
Question Number 75327 by TawaTawa last updated on 09/Dec/19

$$\mathrm{If}\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{n}\:+\:\mathrm{1}} \:\:\:=\:\:\:\mathrm{1}\:+\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{n}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Find}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{formular}\:\mathrm{for}\:\:\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{n}} \:\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{terms}\:\mathrm{of}\:\:\mathrm{n} \\ $$$$\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{find}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{sum}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{first}\:\mathrm{n}\:\mathrm{terms} \\ $$
Commented by malwaan last updated on 11/Dec/19
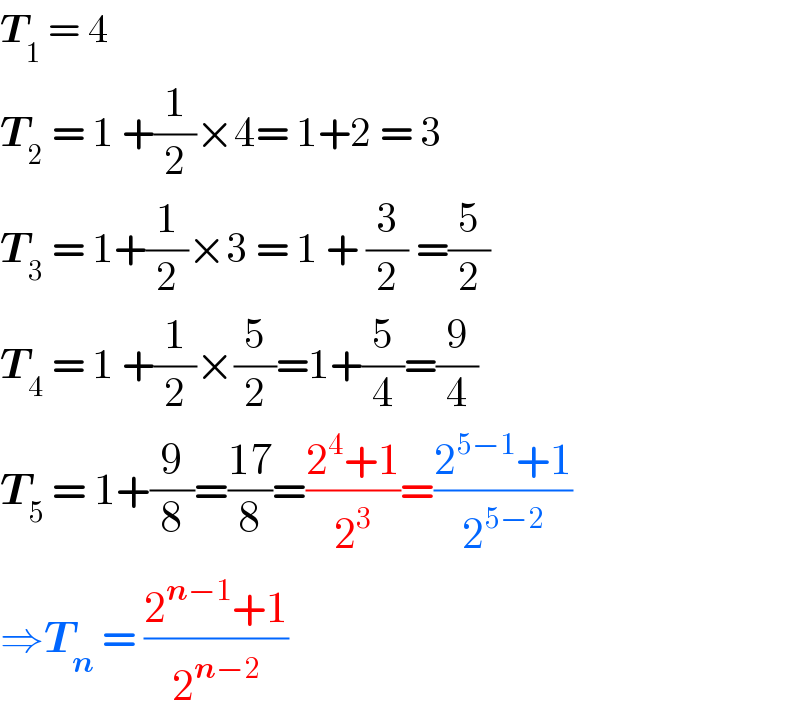
$$\boldsymbol{{T}}_{\mathrm{1}} \:=\:\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{T}}_{\mathrm{2}} \:=\:\mathrm{1}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}×\mathrm{4}=\:\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}\:=\:\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{T}}_{\mathrm{3}} \:=\:\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}×\mathrm{3}\:=\:\mathrm{1}\:+\:\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\:=\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{T}}_{\mathrm{4}} \:=\:\mathrm{1}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}×\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{4}}=\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{T}}_{\mathrm{5}} \:=\:\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{8}}=\frac{\mathrm{17}}{\mathrm{8}}=\frac{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{4}} +\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{3}} }=\frac{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{1}} +\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\boldsymbol{{T}}_{\boldsymbol{{n}}} \:=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}−\mathrm{1}} +\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}−\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 10/Dec/19

