
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 994
Question Number 121315 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 121314 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 121303 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 121302 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 121301 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 121300 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
Question Number 121330 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
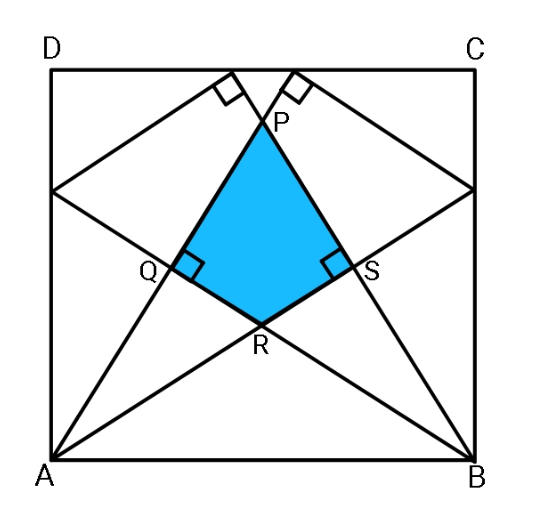
Question Number 121293 Answers: 1 Comments: 6
$$\mathrm{give}\:\mathrm{me}\:\mathrm{difficult}\:\mathrm{problems}\:\mathrm{exponent}\: \\ $$
Question Number 121282 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 121278 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 121264 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 121257 Answers: 2 Comments: 4
Question Number 121256 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 121246 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 121244 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 121235 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 121229 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 121227 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 121225 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 121224 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 121222 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 121237 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 121219 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 121217 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 121215 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 121218 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Pg 989 Pg 990 Pg 991 Pg 992 Pg 993 Pg 994 Pg 995 Pg 996 Pg 997 Pg 998
