
Question Number 7191 by Tawakalitu. last updated on 15/Aug/16
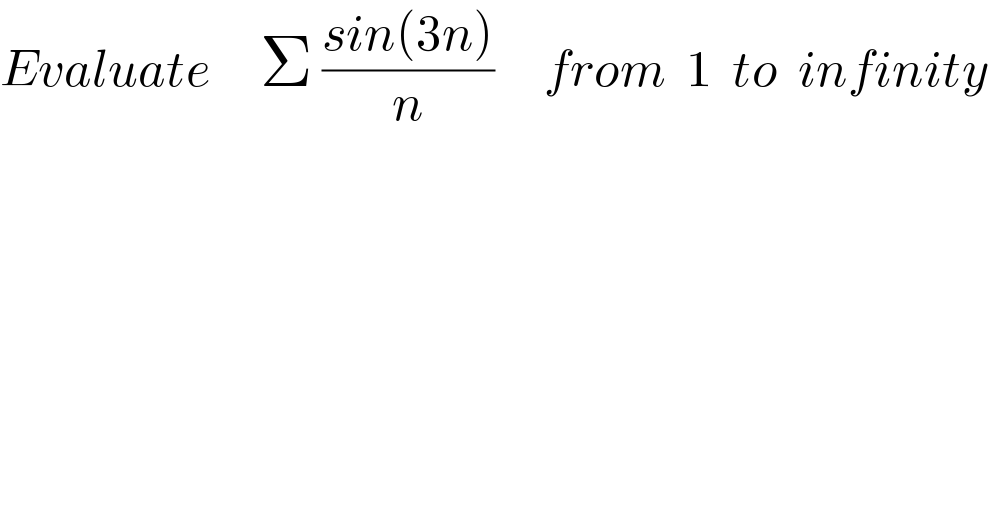
$${Evaluate}\:\:\:\:\:\Sigma\:\frac{{sin}\left(\mathrm{3}{n}\right)}{{n}}\:\:\:\:\:{from}\:\:\mathrm{1}\:\:{to}\:\:{infinity}\: \\ $$
Answered by Yozzia last updated on 15/Aug/16
![Define the function f(x)=x for 0<x<1 , period=2. For Fourier series of f having the form (1) f(x)=(a_0 /2)+Σ_(n=1) ^∞ {a_n cos((nπx)/L)+b_n sin((nπx)/L)}, 2L=2=period⇒L=1, a_0 =(1/L)∫_c ^( c+2L) f(x) dx , c∈R. ∴ For c=0, a_0 =(1/1)∫_0 ^( 2) xdx=(x^2 /2)∣_0 ^2 =2 ⇒(a_0 /2)=1. a_n =(1/L)∫_c ^(c+2L) f(x)cos((nπx)/L)dx n=1,2,3,... Let c=0. ∴ a_n =(1/1)∫_0 ^( 2) xcosnπx dx a_n =(x/(nπ))sinnπx∣_0 ^2 −∫_0 ^2 (1/(nπ))sinnπxdx a_n =(1/(n^2 π^2 ))cosnπx∣_0 ^2 =(1/(n^2 π^2 ))(cos2nπ−1)=0 b_n =(1/L)∫_c ^( c+2L) f(x)sin((nπx)/L)dx (n=1,2,3,...) Take c=0. ∴ b_n =(1/1)∫_0 ^( 2) xsinnπx dx b_n =((−xcosnπx)/(nπ))∣_0 ^2 −∫_0 ^2 ((−cosnπx)/(nπ))dx b_n =((−2)/(nπ))+[(1/(n^2 π^2 ))sinnπx]_0 ^2 b_n =((−2)/(nπ))+0=((−2)/(nπ)) (n≠0). ∴ in (1) x=1+Σ_(n=1) ^∞ ((−2sinnπx)/(nπ)) x=1−(2/π)Σ_(n=1) ^∞ ((sinnπx)/n) Let x=(3/π)∉Z (If x∈Z, x is a point of discontinuity whose output is given by ((f(x+0)+f(x−0))/2)) ∴ (3/π)=1−(2/π)Σ_(n=1) ^∞ ((sin3n)/n) ⇒Σ_(n=1) ^∞ ((sin3n)/n)=(π/2)(1−(3/π)) Σ_(n=1) ^∞ ((sin3n)/n)=((π−3)/2)](Q7194.png)
$${Define}\:{the}\:{function}\: \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)={x}\:{for}\:\mathrm{0}<{x}<\mathrm{1}\:,\:{period}=\mathrm{2}. \\ $$$${For}\:{Fourier}\:{series}\:{of}\:{f}\:{having}\:{the}\:{form} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\frac{{a}_{\mathrm{0}} }{\mathrm{2}}+\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left\{{a}_{{n}} {cos}\frac{{n}\pi{x}}{{L}}+{b}_{{n}} {sin}\frac{{n}\pi{x}}{{L}}\right\}, \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{L}=\mathrm{2}={period}\Rightarrow{L}=\mathrm{1}, \\ $$$${a}_{\mathrm{0}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{L}}\int_{{c}} ^{\:{c}+\mathrm{2}{L}} {f}\left({x}\right)\:{dx}\:,\:{c}\in\mathbb{R}. \\ $$$$\therefore\:{For}\:{c}=\mathrm{0},\:{a}_{\mathrm{0}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\mathrm{2}} {xdx}=\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\mid_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{a}_{\mathrm{0}} }{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{1}. \\ $$$${a}_{{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{L}}\int_{{c}} ^{{c}+\mathrm{2}{L}} {f}\left({x}\right){cos}\frac{{n}\pi{x}}{{L}}{dx}\:\:{n}=\mathrm{1},\mathrm{2},\mathrm{3},... \\ $$$${Let}\:{c}=\mathrm{0}.