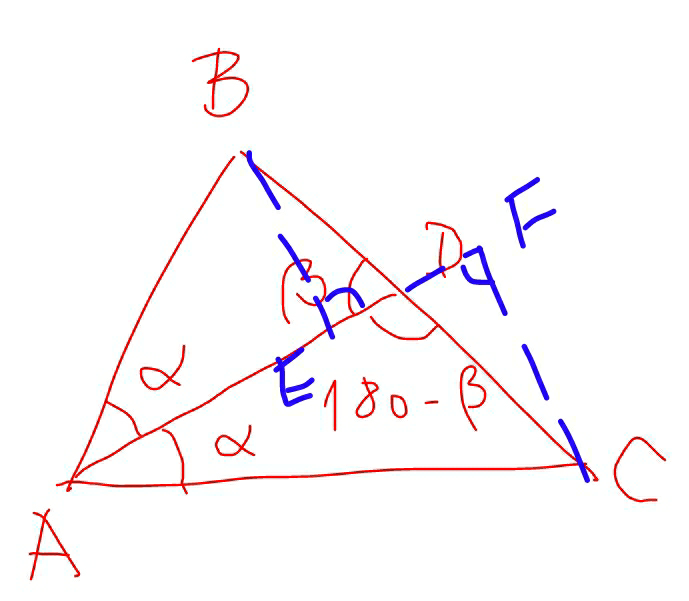
Commented by mrW1 last updated on 31/Dec/17
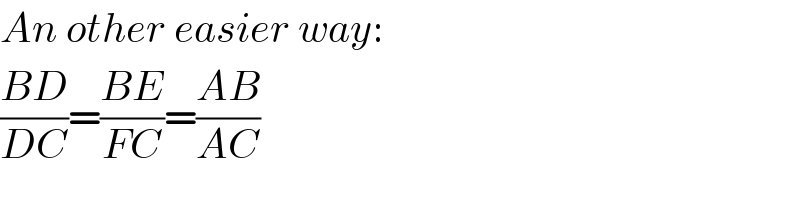
$${An}\:{other}\:{easier}\:{way}: \\ $$$$\frac{{BD}}{{DC}}=\frac{{BE}}{{FC}}=\frac{{AB}}{{AC}} \\ $$
