
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 717
Question Number 147623 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 147622 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 147621 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 147612 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 147611 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
Question Number 147609 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
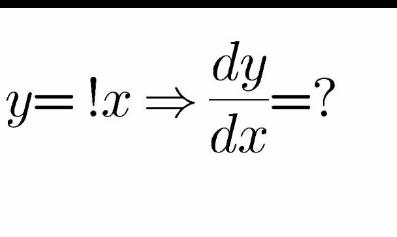
Question Number 147606 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 147603 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 147602 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 147593 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 147587 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
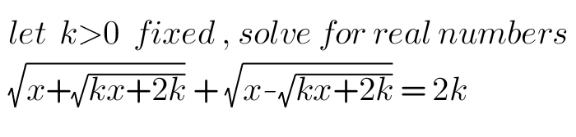
Question Number 147585 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 147582 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 147581 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 147576 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 147573 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 147572 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 147569 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 147566 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 147561 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
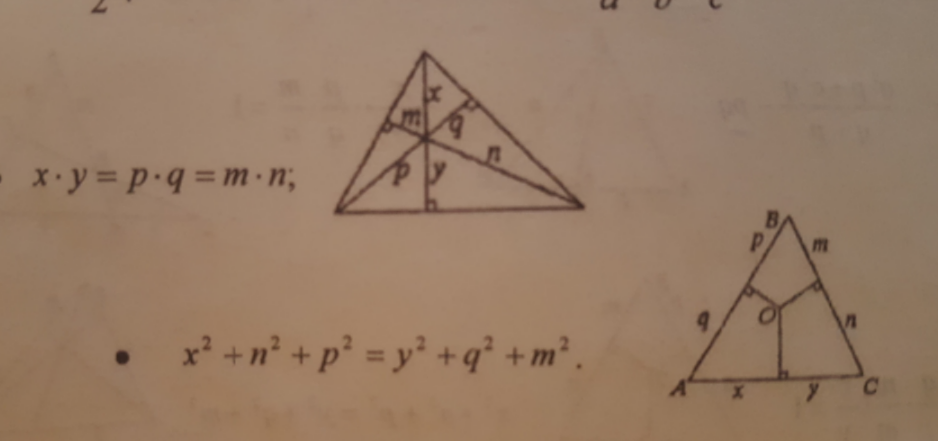
Question Number 147557 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 147554 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 147553 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 147543 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 147539 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 147535 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
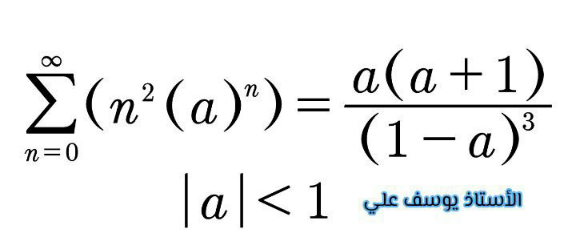
Pg 712 Pg 713 Pg 714 Pg 715 Pg 716 Pg 717 Pg 718 Pg 719 Pg 720 Pg 721
