
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 589
Question Number 161010 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
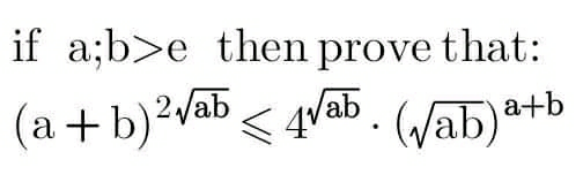
Question Number 161005 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 161003 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
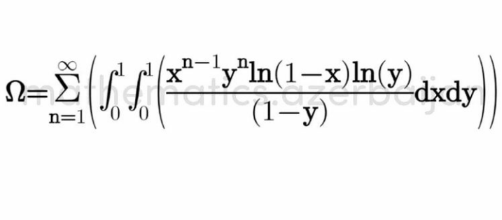
Question Number 161002 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 161000 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 160998 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 160995 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 160993 Answers: 4 Comments: 0

Question Number 160989 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 160988 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 160987 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 160982 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 160981 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 160980 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 160979 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 160976 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 160970 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 160969 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 160968 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 160967 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 161015 Answers: 2 Comments: 1

Question Number 161014 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 160953 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 160950 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 160949 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 160948 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Pg 584 Pg 585 Pg 586 Pg 587 Pg 588 Pg 589 Pg 590 Pg 591 Pg 592 Pg 593
