
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 704
Question Number 149060 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 149045 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 149043 Answers: 1 Comments: 3

Question Number 149042 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 149041 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
Question Number 149040 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 149061 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
$$\mathrm{factorise}\:\:\:\:\mathrm{4}/\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{x}} +\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Question Number 149036 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 149031 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 149030 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 149077 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 149025 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
Question Number 149024 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
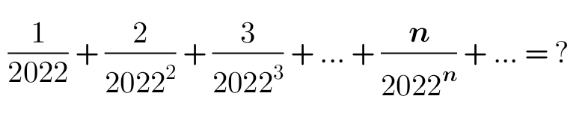
Question Number 149023 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 149008 Answers: 2 Comments: 3

Question Number 148997 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 148994 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\left(\mathrm{102}\right)^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$${easy}\:{way}\:{to}\:{caculate} \\ $$
Question Number 148993 Answers: 2 Comments: 5
Question Number 148992 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
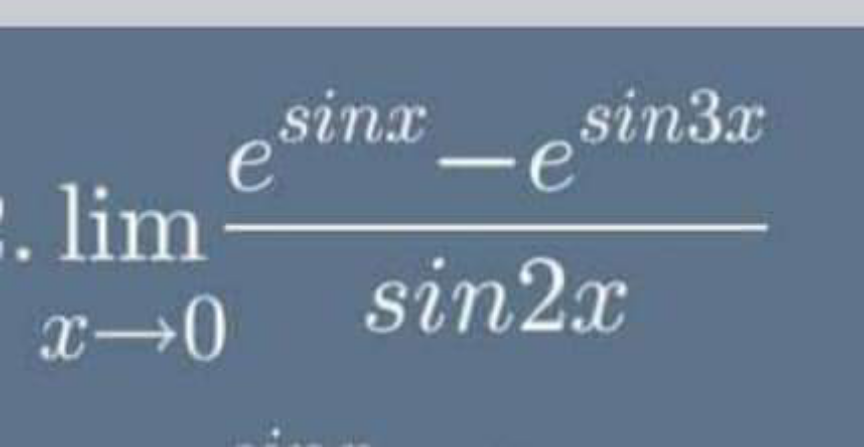
Question Number 148991 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 148990 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 148987 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 148986 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 148981 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 148975 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
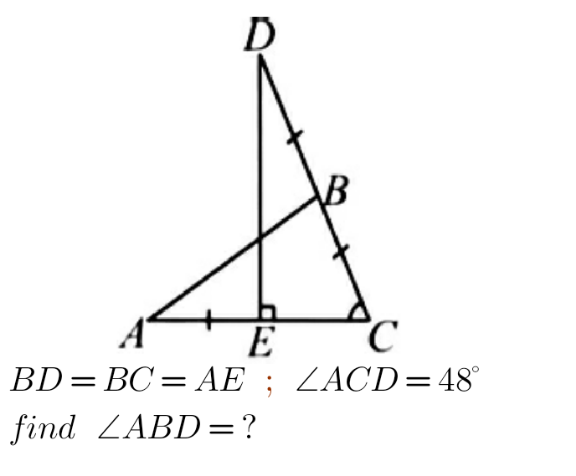
Question Number 149447 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Pg 699 Pg 700 Pg 701 Pg 702 Pg 703 Pg 704 Pg 705 Pg 706 Pg 707 Pg 708
