Question Number 214335 by depressiveshrek last updated on 05/Dec/24
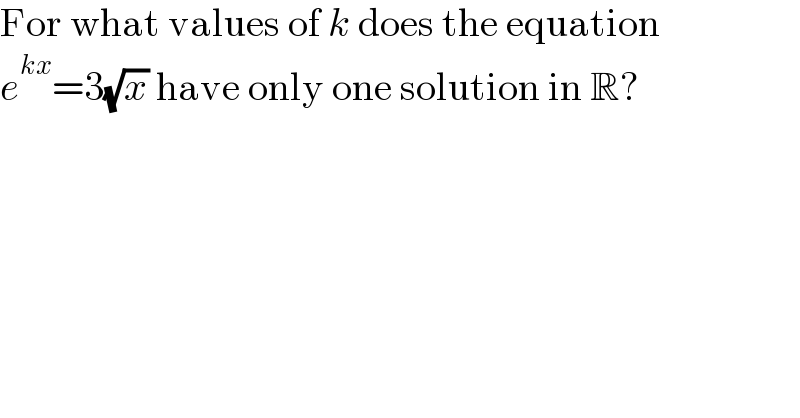
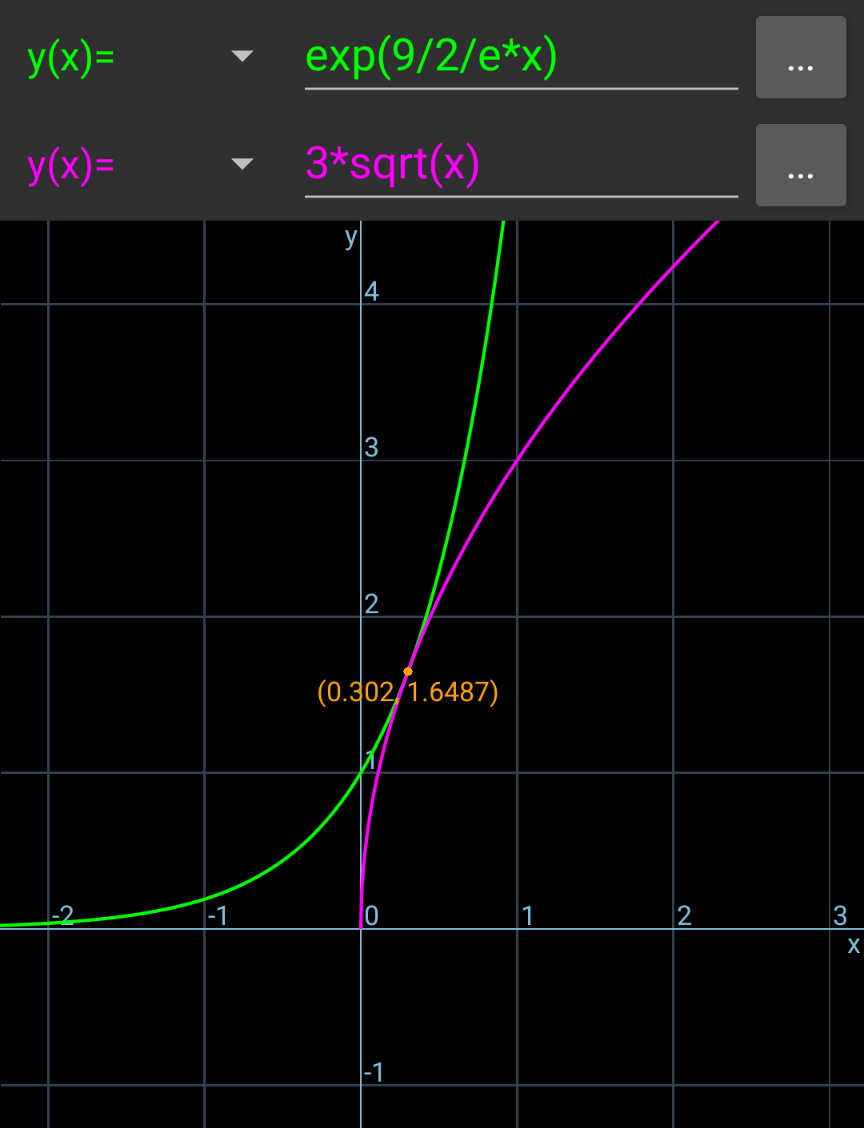
$$\mathrm{For}\:\mathrm{what}\:\mathrm{values}\:\mathrm{of}\:{k}\:\mathrm{does}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{equation} \\ $$$${e}^{{kx}} =\mathrm{3}\sqrt{{x}}\:\mathrm{have}\:\mathrm{only}\:\mathrm{one}\:\mathrm{solution}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathbb{R}? \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 06/Dec/24
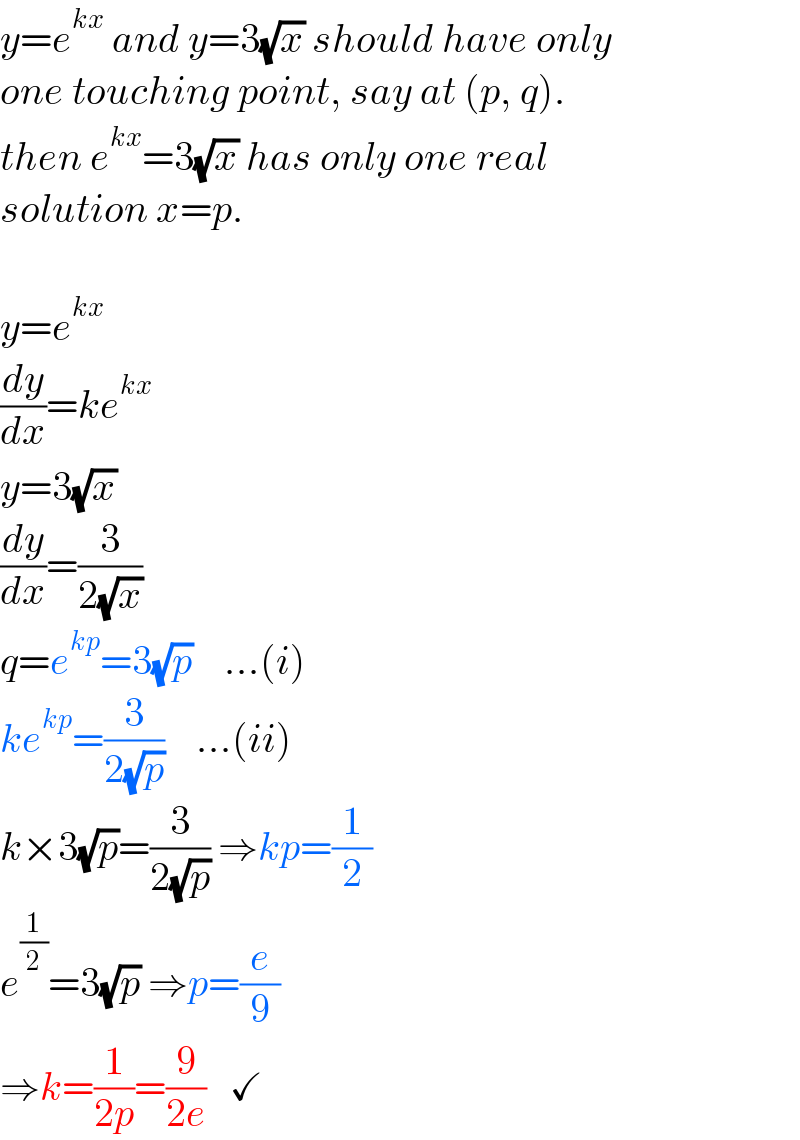
$${y}={e}^{{kx}} \:{and}\:{y}=\mathrm{3}\sqrt{{x}}\:{should}\:{have}\:{only} \\ $$$${one}\:{touching}\:{point},\:{say}\:{at}\:\left({p},\:{q}\right). \\ $$$${then}\:{e}^{{kx}} =\mathrm{3}\sqrt{{x}}\:{has}\:{only}\:{one}\:{real} \\ $$$${solution}\:{x}={p}. \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${y}={e}^{{kx}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}={ke}^{{kx}} \\ $$$${y}=\mathrm{3}\sqrt{{x}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{x}}} \\ $$$${q}={e}^{{kp}} =\mathrm{3}\sqrt{{p}}\:\:\:\:...\left({i}\right) \\ $$$${ke}^{{kp}} =\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{p}}}\:\:\:\:...\left({ii}\right) \\ $$$${k}×\mathrm{3}\sqrt{{p}}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{p}}}\:\Rightarrow{kp}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${e}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} =\mathrm{3}\sqrt{{p}}\:\Rightarrow{p}=\frac{{e}}{\mathrm{9}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{k}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{p}}=\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{2}{e}}\:\:\:\checkmark \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 06/Dec/24