
Question Number 101888 by bemath last updated on 05/Jul/20
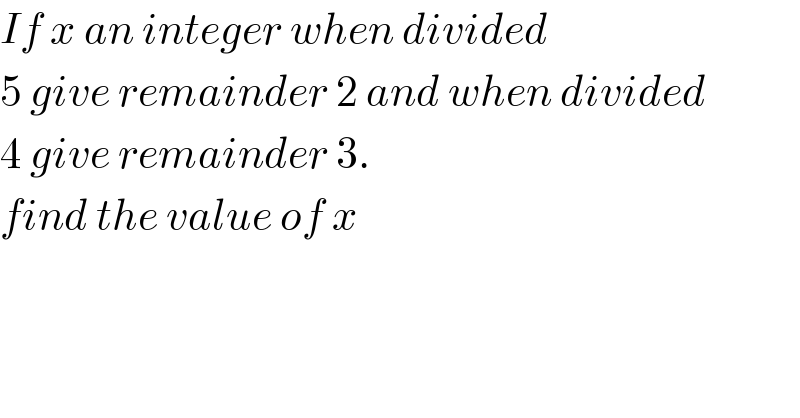
$${If}\:{x}\:{an}\:{integer}\:{when}\:{divided} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}\:{give}\:{remainder}\:\mathrm{2}\:{and}\:{when}\:{divided} \\ $$$$\mathrm{4}\:{give}\:{remainder}\:\mathrm{3}. \\ $$$${find}\:{the}\:{value}\:{of}\:{x} \\ $$
Commented by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 05/Jul/20
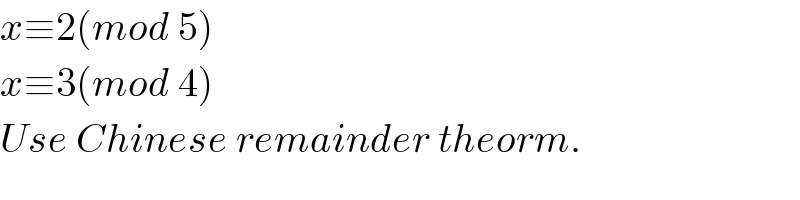
$${x}\equiv\mathrm{2}\left({mod}\:\mathrm{5}\right) \\ $$$${x}\equiv\mathrm{3}\left({mod}\:\mathrm{4}\right) \\ $$$${Use}\:{Chinese}\:{remainder}\:{theorm}. \\ $$
Answered by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 05/Jul/20

$${x}−\mathrm{2}\:{is}\:{divisible}\:{by}\:\mathrm{5} \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{5}{m}+\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${x}−\mathrm{3}\:{is}\:{divisible}\:{by}\:\mathrm{4} \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{4}{n}+\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}{m}+\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{4}{n}+\mathrm{3} \\ $$$${m}=\frac{\mathrm{4}{n}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\:;\:{m},{n}\in\mathbb{N} \\ $$$${n}=\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow{m}=\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{7} \\ $$$${n}=\mathrm{6}\Rightarrow{m}=\mathrm{5}\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{27} \\ $$$${n}=\mathrm{11}\Rightarrow{m}=\mathrm{9}\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{47} \\ $$$$...... \\ $$$$.... \\ $$
Answered by john santu last updated on 05/Jul/20
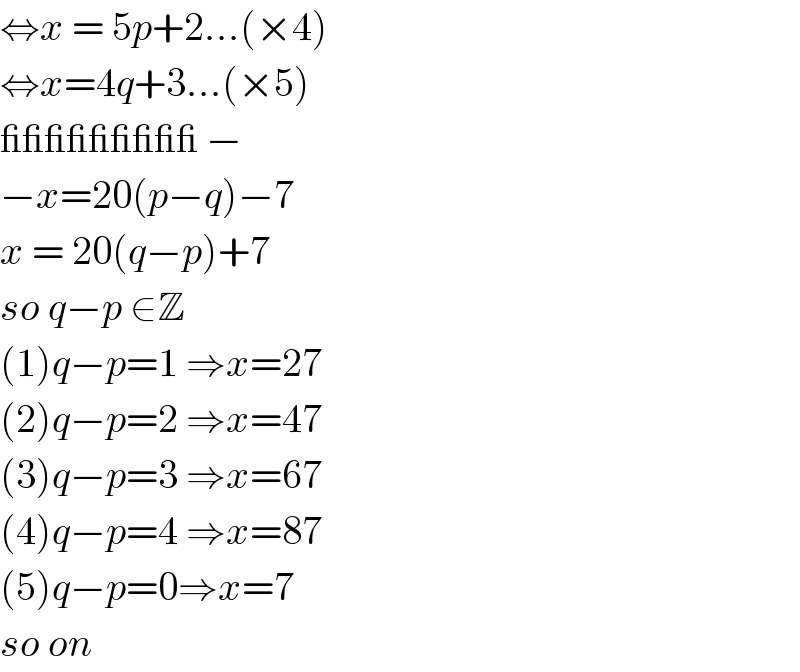
$$\Leftrightarrow{x}\:=\:\mathrm{5}{p}+\mathrm{2}...\left(×\mathrm{4}\right) \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow{x}=\mathrm{4}{q}+\mathrm{3}...\left(×\mathrm{5}\right) \\ $$$$\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\:− \\ $$$$−{x}=\mathrm{20}\left({p}−{q}\right)−\mathrm{7} \\ $$$${x}\:=\:\mathrm{20}\left({q}−{p}\right)+\mathrm{7} \\ $$$${so}\:{q}−{p}\:\in\mathbb{Z} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right){q}−{p}=\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{27} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{2}\right){q}−{p}=\mathrm{2}\:\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{47} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{3}\right){q}−{p}=\mathrm{3}\:\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{67} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{4}\right){q}−{p}=\mathrm{4}\:\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{87}\: \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{5}\right){q}−{p}=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{7} \\ $$$${so}\:{on}\: \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 05/Jul/20
![x≡2[5] and x ≡3 4] ⇒x =5n +2 and x =4m+3 ⇒ 5n+2 =4m+3 let use congruence modulo 5(prime) ⇒ 2^− =−m^− +3^− ⇒m^− = 3^− −2^− =1^− ⇒m =5q+1 ⇒x =4(5q+1)+3 ⇒x =20q +7](Q101938.png)
$$\left.\mathrm{x}\equiv\mathrm{2}\left[\mathrm{5}\right]\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{x}\:\equiv\mathrm{3}\:\:\mathrm{4}\right]\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{x}\:=\mathrm{5n}\:+\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{x}\:=\mathrm{4m}+\mathrm{3}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{5n}+\mathrm{2}\:=\mathrm{4m}+\mathrm{3}\:\:\mathrm{let}\:\mathrm{use}\:\mathrm{congruence}\:\mathrm{modulo}\:\mathrm{5}\left(\mathrm{prime}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\overset{−} {\mathrm{2}}\:=−\overset{−} {\mathrm{m}}\:\:+\overset{−} {\mathrm{3}}\Rightarrow\overset{−} {\mathrm{m}}\:=\:\overset{−} {\mathrm{3}}−\overset{−} {\mathrm{2}}\:=\overset{−} {\mathrm{1}}\:\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{m}\:=\mathrm{5q}+\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{x}\:=\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{5q}+\mathrm{1}\right)+\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{x}\:=\mathrm{20q}\:+\mathrm{7} \\ $$
