
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 654
Question Number 154507 Answers: 2 Comments: 1

Question Number 154649 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 154620 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 154497 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 154495 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 154493 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 154478 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 154476 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
Question Number 154475 Answers: 2 Comments: 4

Question Number 154467 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 154465 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 154458 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 154456 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 154469 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 154444 Answers: 2 Comments: 1

Question Number 154441 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 154440 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 154437 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
Question Number 154434 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 154433 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
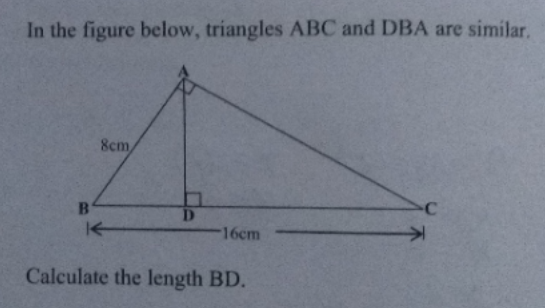
Question Number 154422 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 154421 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 154429 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
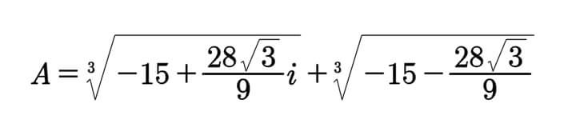
Question Number 154415 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
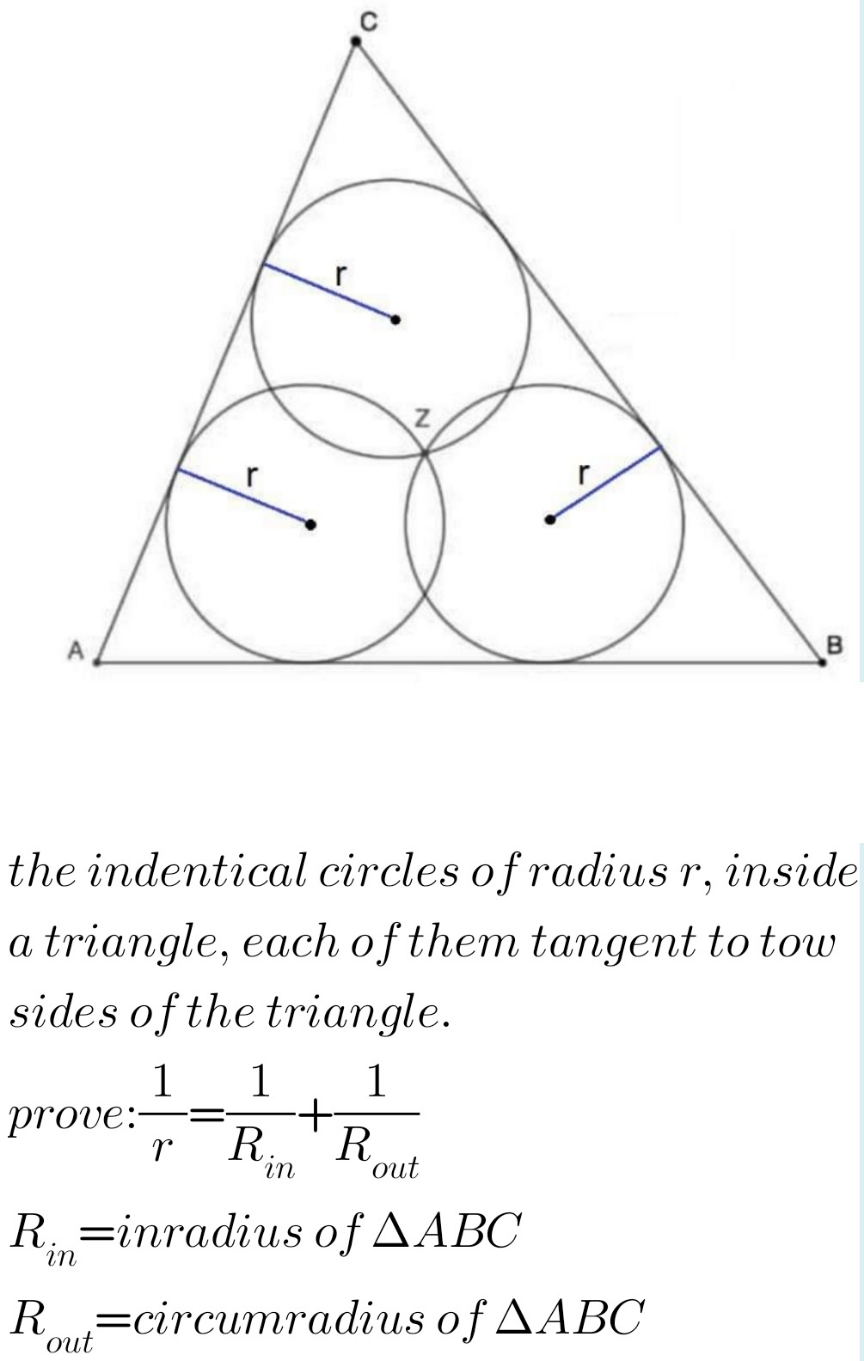
Question Number 154424 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
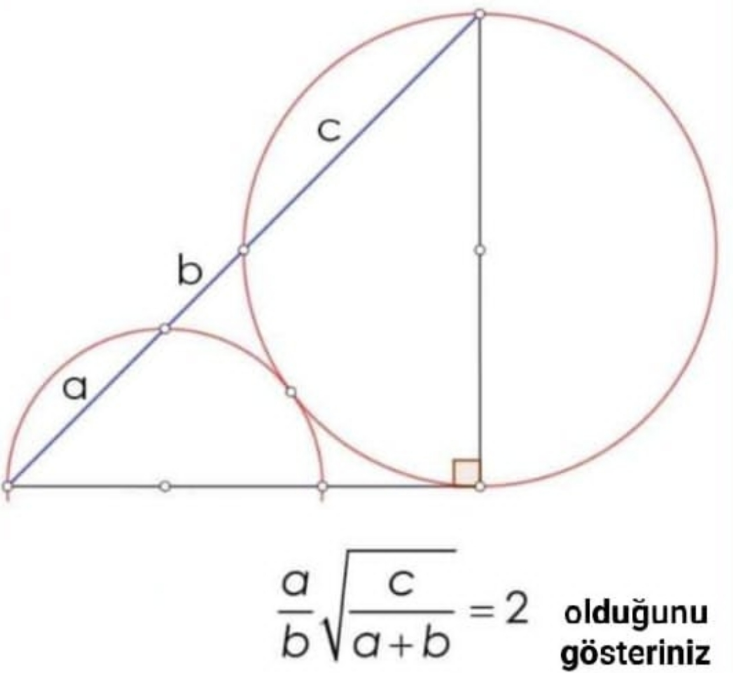
Question Number 154409 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Pg 649 Pg 650 Pg 651 Pg 652 Pg 653 Pg 654 Pg 655 Pg 656 Pg 657 Pg 658
