
Question Number 188984 by normans last updated on 10/Mar/23
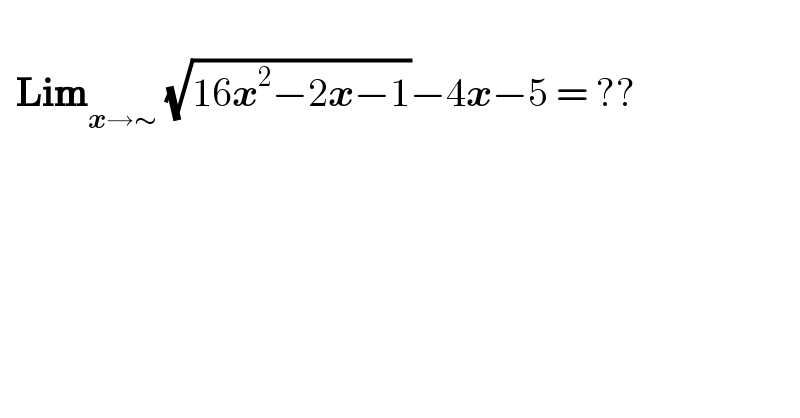
$$ \\ $$$$\:\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{Lim}}_{\boldsymbol{{x}}\rightarrow\sim} \:\sqrt{\mathrm{16}\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{{x}}−\mathrm{1}}−\mathrm{4}\boldsymbol{{x}}−\mathrm{5}\:=\:??\:\:\:\: \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 13/Mar/23
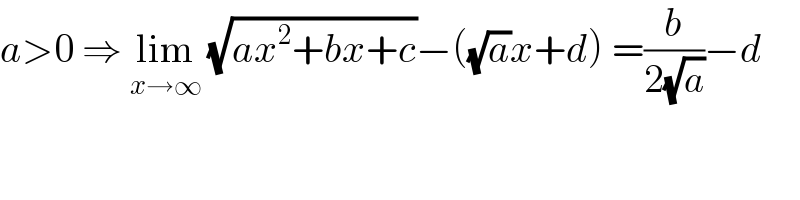
$${a}>\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\sqrt{{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +{bx}+{c}}−\left(\sqrt{{a}}{x}+{d}\right)\:=\frac{{b}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{a}}}−{d} \\ $$
Commented by cortano12 last updated on 13/Mar/23

$$\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{should}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{L}=\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{a}}}\:−\mathrm{d} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by cortano12 last updated on 13/Mar/23
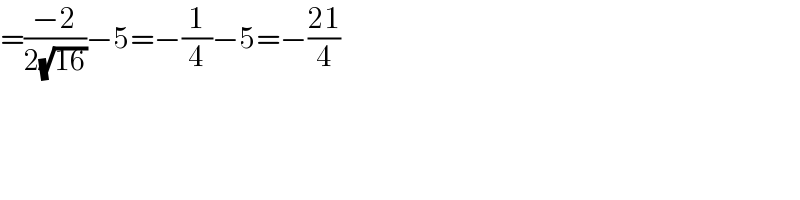
$$=\frac{−\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{16}}}−\mathrm{5}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}−\mathrm{5}=−\frac{\mathrm{21}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 13/Mar/23

$$\mathrm{yes},\:\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{you} \\ $$
Answered by cortano12 last updated on 10/Mar/23
![lim_(x→∞) (√(16x^2 −2x−1))−4x−5 = lim_(x→∞) 4x [ (√(1−(1/(8x))−(1/(16x^2 ))))−1−(5/(4x)) ] [ (1/(4x)) = h ; h→0 ] = lim_(h→0) (1/h) [ (√(1−(1/2)h−h^2 ))−1−5h ] = −5 + lim_(h→0) (((√(1−(1/2)h−h^2 ))−1)/h) = −5+(1/2) lim_(h→0) ((h(−(1/2)−h))/h) =−((21)/4)](Q188991.png)
$$\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{16x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2x}−\mathrm{1}}−\mathrm{4x}−\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$=\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\mathrm{4x}\:\left[\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8x}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{16x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}−\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{4x}}\:\right] \\ $$$$\:\left[\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4x}}\:=\:\mathrm{h}\:;\:\mathrm{h}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}\:\right] \\ $$$$=\:\underset{\mathrm{h}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{h}}\:\left[\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{h}−\mathrm{h}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{5h}\:\right] \\ $$$$=\:−\mathrm{5}\:+\:\underset{\mathrm{h}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{h}−\mathrm{h}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{h}} \\ $$$$=\:−\mathrm{5}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\underset{\mathrm{h}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{h}\left(−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{h}\right)}{\mathrm{h}} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{21}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$
