
IntegrationQuestion and Answers: Page 163
Question Number 101808 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 101793 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 101791 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 101783 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 101775 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 101747 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 101650 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
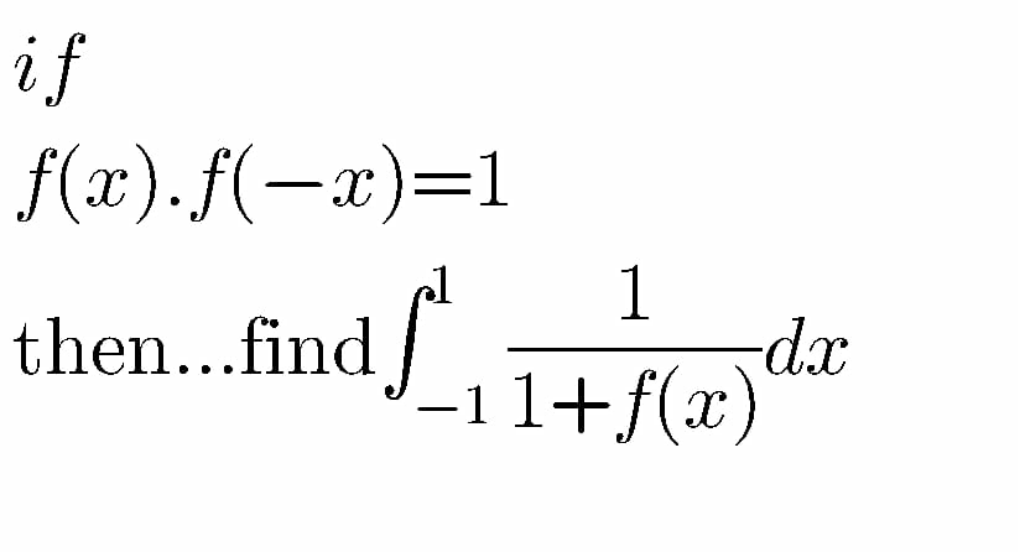
Question Number 101633 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 101608 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 101601 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 101597 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
$$\:\int\:\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{1}+\:{e}^{{x}} \right)\:{dx}\:=\:.. \\ $$
Question Number 101585 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 101860 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
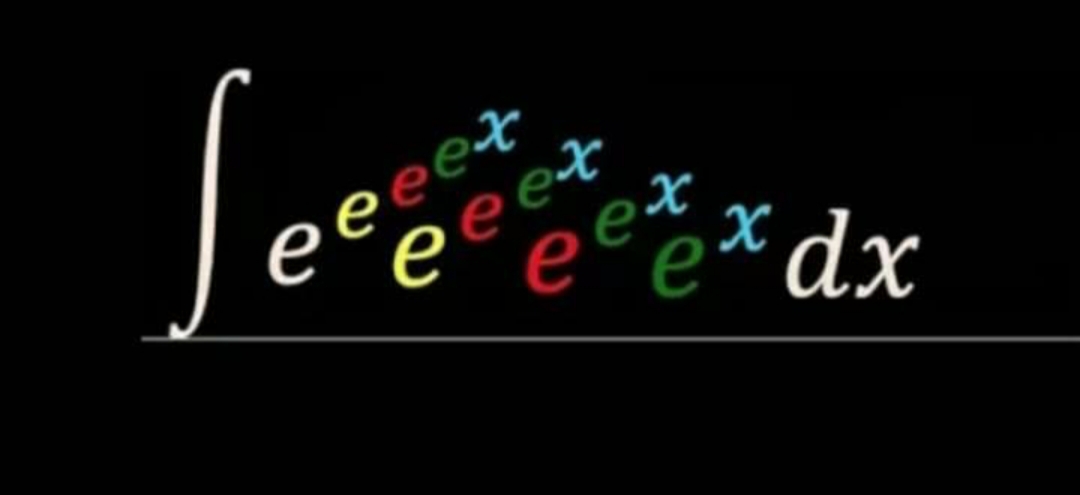
Question Number 101531 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 101493 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 101486 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 101461 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
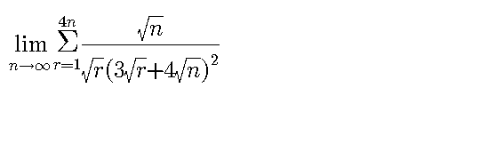
Question Number 101451 Answers: 2 Comments: 1

Question Number 105239 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 101378 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
Question Number 101373 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 101345 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 101328 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 101272 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 101271 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 101270 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Pg 158 Pg 159 Pg 160 Pg 161 Pg 162 Pg 163 Pg 164 Pg 165 Pg 166 Pg 167
