
GeometryQuestion and Answers: Page 81
Question Number 75656 Answers: 0 Comments: 5
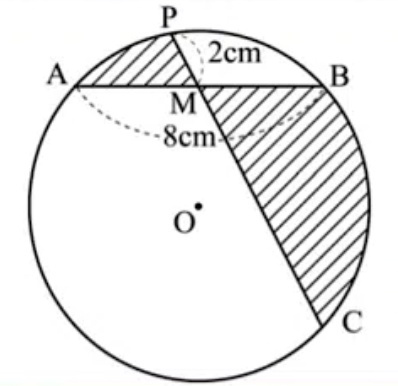
Question Number 75465 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
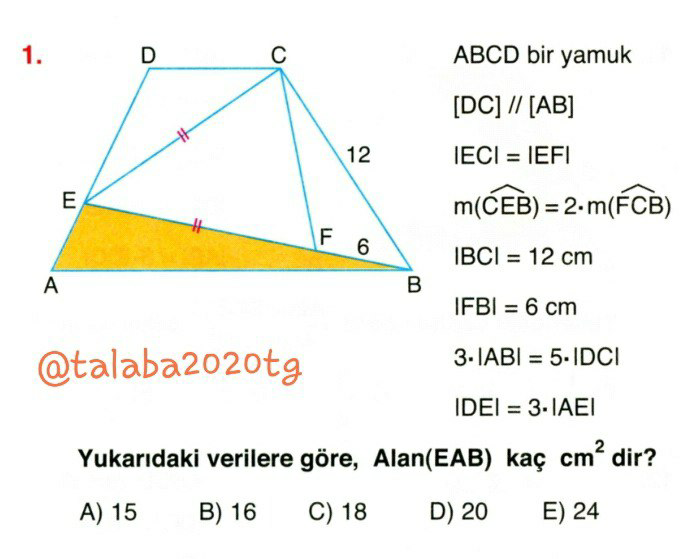
Question Number 75377 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 75376 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 75329 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
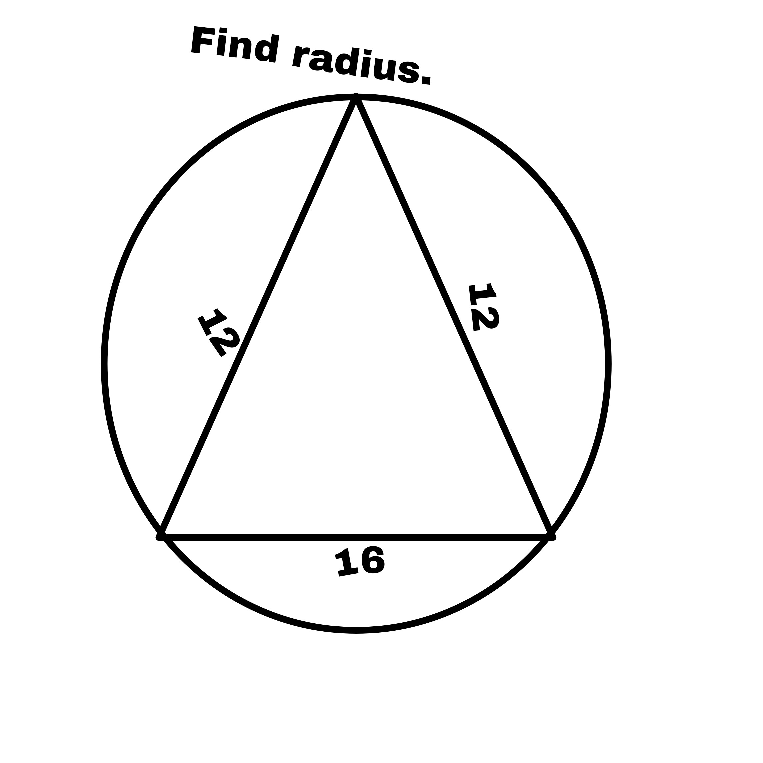
Question Number 75296 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