\:\therefore\:{a}_{{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\mathrm{2}} {xcosn}\pi{x}\:{dx} \\ $$$${a}_{{n}} =\frac{{x}}{{n}\pi}{sinn}\pi{x}\mid_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} −\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}\pi}{sinn}\pi{xdx} \\ $$$${a}_{{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{cosn}\pi{x}\mid_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \pi^{\mathrm{2}} }\left({cos}\mathrm{2}{n}\pi−\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${b}_{{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{L}}\int_{{c}} ^{\:{c}+\mathrm{2}{L}} {f}\left({x}\right){sin}\frac{{n}\pi{x}}{{L}}{dx}\:\:\left({n}=\mathrm{1},\mathrm{2},\mathrm{3},...\right) \\ $$$${Take}\:{c}=\mathrm{0}.\:\therefore\:{b}_{{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\mathrm{2}} {xsinn}\pi{x}\:{dx} \\ $$$${b}_{{n}} =\frac{−{xcosn}\pi{x}}{{n}\pi}\mid_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} −\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{−{cosn}\pi{x}}{{n}\pi}{dx} \\ $$$${b}_{{n}} =\frac{−\mathrm{2}}{{n}\pi}+\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{sinn}\pi{x}\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${b}_{{n}} =\frac{−\mathrm{2}}{{n}\pi}+\mathrm{0}=\frac{−\mathrm{2}}{{n}\pi}\:\:\left({n}\neq\mathrm{0}\right). \\ $$$$\therefore\:{in}\:\left(\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{1}+\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{−\mathrm{2}{sinn}\pi{x}}{{n}\pi} \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\pi}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{sinn}\pi{x}}{{n}} \\ $$$${Let}\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\pi}\notin\mathbb{Z}\:\left({If}\:{x}\in\mathbb{Z},\:{x}\:{is}\:{a}\:{point}\:{of}\:\right. \\ $$$${discontinuity}\:{whose}\:{output}\:{is}\:{given}\:{by} \\ $$$$\left.\frac{{f}\left({x}+\mathrm{0}\right)+{f}\left({x}−\mathrm{0}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\right) \\ $$$$\therefore\:\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\pi}=\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\pi}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{sin}\mathrm{3}{n}}{{n}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{sin}\mathrm{3}{n}}{{n}}=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\pi}\right) \\ $$$$\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{sin}\mathrm{3}{n}}{{n}}=\frac{\pi−\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by Tawakalitu. last updated on 15/Aug/16
$${Am}\:{very}\:{happy}.\:{Thank}\:{you}\:{sir}.\:{i}\:{really}\:{appreciate}. \\ $$
