
IntegrationQuestion and Answers: Page 188
Question Number 88131 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\int\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{2}{x}}}{dx} \\ $$
Question Number 88118 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
$$\int\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)×\sqrt{\mathrm{x}}} \\ $$
Question Number 88104 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{+\infty} \sqrt{\mathrm{3}+{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} }{dx} \\ $$
Question Number 88097 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\int\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\left(\mathrm{2x}−\mathrm{3}\right)^{\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}} } \\ $$
Question Number 88089 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
$$\int\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{{e}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{9}}{dx} \\ $$
Question Number 88071 Answers: 1 Comments: 7

Question Number 88069 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
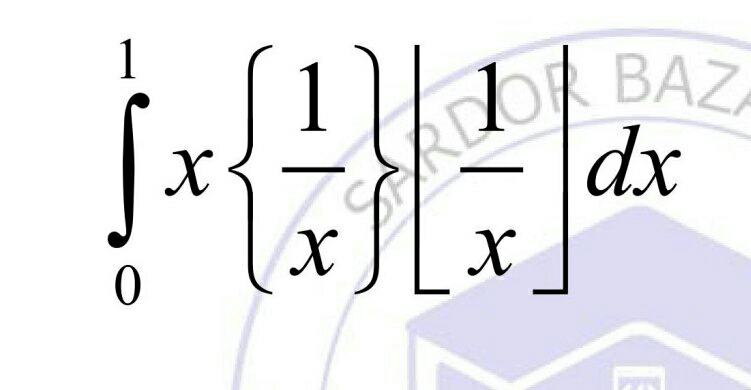
Question Number 88064 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 88045 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 88042 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 88033 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
$${find}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{{sin}\left({x}\right)}{{x}}{dx} \\ $$
Question Number 88026 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 88010 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 88007 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 88003 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 87996 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 87995 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 87994 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 87993 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 87977 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 87969 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 87930 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 87920 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
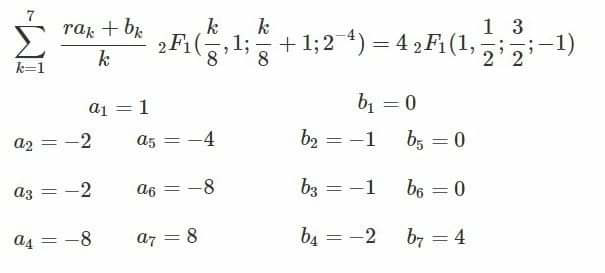
Question Number 87910 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 87903 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 87902 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Pg 183 Pg 184 Pg 185 Pg 186 Pg 187 Pg 188 Pg 189 Pg 190 Pg 191 Pg 192