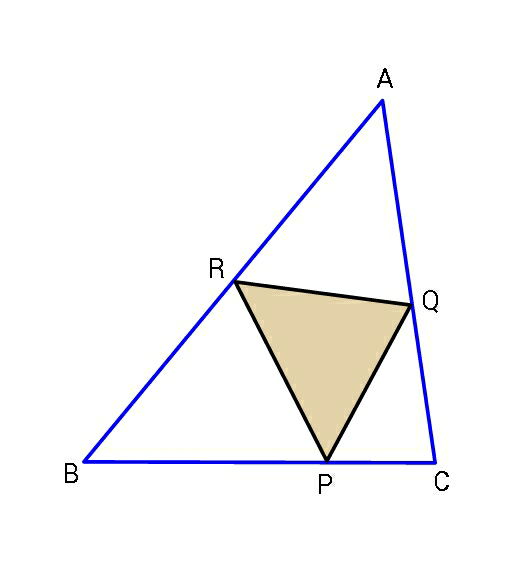
Question Number 75291 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
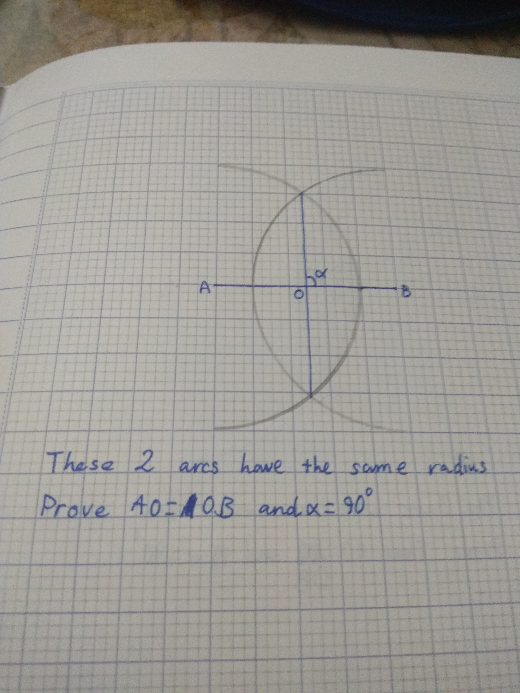
Question Number 75222 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
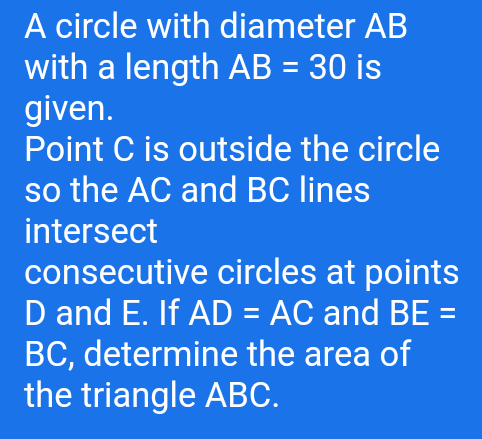
Question Number 75156 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 75105 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
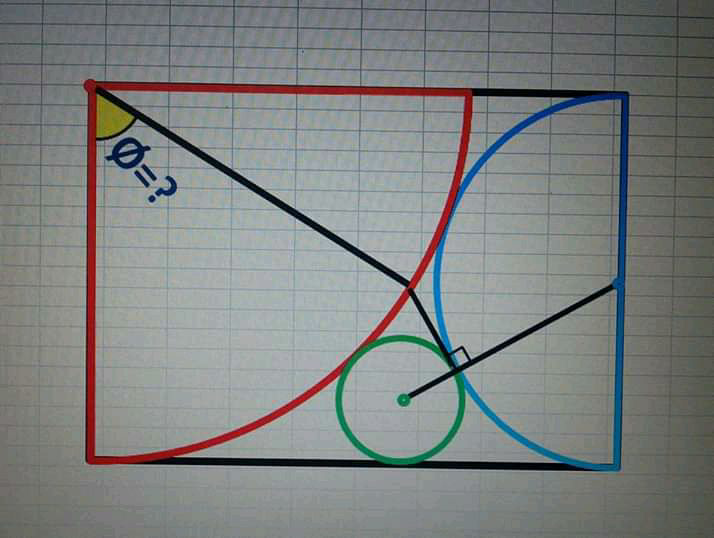
