
OthersQuestion and Answers: Page 59
Question Number 113456 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 113455 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 113354 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 113336 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 113190 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{{logx}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}{dx} \\ $$
Question Number 113185 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 112838 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 112809 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 112707 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 112454 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 112430 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
$$\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\prod}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{{n}} } \\ $$
Question Number 112245 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 112162 Answers: 1 Comments: 3

Question Number 111975 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 111957 Answers: 0 Comments: 31
Question Number 111774 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 111668 Answers: 0 Comments: 6

Question Number 111643 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\left(\frac{\mathrm{7}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)!\left({with}\:{out}\:{calculator}\right) \\ $$
Question Number 111536 Answers: 2 Comments: 2
Question Number 111466 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
$$\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{n}^{{n}} }{{n}!} \\ $$
Question Number 111450 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 111428 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
$$\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{n}^{\mathrm{3}} }{{n}!} \\ $$
Question Number 111132 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 111152 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
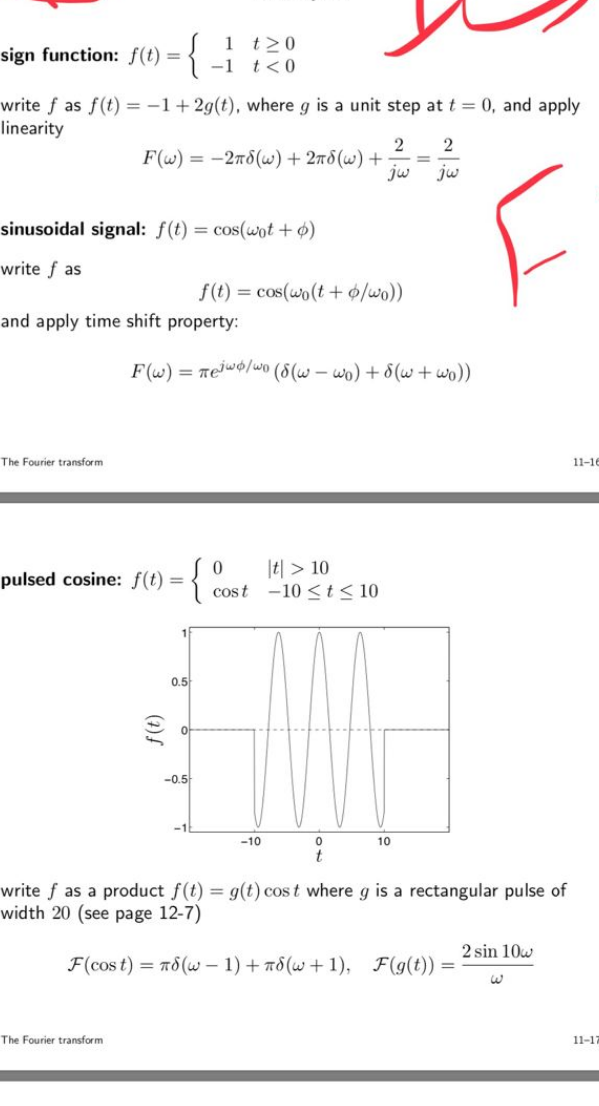
Question Number 111080 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 110860 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

