
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 778
Question Number 142116 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 142115 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 142105 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 142269 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
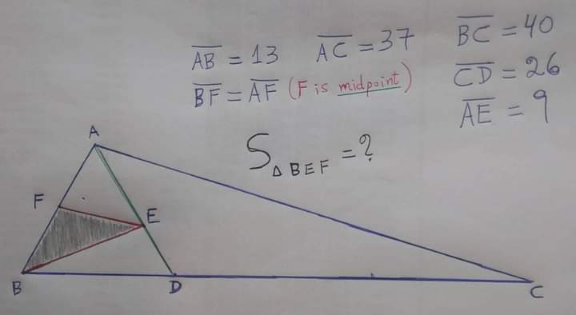
Question Number 142268 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 142100 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\int^{\:} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{t}}\:}\:{dt}=? \\ $$
Question Number 142096 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 142092 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 142085 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 142079 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
Question Number 142061 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 142060 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 142045 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 142041 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
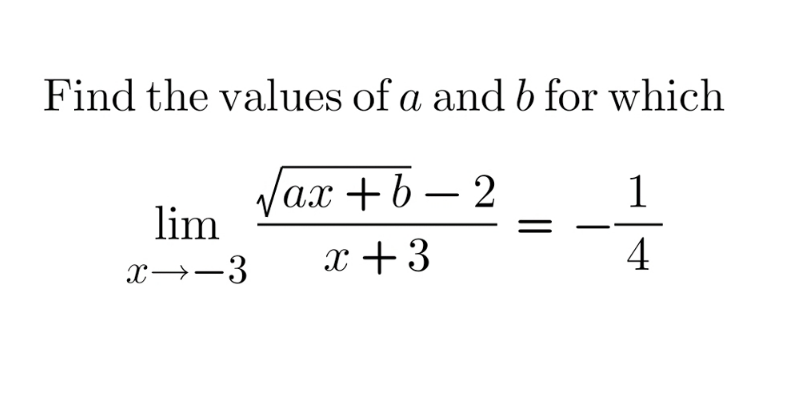
Question Number 142052 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
Question Number 142049 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
$$\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\:\mathrm{3}} {e}^{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } {dx} \\ $$$${help}\:{me}\:{sir}\: \\ $$
Question Number 142035 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 142036 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
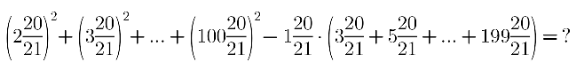
Question Number 142028 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 142023 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 142022 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
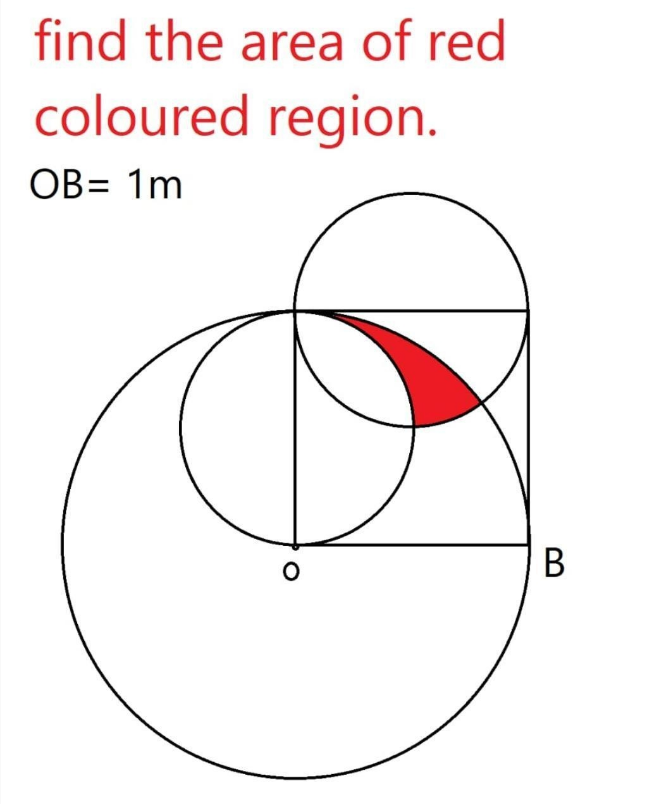
Question Number 142021 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 142017 Answers: 3 Comments: 3
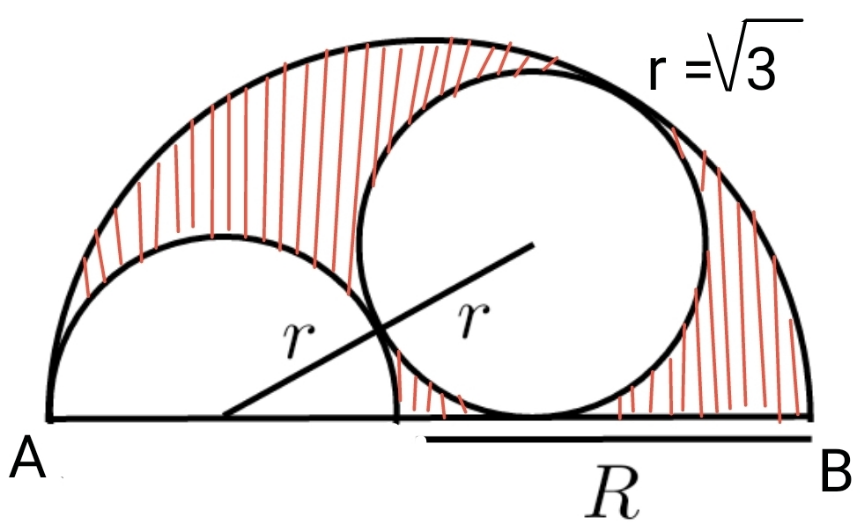
Question Number 142103 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 142010 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 141998 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Pg 773 Pg 774 Pg 775 Pg 776 Pg 777 Pg 778 Pg 779 Pg 780 Pg 781 Pg 782
