
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 665
Question Number 153401 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
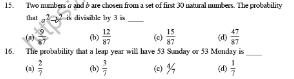
Question Number 153399 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 153398 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 153395 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 153464 Answers: 3 Comments: 1

Question Number 153384 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 153381 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 153374 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
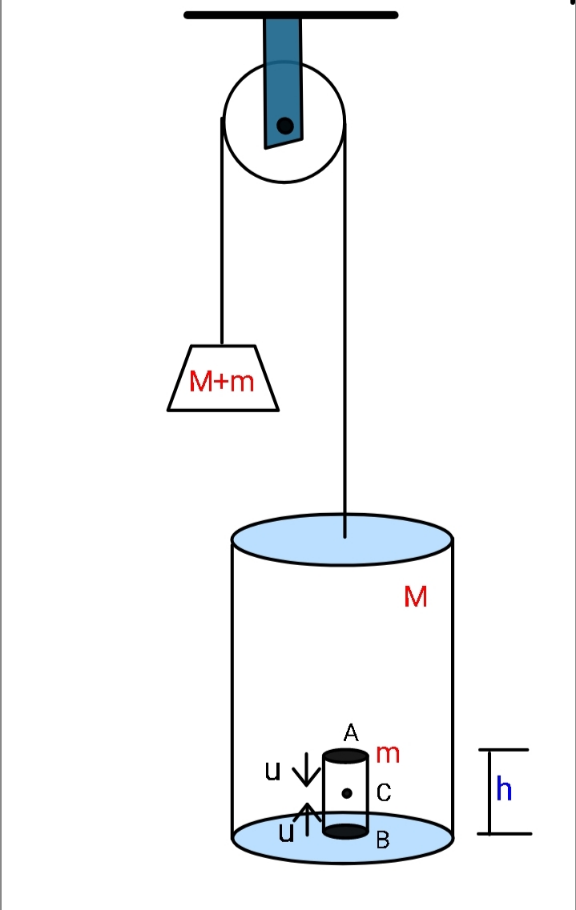
Question Number 153352 Answers: 4 Comments: 0
Question Number 153346 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 153345 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 153342 Answers: 2 Comments: 1

Question Number 153340 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 153339 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 153335 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 153312 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 153263 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 153257 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 153256 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
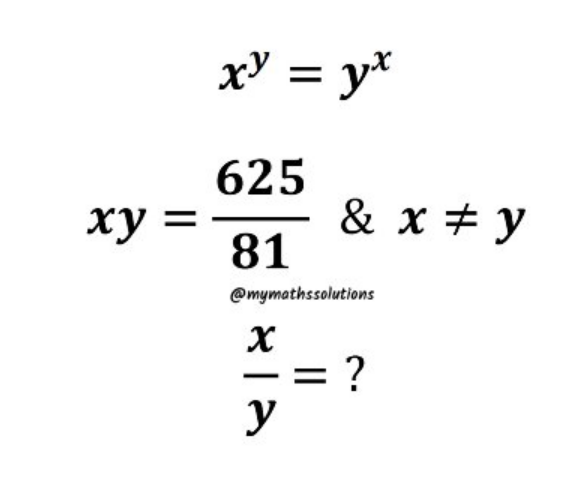
Question Number 153252 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 153249 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
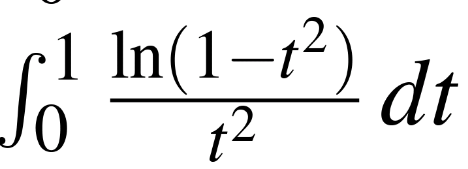
Question Number 153245 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 153239 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
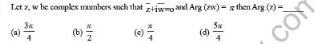
Question Number 153227 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 153226 Answers: 1 Comments: 4

Question Number 153220 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Pg 660 Pg 661 Pg 662 Pg 663 Pg 664 Pg 665 Pg 666 Pg 667 Pg 668 Pg 669
