
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 567
Question Number 163439 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
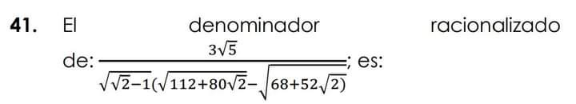
Question Number 163437 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
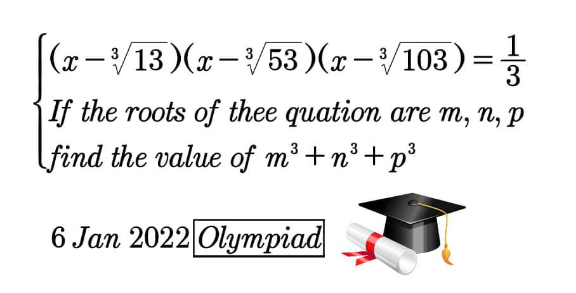
Question Number 163434 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
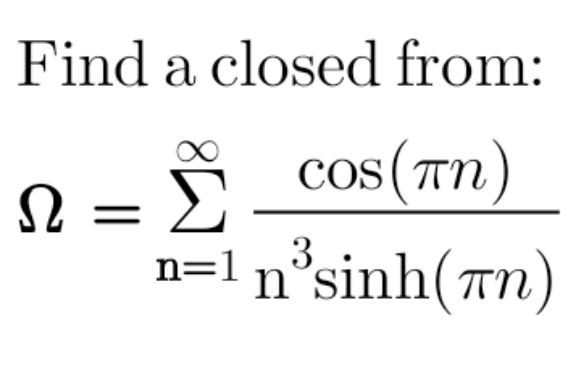
Question Number 163433 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 163432 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 163430 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 163428 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 163414 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 163413 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
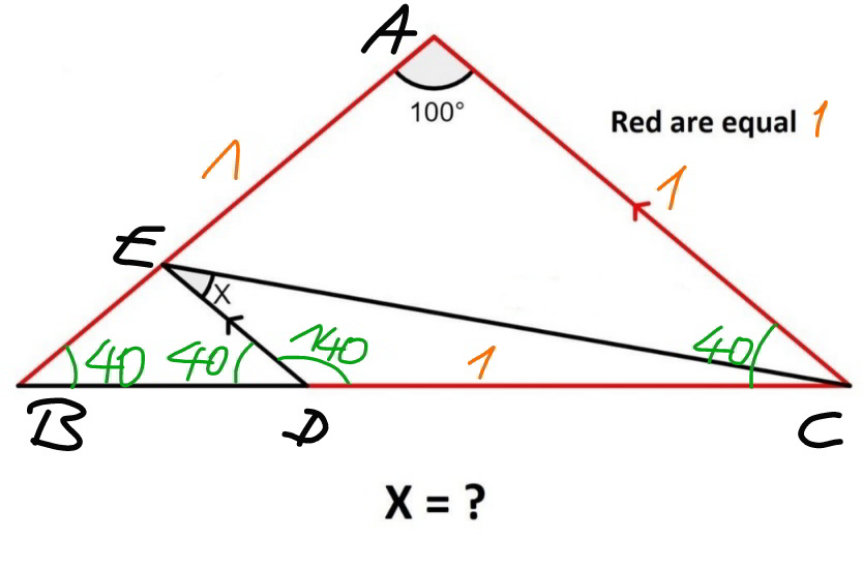
Question Number 163408 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 163402 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 163411 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 163400 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 163397 Answers: 0 Comments: 5

Question Number 163396 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 163393 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 163386 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 163385 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 163384 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
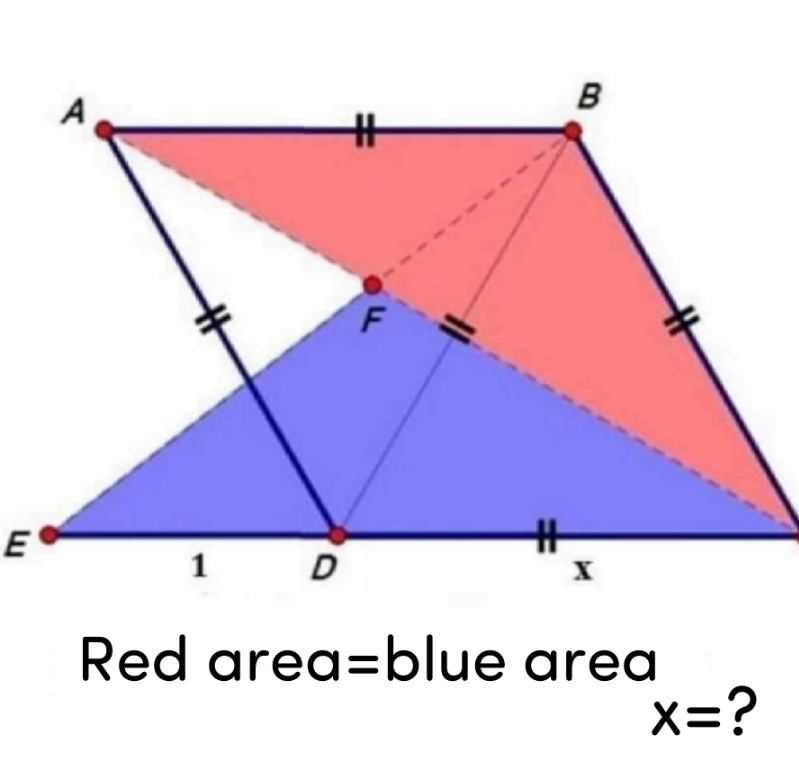
Question Number 163383 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 163435 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 163378 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
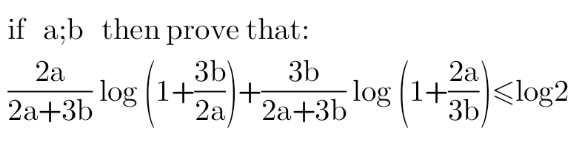
Question Number 163368 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 163367 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 163357 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 163349 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Pg 562 Pg 563 Pg 564 Pg 565 Pg 566 Pg 567 Pg 568 Pg 569 Pg 570 Pg 571
