
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 755
Question Number 144246 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144245 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 144244 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144241 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 144237 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 144234 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\int\:\frac{\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:-\:{x}}}{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }\:{dx}\:=\:? \\ $$
Question Number 144231 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144226 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 144222 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 144221 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 144220 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144219 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144218 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144217 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 144216 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144215 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 144214 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144213 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$${find}\:\int\:\:\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+{cosx}+{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)} \\ $$
Question Number 144212 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 144211 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
$${find}\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{4}} +\mathrm{1}} \\ $$
Question Number 144210 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
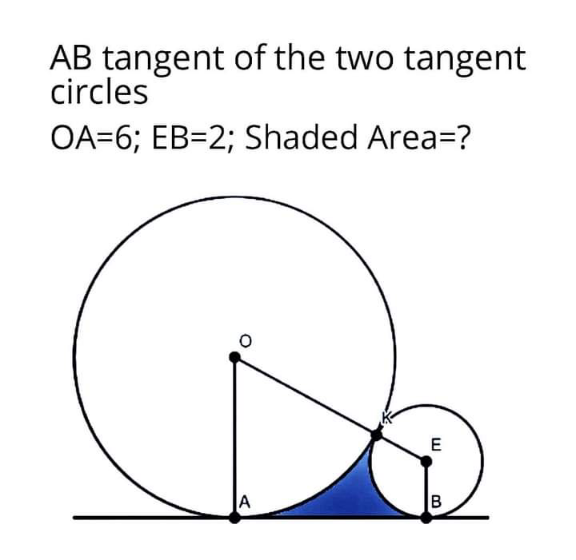
Question Number 144209 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 144204 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144201 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144200 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144196 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Pg 750 Pg 751 Pg 752 Pg 753 Pg 754 Pg 755 Pg 756 Pg 757 Pg 758 Pg 759
