
IntegrationQuestion and Answers: Page 101
Question Number 136481 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\mathrm{50}\pi}{\mathrm{3}}} \mid{sinx}\mid{dx} \\ $$
Question Number 136476 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 136473 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
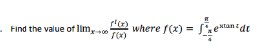
Question Number 136445 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
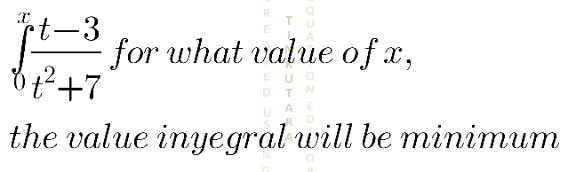
Question Number 136440 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
$$\:\int\:\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{sin}\:^{\mathrm{6}} {x}}\:? \\ $$
Question Number 136425 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
Question Number 136406 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 136405 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 136403 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 136402 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 136401 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 136400 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 136399 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 136396 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 136381 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 136365 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
$$\int\:\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}}\:=? \\ $$
Question Number 136343 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 136333 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 136325 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 136279 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
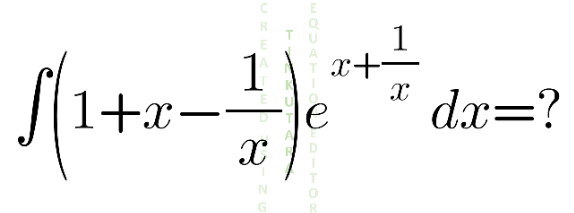
Question Number 136267 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 136211 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 136210 Answers: 5 Comments: 3
Question Number 136197 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 136170 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 136132 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Pg 96 Pg 97 Pg 98 Pg 99 Pg 100 Pg 101 Pg 102 Pg 103 Pg 104 Pg 105