$${please}\:{check}\:{the}\:{question}: \\ $$$${when}\:{giving}\:{a}\:{recursive}\:{sequence}, \\ $$$${the}\:{first}\:{term}\:{T}_{\mathrm{1}} \:{must}\:{be}\:{given}\:{in} \\ $$$${order}\:{to}\:{determine}\:{all}\:{terms}. \\ $$
Commented by TawaTawa last updated on 10/Dec/19
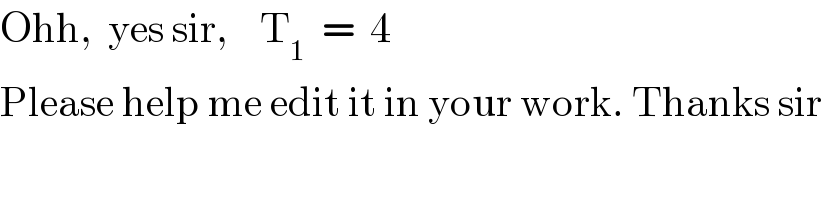
$$\mathrm{Ohh},\:\:\mathrm{yes}\:\mathrm{sir},\:\:\:\:\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{1}} \:\:=\:\:\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Please}\:\mathrm{help}\:\mathrm{me}\:\mathrm{edit}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{your}\:\mathrm{work}.\:\mathrm{Thanks}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 10/Dec/19
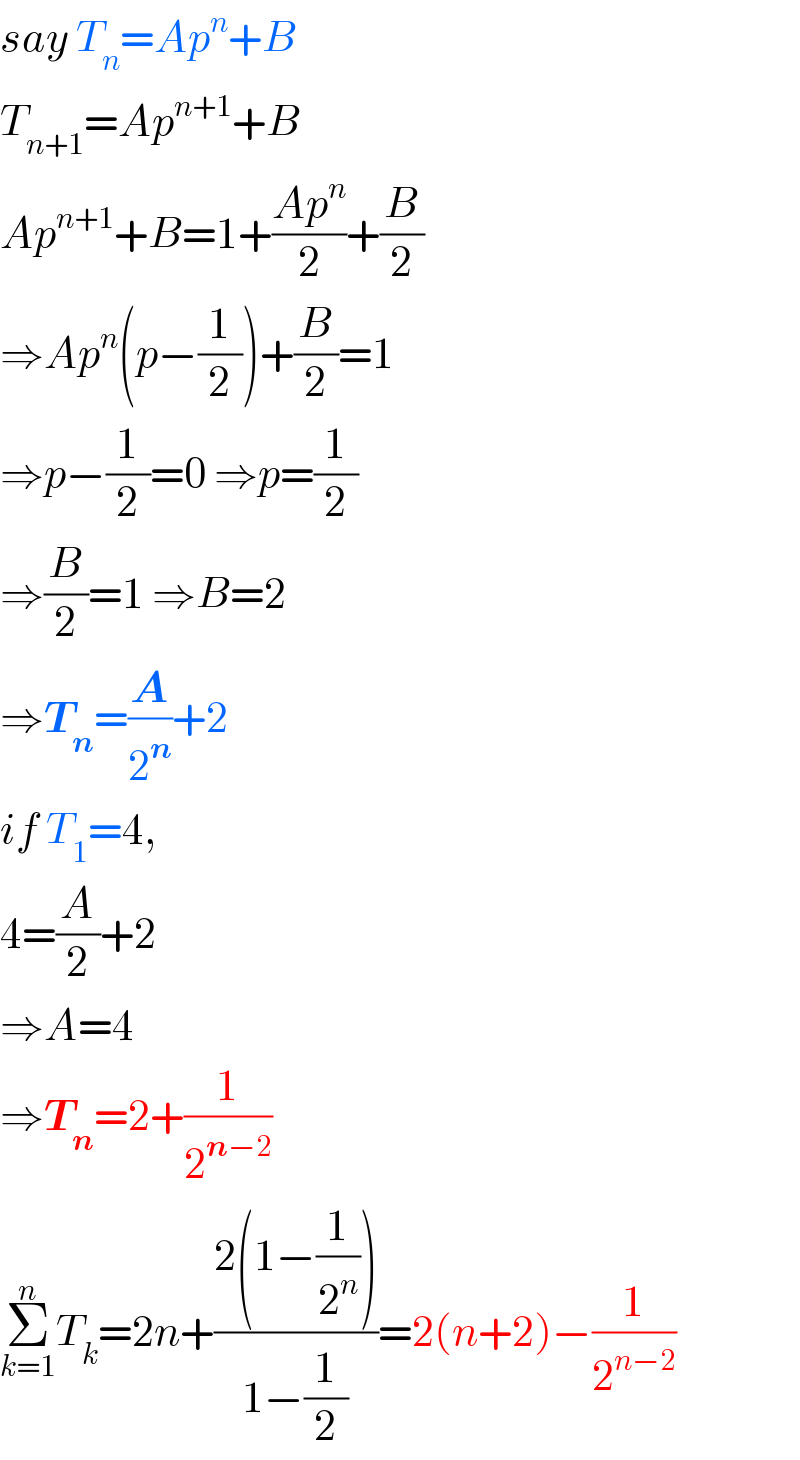
$${say}\:{T}_{{n}} ={Ap}^{{n}} +{B} \\ $$$${T}_{{n}+\mathrm{1}} ={Ap}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} +{B} \\ $$$${Ap}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} +{B}=\mathrm{1}+\frac{{Ap}^{{n}} }{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{{B}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{Ap}^{{n}} \left({p}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)+\frac{{B}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{p}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow{p}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{B}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow{B}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\boldsymbol{{T}}_{\boldsymbol{{n}}} =\frac{\boldsymbol{{A}}}{\mathrm{2}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}} }+\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${if}\:{T}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{4}, \\ $$$$\mathrm{4}=\frac{{A}}{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{A}=\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\boldsymbol{{T}}_{\boldsymbol{{n}}} =\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}−\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}{T}_{{k}} =\mathrm{2}{n}+\frac{\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{{n}} }\right)}{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}}=\mathrm{2}\left({n}+\mathrm{2}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{{n}−\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$
