
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 566
Question Number 163556 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
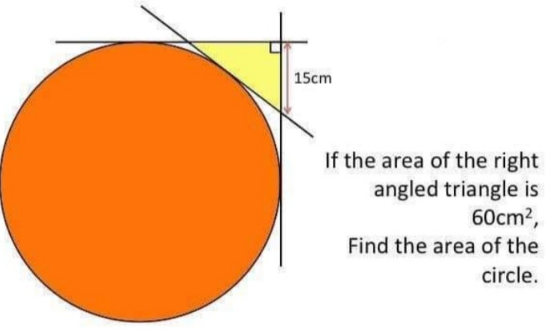
Question Number 163548 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 163536 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 163533 Answers: 0 Comments: 5
Question Number 163527 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
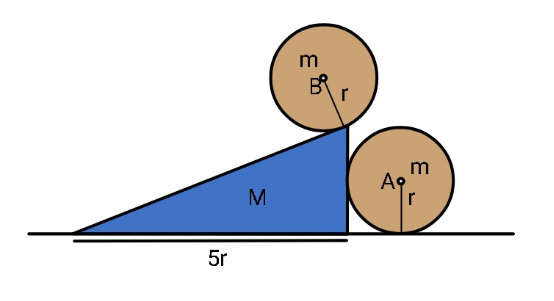
Question Number 163522 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
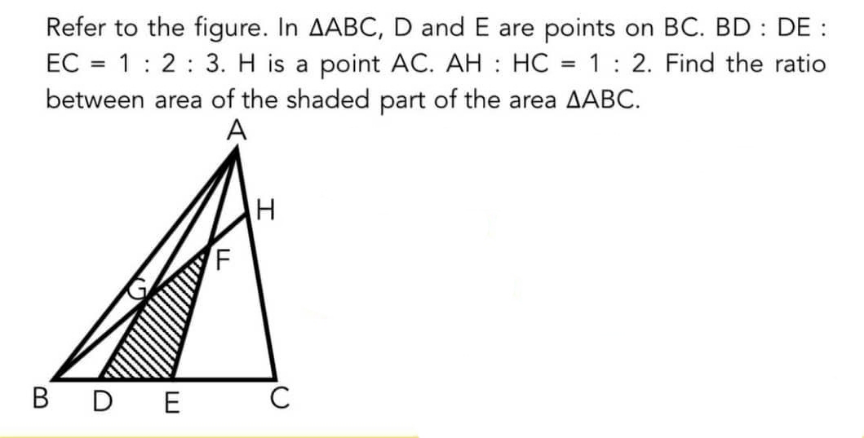
Question Number 163510 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 163508 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 163497 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 163496 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 163490 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 163487 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 163484 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 163483 Answers: 4 Comments: 0

Question Number 163481 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 163473 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 163472 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 163470 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 163469 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 163468 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 163467 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
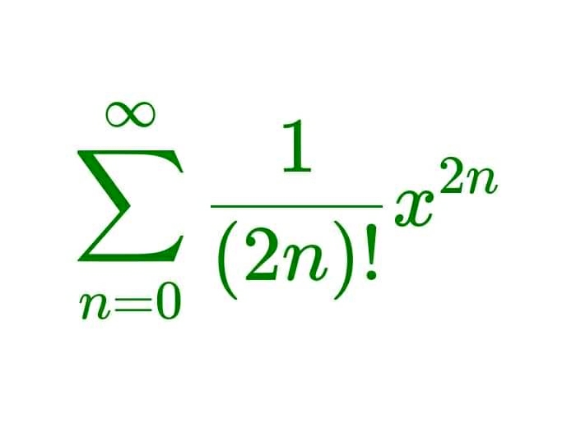
Question Number 163463 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 163457 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 163452 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 163451 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 163443 Answers: 0 Comments: 7
Pg 561 Pg 562 Pg 563 Pg 564 Pg 565 Pg 566 Pg 567 Pg 568 Pg 569 Pg 570