Question Number 75104 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 75058 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 74748 Answers: 1 Comments: 3

Question Number 74747 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
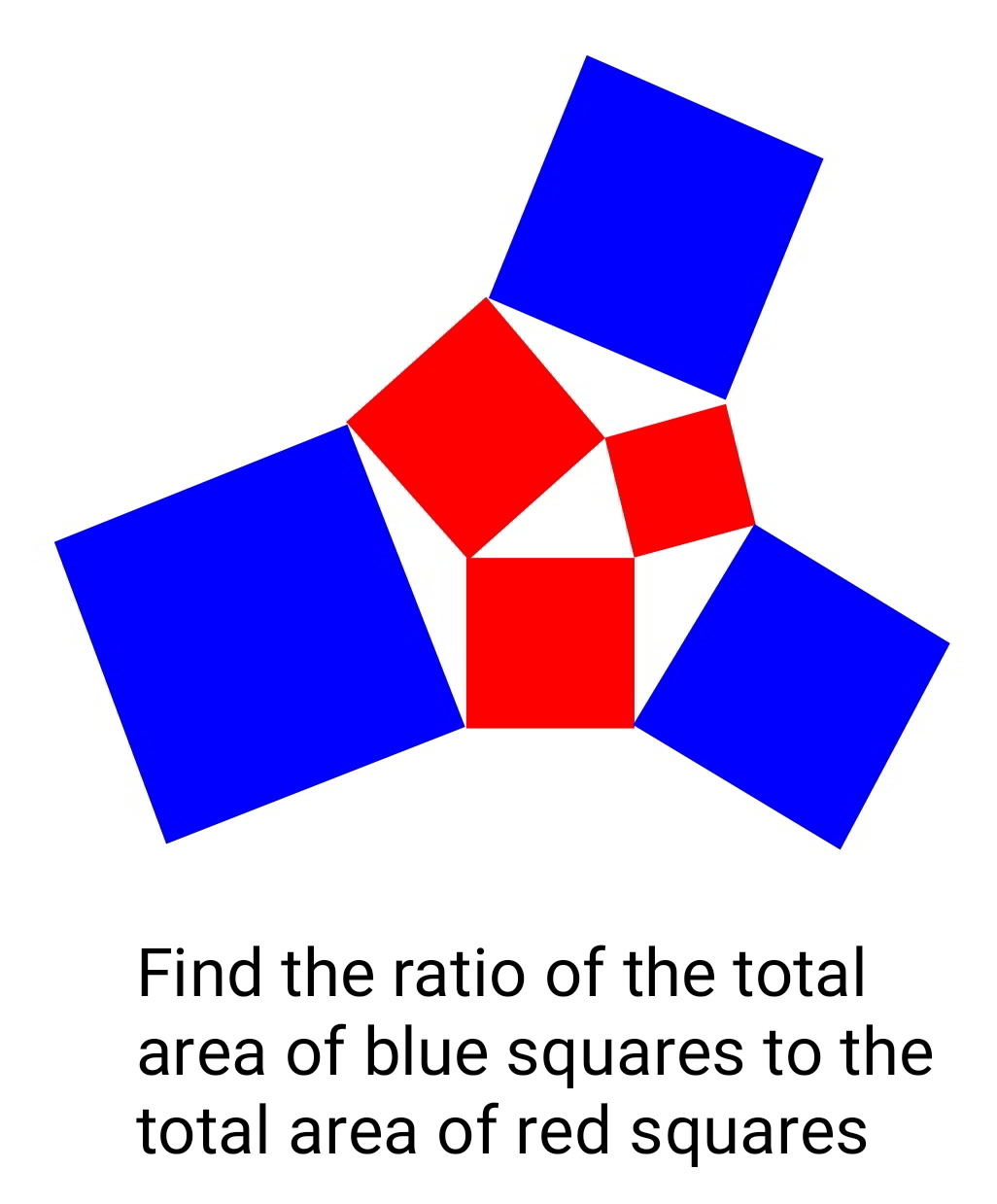
Question Number 74713 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 74726 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
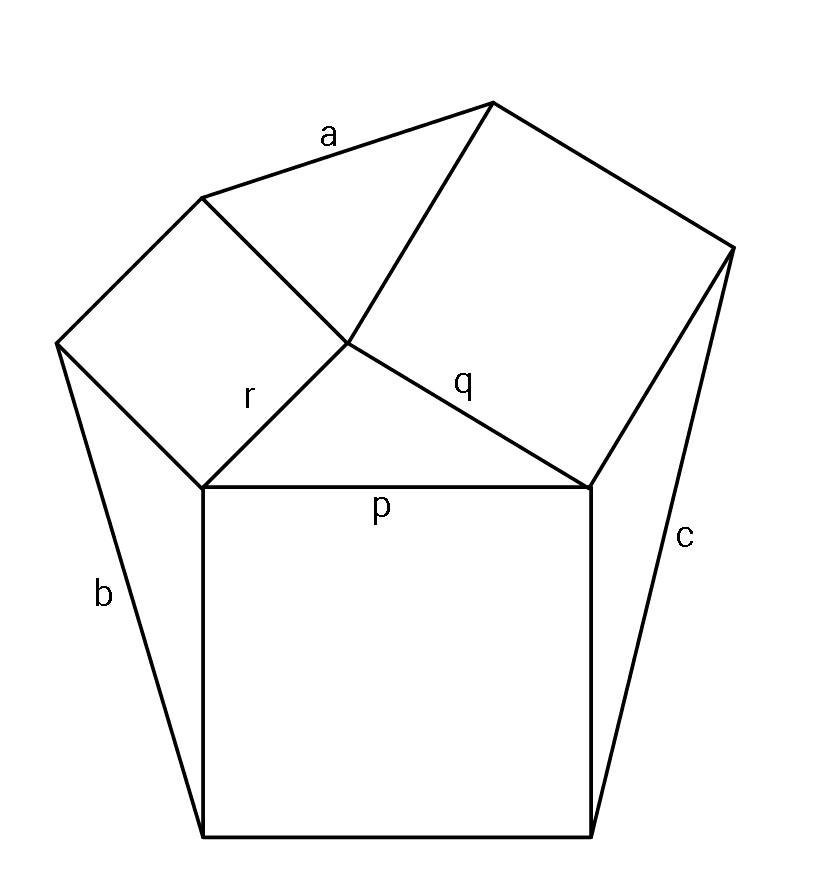
Question Number 74778 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
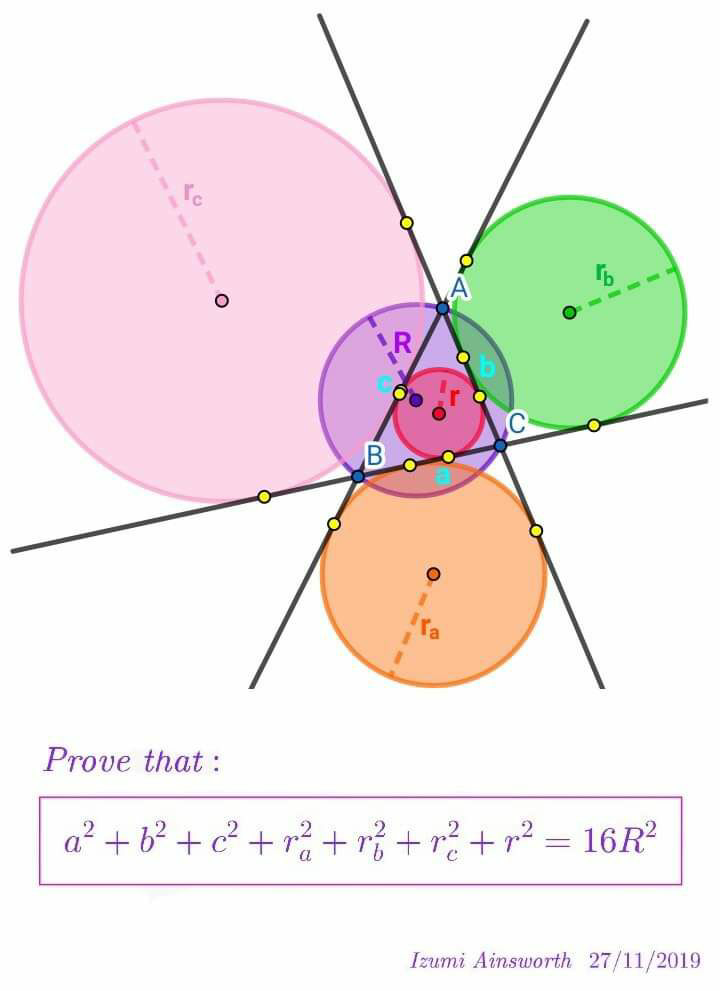
Question Number 74697 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
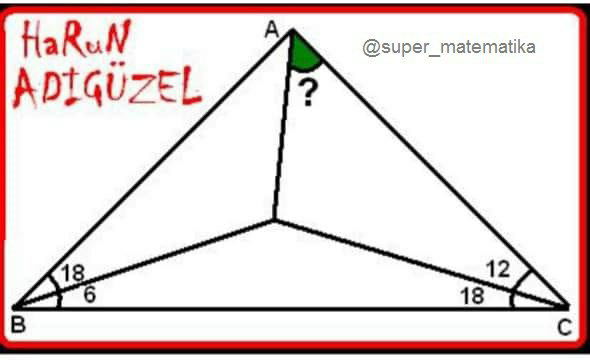
Question Number 74474 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 74509 Answers: 0 Comments: 4

Question Number 74240 Answers: 1 Comments: 3

Question Number 74137 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 74112 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 74087 Answers: 0 Comments: 15
Question Number 73884 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 73828 Answers: 1 Comments: 3

