
OthersQuestion and Answers: Page 18
Question Number 187759 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 187713 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 187662 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 187651 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 187639 Answers: 2 Comments: 1

Question Number 187568 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 187504 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 187498 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 187433 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 187155 Answers: 2 Comments: 2
Question Number 186962 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 186662 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 186636 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:\:{x}^{\mathrm{92}} =? \\ $$
Question Number 186446 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 186437 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 186230 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 186080 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 186077 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 186074 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 186026 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 185996 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 185900 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
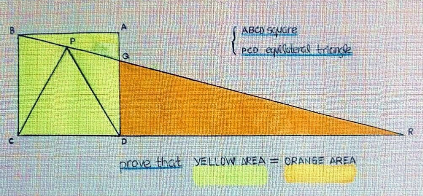
Question Number 185847 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 185786 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 185781 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 185553 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

