
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 756
Question Number 144209 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 144204 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144201 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144200 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144196 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 144190 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144186 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 144187 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144180 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 144177 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 144174 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 144170 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 144169 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 144168 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 144166 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144164 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144162 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 144156 Answers: 1 Comments: 2

Question Number 144152 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 144148 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144143 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\int_{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{a}}} ^{{a}} \frac{{arctg}\left({x}\right)}{{x}}{dx}=??? \\ $$
Question Number 144142 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144139 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 144136 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
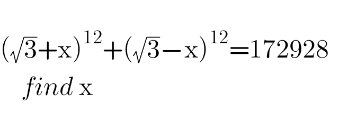
Question Number 144120 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 144118 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Pg 751 Pg 752 Pg 753 Pg 754 Pg 755 Pg 756 Pg 757 Pg 758 Pg 759 Pg 760