Commented by TawaTawa last updated on 10/Dec/19
$$\mathrm{God}\:\mathrm{bless}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{sir}.\:\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{appreciate}\:\mathrm{your}\:\mathrm{time} \\ $$
Commented by TawaTawa last updated on 10/Dec/19
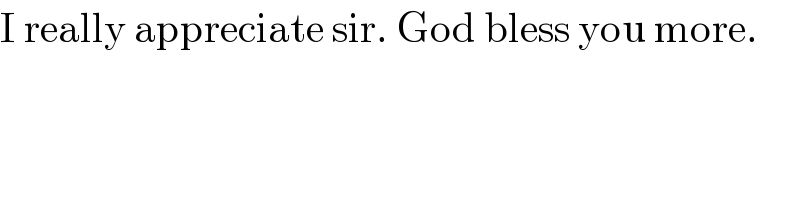
$$\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{really}\:\mathrm{appreciate}\:\mathrm{sir}.\:\mathrm{God}\:\mathrm{bless}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{more}. \\ $$
Commented by TawaTawa last updated on 10/Dec/19
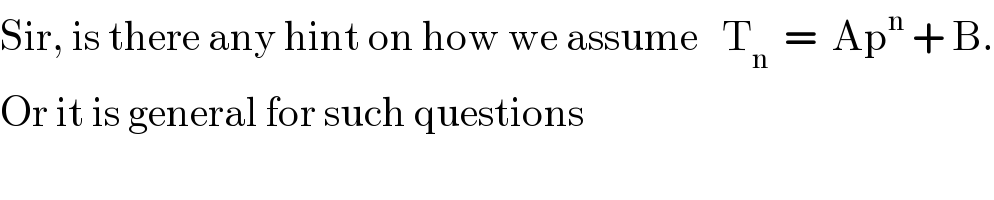
$$\mathrm{Sir},\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{there}\:\mathrm{any}\:\mathrm{hint}\:\mathrm{on}\:\mathrm{how}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{assume}\:\:\:\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{n}} \:\:=\:\:\mathrm{Ap}^{\mathrm{n}} \:+\:\mathrm{B}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{Or}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{general}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{such}\:\mathrm{questions} \\ $$
Commented by TawaTawa last updated on 10/Dec/19
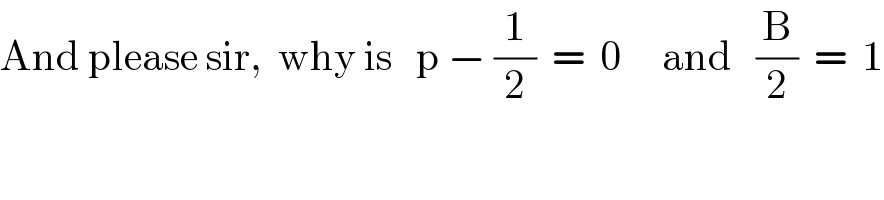
$$\mathrm{And}\:\mathrm{please}\:\mathrm{sir},\:\:\mathrm{why}\:\mathrm{is}\:\:\:\mathrm{p}\:−\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\:=\:\:\mathrm{0}\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{and}\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{B}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\:=\:\:\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by mind is power last updated on 10/Dec/19
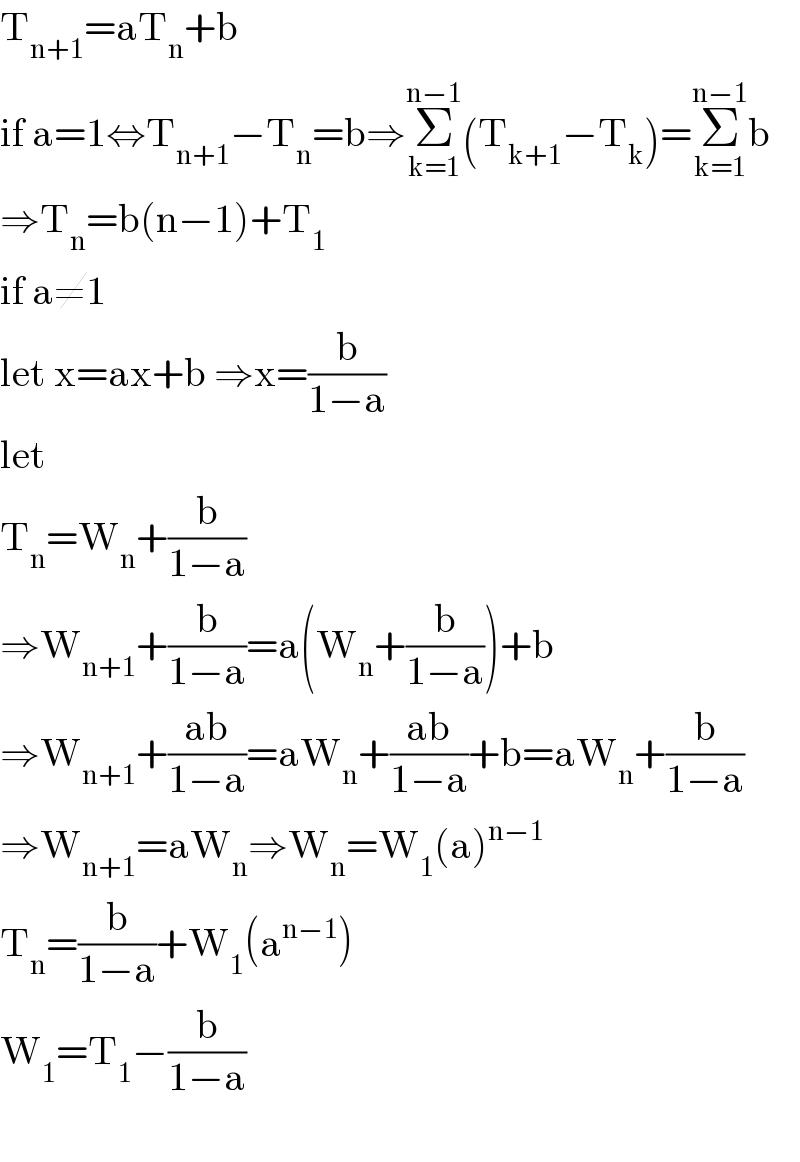
$$\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{aT}_{\mathrm{n}} +\mathrm{b} \\ $$$$\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{a}=\mathrm{1}\Leftrightarrow\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} −\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{n}} =\mathrm{b}\Rightarrow\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} {\sum}}\left(\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{k}+\mathrm{1}} −\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{k}} \right)=\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} {\sum}}\mathrm{b} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{n}} =\mathrm{b}\left(\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}\right)+\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{a}\neq\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{let}\:\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{ax}+\mathrm{b}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{x}=\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{a}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{let}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{n}} =\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{n}} +\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{a}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} +\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{a}}=\mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{n}} +\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{a}}\right)+\mathrm{b} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} +\frac{\mathrm{ab}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{a}}=\mathrm{aW}_{\mathrm{n}} +\frac{\mathrm{ab}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{a}}+\mathrm{b}=\mathrm{aW}_{\mathrm{n}} +\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{a}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{aW}_{\mathrm{n}} \Rightarrow\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{n}} =\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{a}\right)^{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{a}}+\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{a}^{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} \right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{1}} −\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{a}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by TawaTawa last updated on 10/Dec/19
$$\mathrm{God}\:\mathrm{bless}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{sir},\:\mathrm{thanks}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{your}\:\mathrm{time} \\ $$
