
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 754
Question Number 144351 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144356 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144348 Answers: 1 Comments: 3

Question Number 144342 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144340 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 144335 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 144334 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144329 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 144327 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144323 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144322 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144318 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
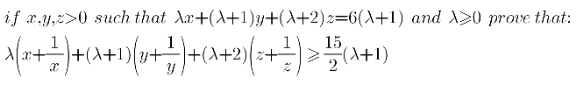
Question Number 144311 Answers: 2 Comments: 2
Question Number 144333 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 144332 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 144307 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
$${lim}_{{n}\rightarrow\infty} \left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right)^{{p}} \\ $$
Question Number 144305 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 144301 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 144300 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 144293 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 144291 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 144282 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144273 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 144272 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 144271 Answers: 3 Comments: 1
Question Number 144270 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Pg 749 Pg 750 Pg 751 Pg 752 Pg 753 Pg 754 Pg 755 Pg 756 Pg 757 Pg 758
