
Question Number 145319 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 04/Jul/21
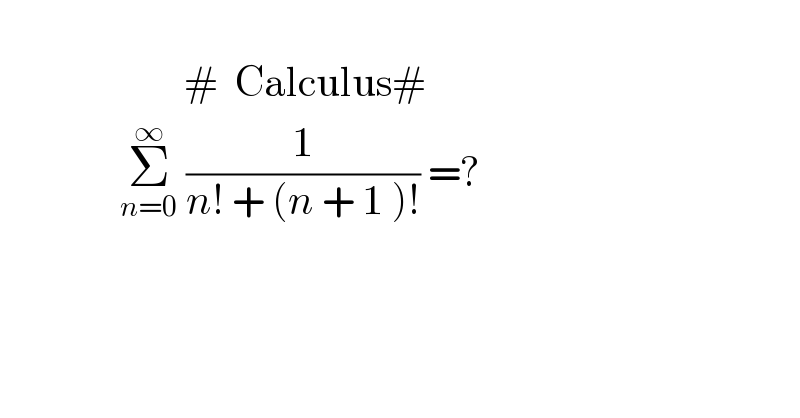
$$\:\:\:\:\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:#\:\:\mathrm{Calculus}# \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}!\:+\:\left({n}\:+\:\mathrm{1}\:\right)!}\:=? \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 04/Jul/21
![Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (1/(n!(n+2))) =∫_0 ^1 Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (x^(n+1) /(n!))dx=∫_0 ^1 xe^x dx=[(x−1)e^x ]_0 ^1 =1](Q145320.png)
$$\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}!\left({n}+\mathrm{2}\right)} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{x}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{{n}!}{dx}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {xe}^{{x}} {dx}=\left[\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right){e}^{{x}} \right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 04/Jul/21

$$\:\mathrm{thanks}\:\mathrm{alot}... \\ $$
